Abstract
Objective: To investigate the intra-articular vascularisation of the synovial pannus in the knee of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with power Doppler ultrasonography (PDS) and an echo contrast agent and correlate the area under the time-intensity curves with the clinical findings and laboratory measures of disease activity.
Method: Forty two patients with RA (31 women, 11 men) with history and signs of knee arthritis, classified according to a modified index of synovitis activity (active, moderately active, and inactive), were studied. Clinical and functional assessment (number of swollen joints, intensity of pain, general health—visual analogue scale, disability index—Health Assessment Questionnaire, Ritchie articular index) and a laboratory evaluation were made on all patients. Disease activity was evaluated using the disease activity score (DAS) and the chronic arthritis systemic index (CASI) for each patient. All patients were examined with conventional ultrasonography and PDS before injection of intravenous ultrasound contrast agent (Levovist). The quantitative estimation of the vascularisation of the synovial membrane was performed with time-intensity curves and calculation of the area under the curves.
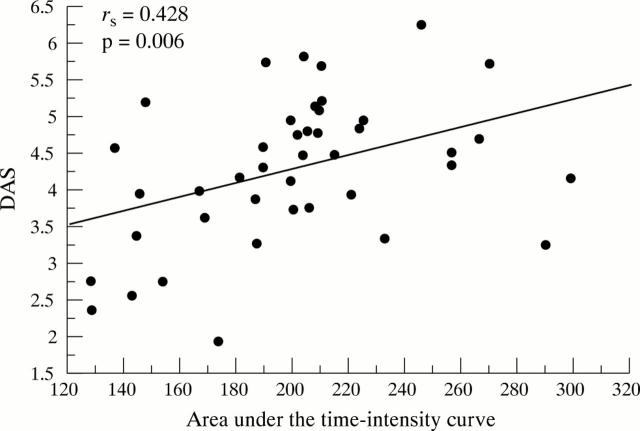
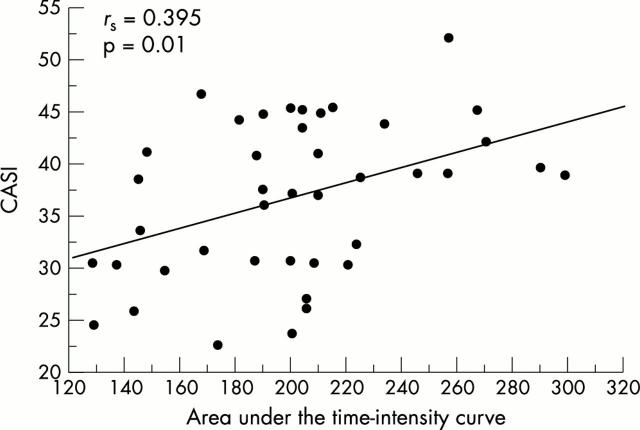
Results: The mean (SD) value of the area underlying time-intensity curves was 216.2 (33.4) in patients with active synovitis, 186.8 (25.8) in patients with moderately active synovitis, and 169.6 (20.6) in those with inactive synovitis. The mean value of the areas differed significantly between the patients with active and those with inactive synovitis (p<0.01). The mean value of the area under the curve of the entire group was weakly correlated with the number of swollen joints (p=0.038), but a strong correlation was found with composite indexes of disease activity such as the DAS (p=0.006) and CASI (p=0.01). No correlation was found with age, disease duration, and other laboratory and clinical variables.
Conclusion: PDS may be a valuable tool to detect fractional vascular volume and to assist clinicians in distinguishing between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pannus. The transit of microbubbles of ultrasound contrast across a tissue can be used to estimate haemodynamic alterations and may have a role in assessing synovial activity and the therapeutic response to treatment of synovitis of the knee joint.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (194.8 KB).
