Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (127.4 KB).
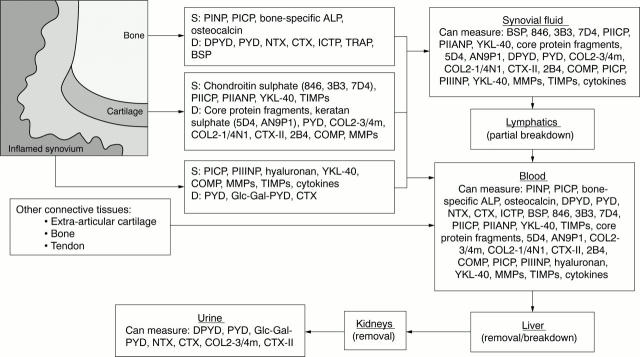
Figure 1 .
Biochemical markers of tissue destruction, inflammation, and repair. Abbreviations and examples of references referring to the use of these markers: S = synthesis marker; D = degradation marker. PINP = amino-terminal type I procollagen propeptide11; PICP = carboxy-terminal type I procollagen propeptide11; bone-specific ALP = bone-specific alkaline phosphatase12; osteocalcin13; DPYD = deoxypyridinoline14; PYD= pyridinoline15; Glc-Gal-PYD = glucosyl-galactosyl-pyridinoline; NTX= type I collagen N-terminal telopeptide16; CTX = type I collagen C-terminal telopeptide-217; ICTP = type I collagen C-terminal telopeptide-1; TRAP = plasma tartrate resistant acid phosphatase18; BSP = bone sialoprotein19; chondroitin sulphate epitopes 846, 3B3, and 7D420 21; PIICP = carboxy-terminal type II procollagen propeptide20; PIIANP = amino-terminal type IIA procollagen propeptide; YKL-4022; aggrecan core protein fragments23; keratan sulphate epitopes 5D424 AN9P125; collagen type II neoepitopes COL2-3/4m, COL2-1/4N126; CTX-II = type II collagen C-terminal telopeptide; COMP = cartilage oligomeric protein27; MMPs = matrix metalloproteinases28; TIMPs = tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases28; PIIINP = amino-terminal type III procollagen propeptide.13
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belcher C., Yaqub R., Fawthrop F., Bayliss M., Doherty M. Synovial fluid chondroitin and keratan sulphate epitopes, glycosaminoglycans, and hyaluronan in arthritic and normal knees. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 May;56(5):299–307. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.5.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billinghurst R. C., Dahlberg L., Ionescu M., Reiner A., Bourne R., Rorabeck C., Mitchell P., Hambor J., Diekmann O., Tschesche H. Enhanced cleavage of type II collagen by collagenases in osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1997 Apr 1;99(7):1534–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI119316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortet B., Flipo R. M., Pigny P., Duquesnoy B., Boersma A., Marchandise X., Delcambre B. Is bone turnover a determinant of bone mass in rheumatoid arthritis? J Rheumatol. 1998 Dec;25(12):2339–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastell R., Robins S. P., Colwell T., Assiri A. M., Riggs B. L., Russell R. G. Evaluation of bone turnover in type I osteoporosis using biochemical markers specific for both bone formation and bone resorption. Osteoporos Int. 1993 Sep;3(5):255–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01623829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnero P., Jouvenne P., Buchs N., Delmas P. D., Miossec P. Uncoupling of bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis patients with or without joint destruction: assessment with serum type I collagen breakdown products. Bone. 1999 Apr;24(4):381–385. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(98)00193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnero P., Rousseau J. C., Delmas P. D. Molecular basis and clinical use of biochemical markers of bone, cartilage, and synovium in joint diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 May;43(5):953–968. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200005)43:5<953::AID-ANR1>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B. The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Sep;43(9):1916–1926. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<1916::AID-ANR2>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald R. A. Monitoring collagen degradation in patients with arthritis. The search for suitable surrogates. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Sep;39(9):1455–1465. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G. M., Spector T. D., Delmas P. D. Markers of bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis. Effects of corticosteroids and hormone replacement therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jul;38(7):902–906. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Weisman M., O'Dell J., Scott T., Krusemeier M., Visor J., Swindlehurst C. Chondrex: new marker of joint disease. Clin Chem. 1998 Mar;44(3):509–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein G., Franke S., Müller A., Bräunig E., Eidner T., Stein G. The determination of pyridinium crosslinks in urine and serum as a possible marker of cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1997 Mar;16(2):167–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02247846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Saxne T. Molecular markers of processes in cartilage in joint disease. Br J Rheumatol. 