Abstract
Three patients are described with severe systemic atherosclerosis, including aortic occlusion, in the presence of a spectrum of risk factors, including hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension, a positive family history of cardiovascular problems, and hyperhomocysteinaemia. In all three patients high levels of anticardiolipin antibodies were found. The possible pathogenic role of antiphospholipid antibodies in atherosclerosis in the context of hyperhomocysteinaemia in these patients is discussed.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (104.7 KB).
Figure 1 .
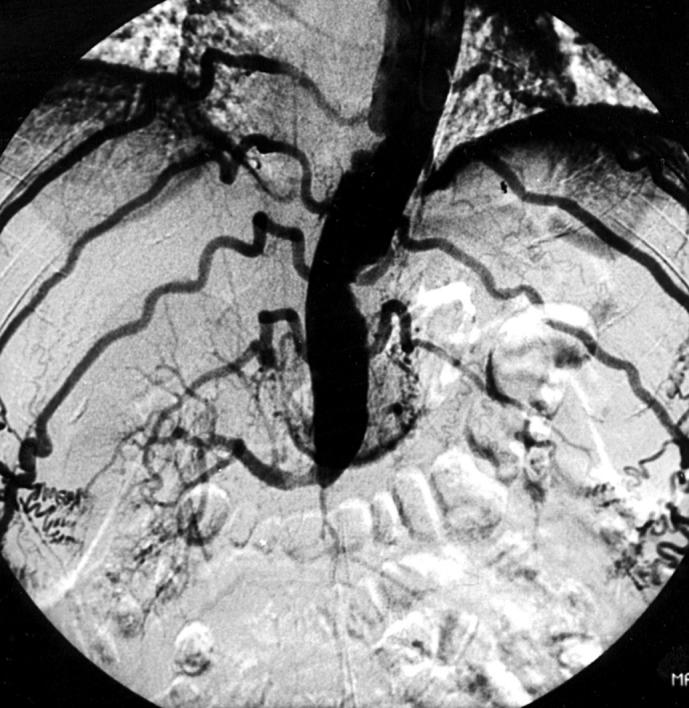
Angiograph showing an occluded aorta. Huge intercostal arteries feeding collaterals over the abdominal wall to the pelvic and leg arteries can be seen. Severe atheromatous plaques, an occluded left renal artery, and an occluded coeliac trunk are present.