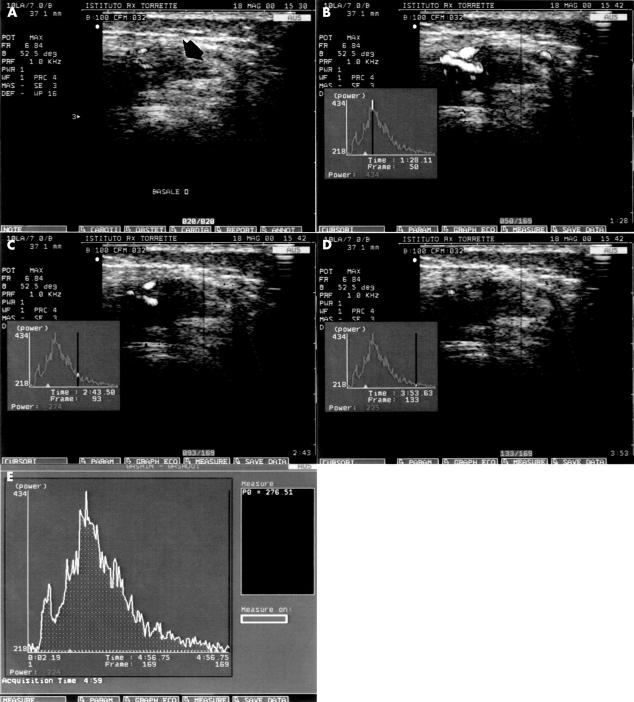
Figure 1 .
Active synovitis. The figure shows the contrast enhancement curve after the IV administration of Levovist (B, C, D) and the corresponding bidimensional PDS image of the synovial pannus detected in the suprapatellar transverse scan, with the knee joint in moderate flexion (30°) (arrow), before (A) and after (B, C, D) the contrast agent, as well as the area under the time-intensity curve (E).
Figure 2 .
Correlation between the area under the time-intensity curve and the disease activity score (DAS) (Spearman's rank correlation test).
Figure 3 .
Correlation between the area under the time-intensity curve and the chronic arthritis systemic index (CASI) (Spearman's rank correlation test).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus M., Burmester G. R., Gerber T., Grassi W., Machold K. P., Swen W. A., Wakefield R. J., Manger B., Working Group for Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in the EULAR Standing Committee on International Clinical Studies including Therapeutic Trials Guidelines for musculoskeletal ultrasound in rheumatology. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Jul;60(7):641–649. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.7.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus M., Kamradt T., Sandrock D., Loreck D., Fritz J., Wolf K. J., Raber H., Hamm B., Burmester G. R., Bollow M. Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1232–1245. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1232::AID-ANR21>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomley M. J., Cooke J. C., Unger E. C., Monaghan M. J., Cosgrove D. O. Microbubble contrast agents: a new era in ultrasound. BMJ. 2001 May 19;322(7296):1222–1225. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7296.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boini S., Guillemin F. Radiographic scoring methods as outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis: properties and advantages. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Sep;60(9):817–827. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. F., Pincus T., Huston J. W., 3rd, Brooks R. H., Nance E. P., Jr, Kaye J. J. Measures of activity and damage in rheumatoid arthritis: depiction of changes and prediction of mortality over five years. Arthritis Care Res. 1997 Dec;10(6):381–394. doi: 10.1002/art.1790100606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinal E., Lafortune M., Burns P. Power Doppler US in synovitis: reality or artifact? Radiology. 1996 Sep;200(3):868–869. doi: 10.1148/radiology.200.3.8756948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correas J. M., Bridal L., Lesavre A., Méjean A., Claudon M., Hélénon O. Ultrasound contrast agents: properties, principles of action, tolerance, and artifacts. Eur Radiol. 2001;11(8):1316–1328. doi: 10.1007/s003300100940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraccioli G. F., Salaffi F., Troise-Rioda W., Bartoli E. The Chronic Arthritis Systemic Index (CASI). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 May-Jun;12(3):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraccioli G., Bartoli E., Salaffi F., Peroni M. The Chronic Arthritis Systemic Index: a nomogram to assess the activity and severity of chronic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1180–1181. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex E., Jonsson K., Johnson U., Eberhardt K. Development of radiographic damage during the first 5-6 yr of rheumatoid arthritis. A prospective follow-up study of a Swedish cohort. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;35(11):1106–1115. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.11.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocco U., Cozzi L., Rubaltelli L., Rigon C., De Candia A., Tregnaghi A., Gallo C., Favaro M. A., Chieco-Bianchi F., Baldovin M. Long-term sonographic follow-up of rheumatoid and psoriatic proliferative knee joint synovitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Feb;35(2):155–163. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Spitz P., Kraines R. G., Holman H. R. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Feb;23(2):137–145. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovagnorio F., Martinoli C., Coari G. Power Doppler sonography in knee arthritis--a pilot study. Rheumatol Int. 2001 Apr;20(3):101–104. doi: 10.1007/s002960000082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi W., Filippucci E., Farina A., Salaffi F., Cervini C. Ultrasonography in the evaluation of bone erosions. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Feb;60(2):98–103. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi W., Lamanna G., Farina A., Cervini C. Synovitis of small joints: sonographic guided diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Oct;58(10):595–597. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.10.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund M., Ostergaard M., Jensen K. E., Madsen J. L., Skjødt H., Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and scintigraphy of the finger joints: one year follow up of patients with early arthritis. The TIRA Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jul;59(7):521–528. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.7.