Abstract
OBJECTIVES—To evaluate the effect of anti-TNFα on the Th1 and Th2 cytokines in patients with spondyloarthropathy (SpA). METHODS—Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were obtained from 20 patients with active SpA treated with infliximab (5 mg/kg). For comparison, PBMC were also obtained from 15 healthy controls and 19 patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). After stimulation with PMA/ionomycin, the intracellular cytokines interleukin (IL)2, IL4, IL10, and interferon (IFN)γ were determined in CD3+ T cells and in CD3+/CD56+ natural killer (NK) T cells by flow cytometry. RESULTS—At baseline the percentage of T cells positive for IFNγ (p=0.020) and IL2 (p=0.046) was decreased in patients with SpA compared with healthy controls, while IL10 (p=0.001) was increased. This cytokine profile, confirmed by the mean fluorescence intensities (MFI), was more pronounced in CD3+/CD8- cells and contrasted with higher IL2 production in RA. NK T cells, characterised by high IL4 and IL10 numbers, were also increased in patients with SpA (p=0.017). Treatment with infliximab induced a significant and persistent increase in IFNγ and IL2 in patients with SpA. Moreover, there was a transient decrease in IL10 and NK T cells in patients with high baseline values, resulting in values comparable with those of healthy controls. This switch in cytokine profile was seen in both the CD3+/CD8- and CD3+/CD8+ subsets. CONCLUSIONS—Before treatment patients with SpA had an impaired Th1 cytokine profile compared with healthy controls and patients with RA. TNFα blockade induced restoration of the Th1 cytokines, resulting in a normal cytokine balance. These data confirm the effect of anti-TNFα on the immune changes in SpA, and provide insights into the mechanisms involved in TNFα blockade.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (165.4 KB).
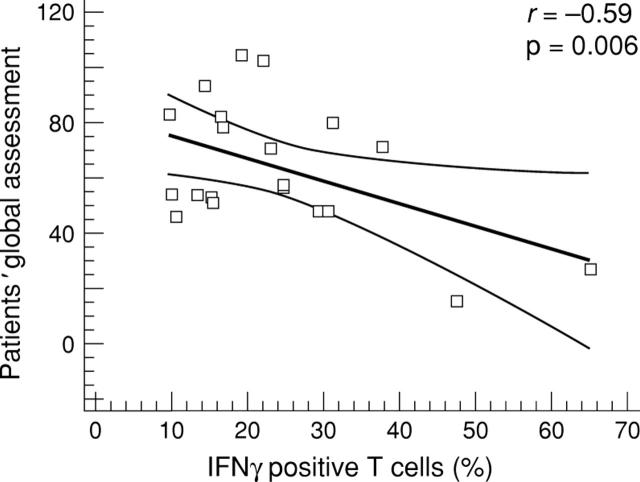
Figure 1 .
Relation between the percentage of IFNγ positive peripheral blood T cells analysed by flow cytometry and the patients' global assessment (100 mm visual analogue scale) in 20 patients with spondyloarthropathy. A significant inverse correlation was found (r=-0.59, p=0.006).
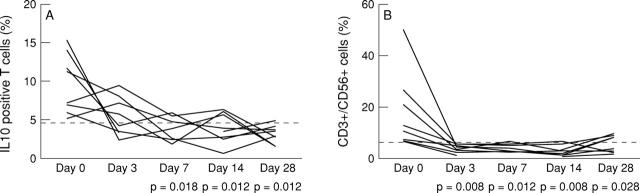
Figure 2 .
