Abstract
Methods: Synovial biopsy specimens from 11 patients with longstanding RA (median disease duration 21 years) and eight with early RA (median disease duration five months) were investigated. Apoptosis (TUNEL method combined with morphological analysis), cell surface markers (CD3, CD68), cytokines (interleukin (IL) 1α, IL1ß, tumour necrosis factor α, and IL6), and FLIP expression were evaluated. Computer assisted image analysis was used for quantification.
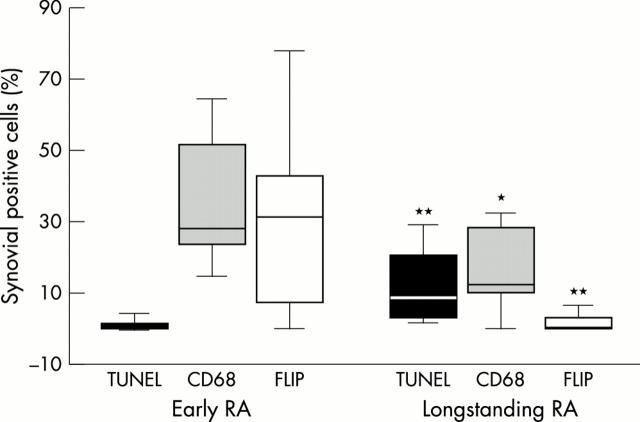
Results: The apoptosis level in RA synovium was significantly higher in the group of patients with longstanding RA than in the patients with early RA (8.8% v 0.6%, p=0.001), while the number of macrophages and FLIP expression were higher in the group with early disease than in the group with longstanding RA (16.2% v 8.3%, p=0.02 and 31.1% v 0.2%, p=0.001 respectively). All three markers correlated significantly with disease duration (R=-0.7, p<0.001 for FLIP, R=0.6, p=0.001 for apoptosis, and R=-0.5, p<0.05 for CD68). Cytokine expression and T cell score were not significantly different in early RA from longstanding RA. No differences were seen between patients treated or not treated with corticosteroids or between patients treated or not treated with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that RA synovial macrophages are resistant to apoptosis in early RA and express high levels of FLIP. During natural or drug modified disease progression the apoptotic mechanism may be restored with a specific increase of synovial apoptosis in patients with longstanding arthritis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (138.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
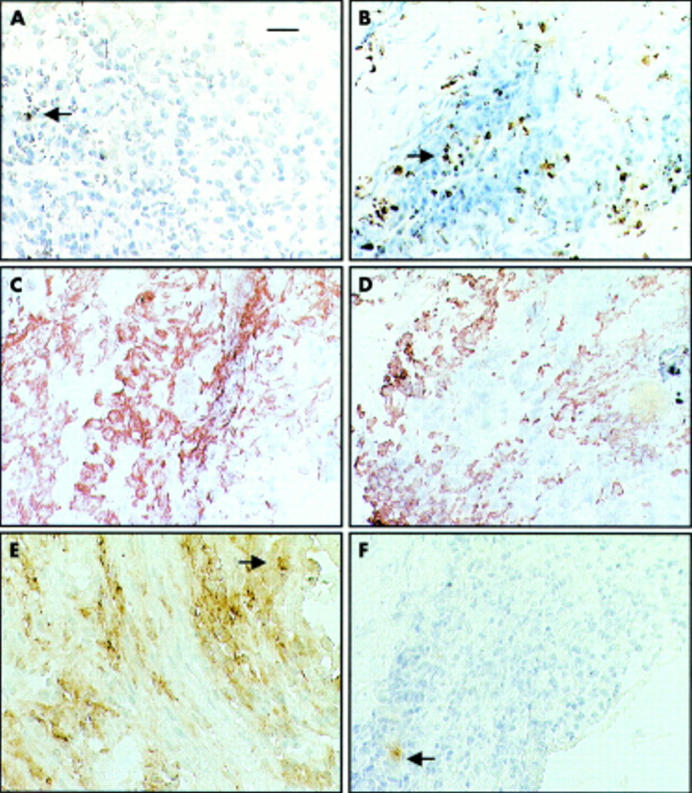
Brown (diaminobenzidine) immunoperoxidase staining for TUNEL, CD68, and FLIP positive cells in serial sections from frozen synovial biopsy specimens counterstained with haematoxylin. (A) TUNEL in early RA (case 1); (B) TUNEL in longstanding RA (case 2); (C) CD68 in early RA (case 1); (D) CD68 in longstanding RA (case 2); (E) FLIP in early RA (case 1); (F) FLIP in longstanding RA (case 2). Original magnification x340, the bar represent 15 µm.
Figure 2 .
Differences between apoptosis, CD68, and FLIP expression in early compared with longstanding RA. Horizontal lines represent median values and whiskers the non-outliers values. Statistical analysis was performed using the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. *p<0.05; **p<0.01.