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad S., Hedfors E. Intraarticular variation in synovitis. Local macroscopic and microscopic signs of inflammatory activity are significantly correlated. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Sep;28(9):977–986. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magarelli N., Guglielmi G., Di Matteo L., Tartaro A., Mattei P. A., Bonomo L. Diagnostic utility of an echo-contrast agent in patients with synovitis using power Doppler ultrasound: a preliminary study with comparison to contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol. 2001;11(6):1039–1046. doi: 10.1007/s003300000650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinoli C., Derchi L. E. Gain setting in power Doppler US. Radiology. 1997 Jan;202(1):284–285. doi: 10.1148/radiology.202.1.8988227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinoli C., Pretolesi F., Crespi G., Bianchi S., Gandolfo N., Valle M., Derchi L. E. Power Doppler sonography: clinical applications. Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 (Suppl 2):S133–S140. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen F. M., Stewart N., Crabbe J., Robinson E., Yeoman S., Tan P. L., McLean L. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Jun;57(6):350–356. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.6.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherin D., Fitzgerald O., Bresnihan B. Clinical improvement and radiological deterioration in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence that the pathogenesis of synovial inflammation and articular erosion may differ. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Dec;35(12):1263–1268. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.12.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. S., Laing T. J., McCarthy C. J., Adler R. S. Power Doppler sonography of synovitis: assessment of therapeutic response--preliminary observations. Radiology. 1996 Feb;198(2):582–584. doi: 10.1148/radiology.198.2.8596870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Hansen M., Stoltenberg M., Gideon P., Klarlund M., Jensen K. E., Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging-determined synovial membrane volume as a marker of disease activity and a predictor of progressive joint destruction in the wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 May;42(5):918–929. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199905)42:5<918::AID-ANR10>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranza R., Marchesoni A., Calori G., Bianchi G., Braga M., Canazza S., Canesi B., Fumagalli M., Mastaglio C., Mathieu A. The Italian version of the Functional Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire. A reliable instrument for multicenter studies on rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993 Mar-Apr;11(2):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubaltelli L., Fiocco U., Cozzi L., Baldovin M., Rigon C., Bortoletto P., Tregnaghi A., Melanotte P. L., di Maggio C., Todesco S. Prospective sonographic and arthroscopic evaluation of proliferative knee joint synovitis. J Ultrasound Med. 1994 Nov;13(11):855–862. doi: 10.7863/jum.1994.13.11.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaffi F., Ferraccioli G., Peroni M., Carotti M., Bartoli E., Cervini C. Progression of erosion and joint space narrowing scores in rheumatoid arthritis assessed by nonlinear models. J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;21(9):1626–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. A., Völker L., Zacher J., Schläfke M., Ruhnke M., Gromnica-Ihle E. Colour Doppler ultrasonography to detect pannus in knee joint synovitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000 Jul-Aug;18(4):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai K., Yamato M., Yamaguchi T., Ohno W. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Aug;37(8):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. W., Silman A. J., Kirwan J. R., Currey H. L. Articular indices of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with the acute-phase response. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jun;30(6):618–623. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Wade M., Mapp P. I., Blake D. R. Focally regulated endothelial proliferation and cell death in human synovium. Am J Pathol. 1998 Mar;152(3):691–702. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther M., Harms H., Krenn V., Radke S., Faehndrich T. P., Gohlke F. Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):331–338. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<331::AID-ANR50>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., Theunisse L. A., Lubberts E. W., van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Nov;49(11):916–920. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.11.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M., van Riel P. L., van de Putte L. B. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20(3):579–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Validity of single variables and composite indices for measuring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Feb;51(2):177–181. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]