Abstract
OBJECTIVES—Cellular and humoral immunity to collagen and cartilage proteoglycan were shown in patients with osteoarthritis (OA). Inflammatory infiltration containing T and B lymphocytes and macrophages, which are HLA-DR positive, is often seen in the synovial membrane of patients with OA. An analysis of the DNA restriction enzyme patterns of T lymphocytes from the OA synovium showed an oligoclonal pattern of T cell receptor β chain gene rearrangements. No similar studies of B cell clonality have previously been performed. This study aimed at determining the clonal characteristics of the B cells in the OA synovium. METHODS—A reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction of the immunoglobulin transcripts of B cells in the synovial membranes from six patients with OA was performed and the products were analysed by a single strand conformation polymorphism analysis. RESULTS—Several dominant bands were seen in all samples and some of the dominant bands were common among the two or three separate regions of each synovial sample. CONCLUSION—Infiltrated B cells are oligoclonal, and an antigen driven immune response may play a part in the progression of the disease process in OA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (166.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
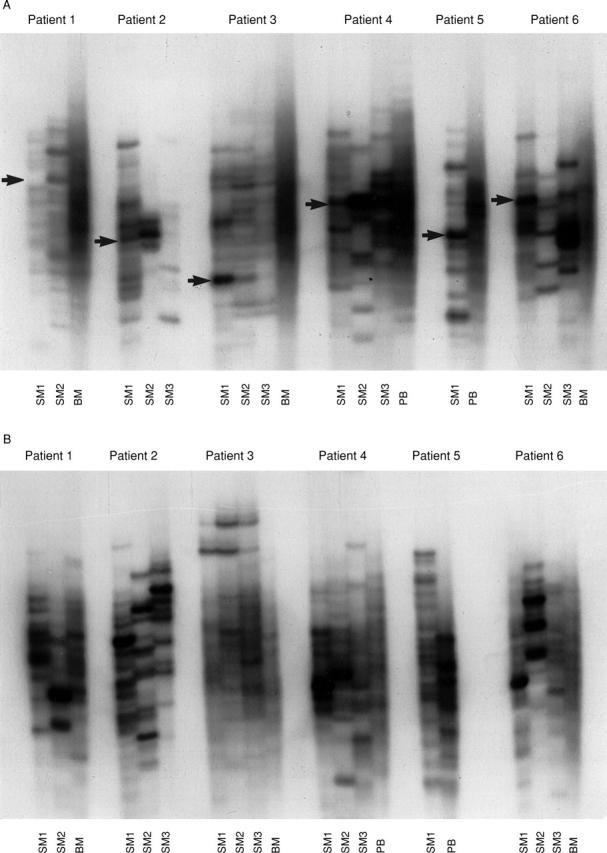
(A) Results of a µ RT-PCR-SSCP analysis of B cells from the synovial membranes (SM), bone marrow (BM), and peripheral blood (PB) from patients with osteoarthritis 1-6. The positions of the bands sequence-analysed are shown by arrows. (B) The results of a γ RT-PCR-SSCP analysis.