Peripheral blood T cells of patients with spondyloarthropathy with high baseline values for IL10 and NK T cells were analysed by flow cytometry at baseline and at days 3, 7, 14, and 28 of treatment with anti-TNFα (infliximab 5 mg/kg on days 0, 14, and 42). The upper limit of normal values, defined as more than the mean + 2 SD of the healthy control group, is indicated by the dotted line. (A) Decrease in the percentage of IL10 positive cells in the CD3+ population in patients with high baseline values (n=8). (B) Decrease in the percentage of CD3+/CD56+ cells in the CD3+ population in patients with high baseline values (n=9).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K., Murphy K. M., Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996 Oct 31;383(6603):787–793. doi: 10.1038/383787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Yin Z., Spiller I., Siegert S., Rudwaleit M., Liu L., Radbruch A., Sieper J. Low secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha, but no other Th1 or Th2 cytokines, by peripheral blood mononuclear cells correlates with chronicity in reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Oct;42(10):2039–2044. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2039::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cañete J. D., Martínez S. E., Farrés J., Sanmartí R., Blay M., Gómez A., Salvador G., Muñoz-Gómez J. Differential Th1/Th2 cytokine patterns in chronic arthritis: interferon gamma is highly expressed in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis compared with seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Apr;59(4):263–268. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudepierre P., Rymer J. C., Chevalier X. IL-10 plasma levels correlate with disease activity in spondyloarthropathy. J Rheumatol. 1997 Aug;24(8):1659–1661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. B., Katsikis P. D., Chu C. Q., Thomssen H., Webb L. M., Maini R. N., Londei M., Feldmann M. High level of interleukin-10 production by the activated T cell population within the rheumatoid synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jul;38(7):946–952. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantin A., Loubet-Lescoulié P., Lambert N., Yassine-Diab B., Abbal M., Mazières B., de Préval C., Cantagrel A. Antiinflammatory and immunoregulatory action of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence of increased interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 gene expression demonstrated in vitro by competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):48–57. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<48::AID-ART7>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope A. P., Londei M., Chu N. R., Cohen S. B., Elliott M. J., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Chronic exposure to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in vitro impairs the activation of T cells through the T cell receptor/CD3 complex; reversal in vivo by anti-TNF antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):749–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI117394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cush J. J., Splawski J. B., Thomas R., McFarlin J. E., Schulze-Koops H., Davis L. S., Fujita K., Lipsky P. E. Elevated interleukin-10 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):96–104. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferran C., Dautry F., Mérite S., Sheehan K., Schreiber R., Grau G., Bach J. F., Chatenoud L. Anti-tumor necrosis factor modulates anti-CD3-triggered T cell cytokine gene expression in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2189–2196. doi: 10.1172/JCI117215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funauchi M., Yu H., Sugiyama M., Ikoma S., Ohno M., Kinoshita K., Hamada K., Kanamaru A. Increased interleukin-4 production by NK T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 1999 Aug;92(2):197–202. doi: 10.1006/clim.1999.4742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., Lindberg A. A., Mäki-Ikola O., von Essen R., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Isomäki H., Saario R., Arnold W. J., Toivanen A. Salmonella lipopolysaccharide in synovial cells from patients with reactive arthritis. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):685–688. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90804-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., von Essen R., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Isomäki O., Pekkola-Heino K., Merilahti-Palo R., Saario R., Isomäki H., Toivanen A. Yersinia antigens in synovial-fluid cells from patients with reactive arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 26;320(4):216–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901263200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illés Z., Kondo T., Newcombe J., Oka N., Tabira T., Yamamura T. Differential expression of NK T cell V alpha 24J alpha Q invariant TCR chain in the lesions of multiple sclerosis and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Immunol. 2000 Apr 15;164(8):4375–4381. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.8.4375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomaki P., Luukkainen R., Saario R., Toivanen P., Punnonen J. Interleukin-10 functions as an antiinflammatory cytokine in rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Mar;39(3):386–395. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakoshi N. N., Greiner D. L., Rossini A. A., Mordes J. P. Diabetes prone BB rats are severely deficient in natural killer T cells. Autoimmunity. 1999;31(1):1–14. doi: 10.3109/08916939908993854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamradt T., Burmester G. R. Cytokines and arthritis: is the Th1/Th2 paradigm useful for understanding pathogenesis? J Rheumatol. 1998 Jan;25(1):6–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leite-de-Moraes M. C., Dy M. Natural killer T cells: a potent cytokine-producing cell population. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1997 Sep;8(3):229–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubet-Lescoulié P., Constantin A., Mazières B., Tkaczuk J., de Préval C., Cantagrel A. Decreased peripheral blood T cell cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1999;28(4):244–251. doi: 10.1080/03009749950155625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice M. M., van der Graaff W. L., Leow A., Breedveld F. C., van Lier R. A., Verweij C. L. Treatment with monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody results in an accumulation of Th1 CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Oct;42(10):2166–2173. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2166::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mieza M. A., Itoh T., Cui J. Q., Makino Y., Kawano T., Tsuchida K., Koike T., Shirai T., Yagita H., Matsuzawa A. Selective reduction of V alpha 14+ NK T cells associated with disease development in autoimmune-prone mice. J Immunol. 1996 May 15;156(10):4035–4040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., van den Berg W. Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Dec;40(12):2105–2115. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K. J., Grom A. A., Thompson S. D., Lieuwen D., Passo M. H., Glass D. N. Contrasting cytokine profiles in the synovium of different forms of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile spondyloarthropathy: prominence of interleukin 4 in restricted disease. J Rheumatol. 1998 Jul;25(7):1388–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson N., Bremell T., Tarkowski A., Carlsten H. Protective role of NK1.1+ cells in experimental Staphylococcus aureus arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Jul;117(1):63–69. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima S., Saeki Y., Mima T., Sasai M., Nishioka K., Ishida H., Shimizu M., Suemura M., McCloskey R., Kishimoto T. Long-term follow-up of the changes in circulating cytokines, soluble cytokine receptors, and white blood cell subset counts in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) after monoclonal anti-TNF alpha antibody therapy. J Clin Immunol. 1999 Sep;19(5):305–313. doi: 10.1023/a:1020543625282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirmez C., Yamamura M., Uyemura K., Paes-Oliveira M., Conceiço-Silva F., Modlin R. L. Cytokine patterns in the pathogenesis of human leishmaniasis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1390–1395. doi: 10.1172/JCI116341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudwaleit M., Yin Z., Siegert S., Grolms M., Radbruch A., Braun J., Sieper J. Response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a decrease of T cell derived tumour necrosis factor alpha, increase of interleukin 10, and predicted by the initial concentration of interleukin 4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Apr;59(4):311–314. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaak J., Hermann E., Ringhoffer M., Probst P., Gallati H., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Fleischer B. Predominance of Th1-type T cells in synovial fluid of patients with Yersinia-induced reactive arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):2771–2776. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerwegh A. J., De Clerck L. S., De Schutter L., Bridts C. H., Verbruggen A., Stevens W. J. Flow cytometric detection of type 1 (IL-2, IFN-gamma) and type 2 (IL-4, IL-5) cytokines in T-helper and T-suppressor/cytotoxic cells in rheumatoid arthritis, allergic asthma and atopic dermatitis. Cytokine. 1999 Oct;11(10):783–788. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1998.0483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieling P. A., Wang X. H., Gately M. K., Oliveros J. L., McHugh T., Barnes P. F., Wolf S. F., Golkar L., Yamamura M., Yogi Y. IL-12 regulates T helper type 1 cytokine responses in human infectious disease. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 15;153(8):3639–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Braun J. Pathogenesis of spondylarthropathies. Persistent bacterial antigen, autoimmunity, or both? Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Nov;38(11):1547–1554. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Makino Y., Cui J., Masuda K., Kawano T., Sato H., Kondo E., Koseki H. V alpha 14+ NK T cells: a novel lymphoid cell lineage with regulatory function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996 Dec;98(6 Pt 2):S263–S269. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Gilroy C. B., Thomas B. J., Keat A. C. Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis DNA in joints of reactive arthritis patients by polymerase chain reaction. Lancet. 1992 Jul 11;340(8811):81–82. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90399-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Baeten D., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Z., Braun J., Neure L., Wu P., Liu L., Eggens U., Sieper J. Crucial role of interleukin-10/interleukin-12 balance in the regulation of the type 2 T helper cytokine response in reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Oct;40(10):1788–1797. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin Z., Siegert S., Neure L., Grolms M., Liu L., Eggens U., Radbruch A., Braun J., Sieper J. The elevated ratio of interferon gamma-/interleukin-4-positive T cells found in synovial fluid and synovial membrane of rheumatoid arthritis patients can be changed by interleukin-4 but not by interleukin-10 or transforming growth factor beta. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Nov;38(11):1058–1067. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.11.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Jansen J., Levi M., ten Cate H., ten Cate J. W., van Deventer S. J. Regulation of interleukin 10 release by tumor necrosis factor in humans and chimpanzees. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1985–1988. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]