Abstract
Objectives: To obtain evidence for dose response and to extend evidence of safety and efficacy for B lymphocyte depletion in rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: Twenty two patients with rheumatoid arthritis received a total of 29 treatments with five different combinations of rituximab (RTX), cyclophosphamide (CP), and/or high dose prednisolone (PR) on an open basis as follows; cohort I: RTX 1400 mg/m2, CP 750x2+PR; cohort II: RTX 300–700 mg/m2, -CP±PR); cohort III: RTX 600–700 mg/m2, CP 750x2+PR; cohort IV: RTX 1200 mg/m2, CP 750x2-PR; cohort V: RTX 500 mg/m2, CP 750x2+PR. American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria of improvement at six months were chosen as the primary outcome measure. Disease activity scores and total duration of improvement and of B cytopenia were also recorded.
Results: No major adverse events attributable to treatment were seen. ACR grades of improvement at six months were as follows: cohort I: ACR70x3, ACR50x2; cohort II: ACR20x1, ACR0x3; cohort III: ACR70x6, ACR50x2, ACR20x2; cohort IV: ACR70x2, ACR50x2, ACR20x1, ACR0x1; cohort V: ACR0x4.
Conclusions: B lymphocyte depletion in rheumatoid arthritis has so far proved to be safe and associated with major improvement with protocols including RTX 600 mg/m2 or more and CP, but not with more limited protocols. These observations provide an initial basis for the design of formal trials of B cell depletion and other B cell directed treatments, including a phase II controlled trial now in progress.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (133.4 KB).
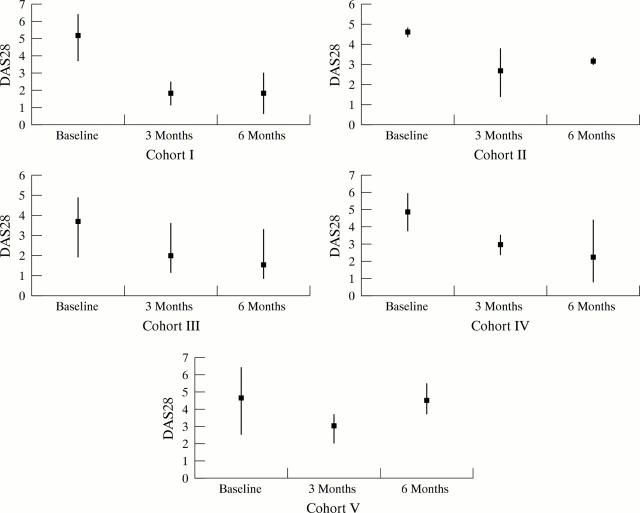
Figure 1 .
Mean modified disease activity score (DAS28) for each cohort. Bars indicate minimum and maximum values.
Figure 2 .
Mean total serum immunoglobulin levels. Bars indicate minimum and maximum levels.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams V. M., Cambridge G., Lydyard P. M., Edwards J. C. Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha production by adhered human monocytes: a key role for Fcgamma receptor type IIIa in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):608–616. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200003)43:3<608::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia A., Blades S., Cambridge G., Edwards J. C. Differential distribution of Fc gamma RIIIa in normal human tissues and co-localization with DAF and fibrillin-1: implications for immunological microenvironments. Immunology. 1998 May;94(1):56–63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1998.00491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuczman M. S. CHOP plus rituximab chemoimmunotherapy of indolent B-cell lymphoma. Semin Oncol. 1999 Oct;26(5 Suppl 14):88–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. C., Cambridge G. Sustained improvement in rheumatoid arthritis following a protocol designed to deplete B lymphocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Feb;40(2):205–211. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Carter R. H. The CD19/CR2/TAPA-1 complex of B lymphocytes: linking natural to acquired immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:127–149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Katz L. M., Lightfoot R., Jr, Paulus H., Strand V. American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jun;38(6):727–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal A. K., Press O. W. Clinical applications of anti-CD20 antibodies. J Lab Clin Med. 1999 Nov;134(5):445–450. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(99)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Versendaal H., Jonker M., Bresnihan B., Post W. J., t Hart B. A., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Asymptomatic synovitis precedes clinically manifest arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Aug;41(8):1481–1488. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199808)41:8<1481::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Elliott M., Brennan F. M., Williams R. O., Feldmann M. TNF blockade in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for therapy and pathogenesis. APMIS. 1997 Apr;105(4):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1997.tb00567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney D. G., Grillo-López A. J., Bodkin D. J., White C. A., Liles T. M., Royston I., Varns C., Rosenberg J., Levy R. IDEC-C2B8: results of a phase I multiple-dose trial in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1997 Oct;15(10):3266–3274. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1997.15.10.3266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Nardella F. A. IgG rheumatoid factors and self-association of these antibodies. Clin Rheum Dis. 1985 Dec;11(3):551–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardella F. A., Dayer J. M., Roelke M., Krane S. M., Mannik M. Self-associating IgG rheumatoid factors stimulate monocytes to release prostaglandins and mononuclear cell factor that stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin production by synovial cells. Rheumatol Int. 1983;3(4):183–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00541598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reff M. E., Carner K., Chambers K. S., Chinn P. C., Leonard J. E., Raab R., Newman R. A., Hanna N., Anderson D. R. Depletion of B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20. Blood. 1994 Jan 15;83(2):435–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosnek E., Lanzavecchia A. Efficient and selective presentation of antigen-antibody complexes by rheumatoid factor B cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):487–489. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. K., Seipelt E., Sieper J. Divergent T-cell cytokine patterns in inflammatory arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):869–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Capel P. J. Human IgG Fc receptor heterogeneity: molecular aspects and clinical implications. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90166-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]