1991;30 (Suppl 1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., Neame P. J., Sandy J. D. The structure of aggrecan fragments in human synovial fluid. Evidence that aggrecanase mediates cartilage degradation in inflammatory joint disease, joint injury, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Sep;36(9):1214–1222. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manicourt D. H., Fujimoto N., Obata K., Thonar E. J. Serum levels of collagenase, stromelysin-1, and TIMP-1. Age- and sex-related differences in normal subjects and relationship to the extent of joint involvement and serum levels of antigenic keratan sulfate in patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Dec;37(12):1774–1783. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar E. T., Lems W. F., Dijkmans B. A., de Koning M. H., van de Stadt R. J., Voskuyl A. E. Levels of markers of bone resorption are moderately increased in patients with inactive rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Jul;39(7):742–744. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.7.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Månsson B., Carey D., Alini M., Ionescu M., Rosenberg L. C., Poole A. R., Heinegård D., Saxne T. Cartilage and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Differences between rapid and slow progression of disease identified by serum markers of cartilage metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1071–1077. doi: 10.1172/JCI117753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller A., Hein G., Franke S., Herrmann D., Henzgen S., Roth A., Stein G. Quantitative analysis of pyridinium crosslinks of collagen in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis using high-performance liquid chromatography. Rheumatol Int. 1996;16(1):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01419951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Webber C., Reiner A., Roughley P. J. Studies of a monoclonal antibody to skeletal keratan sulphate. Importance of antibody valency. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):849–856. doi: 10.1042/bj2600849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury C., Sharif M. Relations between synovial fluid and serum concentrations of osteocalcin and other markers of joint tissue turnover in the knee joint compared with peripheral blood. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Sep;56(9):558–561. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.9.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Glennås A., Kvien T. K., Melby K., Heinegård D. Release of cartilage macromolecules into the synovial fluid in patients with acute and prolonged phases of reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jan;36(1):20–25. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Zunino L., Heinegård D. Increased release of bone sialoprotein into synovial fluid reflects tissue destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):82–90. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif M., Salisbury C., Taylor D. J., Kirwan J. R. Changes in biochemical markers of joint tissue metabolism in a randomized controlled trial of glucocorticoid in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jul;41(7):1203–1209. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1203::AID-ART9>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohmé J. F., Seibel M. J., Silverberg S. J., Robins S. P., Bilezikian J. P. Biochemical markers of bone metabolism. Z Rheumatol. 1991 May-Jun;50(3):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsakonas E., Fitzgerald A. A., Fitzcharles M. A., Cividino A., Thorne J. C., M'Seffar A., Joseph L., Bombardier C., Esdaile J. M. Consequences of delayed therapy with second-line agents in rheumatoid arthritis: a 3 year followup on the hydroxychloroquine in early rheumatoid arthritis (HERA) study. J Rheumatol. 2000 Mar;27(3):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A., van der Heijde D. M. Can we predict aggressive disease? Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1997 Feb;11(1):27–48. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(97)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide A., Jacobs J. W., Bijlsma J. W., Heurkens A. H., van Booma-Frankfort C., van der Veen M. J., Haanen H. C., Hofman D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., ter Borg E. J. The effectiveness of early treatment with "second-line" antirheumatic drugs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Apr 15;124(8):699–707. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-8-199604150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]