Abstract
Background: It was hypothesised that negative RA related illness cognitions are strongly related to the neuroticism trait and act as a common factor behind other self reported subjective symptoms (pain and ADL status), mood, and positive RA related illness cognitions; but are unrelated to objective indices of impairment (disease duration, C reactive protein (CRP), and joint stiffness).
Objective: To examine the relative influence of negative illness cognitions and neuroticism versus degree of impairment on subjective symptoms, positive illness cognitions, and mood in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Structural equation modelling analyses (LISREL) were performed on two independent samples of patients with RA consisting of 212 outpatients and 105 inpatients, respectively.
Results: The hypotheses were largely confirmed. Firstly, negative RA cognitions were found to be dependent on neuroticism. Secondly, negative RA cognitions had a strong and dominating influence on all other self reported data. Subjective symptoms were equally well explained by negative RA cognitions as by degree of impairment. No relations were found between negative RA cognitions (or neuroticism) and degree of impairment.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that neuroticism, recognised as a relatively stable personality trait, strongly influences self rated symptoms and wellbeing in RA. This has important clinical implications concerning the use of standardised self rating questionnaires commonly used to assess illness status in RA and the long term effectiveness of psychological interventions and patient training courses in RA rehabilitation.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (180.4 KB).
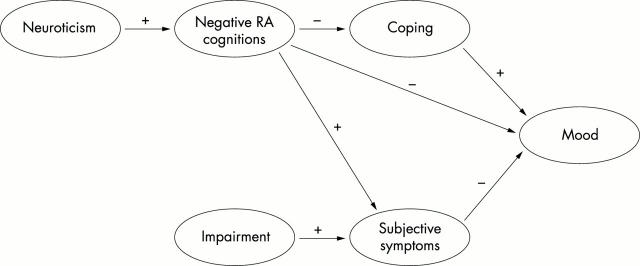
Figure 1 .
Hypothesised structural model between the latent variables. Note that the model with neuroticism included was only tested in sample 1. Positive influences are marked + and negative-.
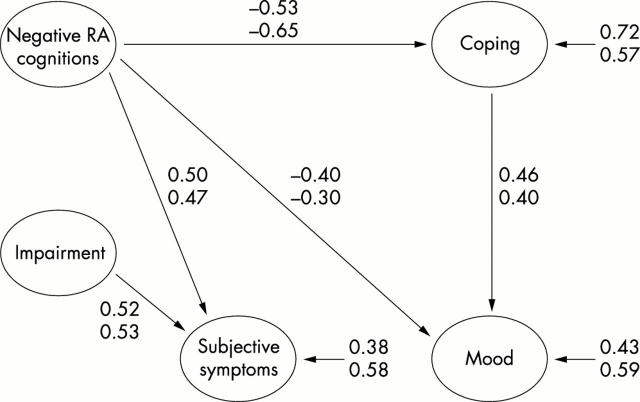
Figure 2 .
Structural model obtained between the five latent variables (neuroticism excluded). Only the significant parameter estimates (p<0.05) are illustrated. The estimates from sample 1 are shown above those for sample 2. The proportions of explained variance of the dependent latent variables are shown with small arrows.
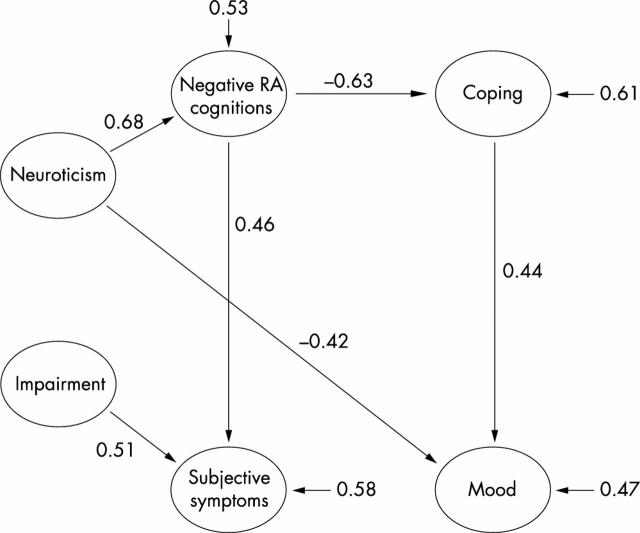
Figure 3 .
Path model obtained with neuroticism included (sample 2). Only the significant parameter estimates (p<0.05) are illustrated. The estimates from sample 1 are shown above those for sample 2. The proportions of explained variance of the dependent latent variables are shown with small arrows.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affleck G., Tennen H., Urrows S., Higgins P. Neuroticism and the pain-mood relation in rheumatoid arthritis: insights from a prospective daily study. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1992 Feb;60(1):119–126. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.60.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlmén M., Bjelle A., Sullivan M. Prediction of team care effects in outpatients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1991 Nov;18(11):1655–1661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustinsson L. E., Sullivan L., Sullivan M. Physical, psychologic, and social function in chronic pain patients after epidural spinal electrical stimulation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1986 Mar;11(2):111–119. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198603000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger N., Schilling E. A. Personality and the problems of everyday life: the role of neuroticism in exposure and reactivity to daily stressors. J Pers. 1991 Sep;59(3):355–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.1991.tb00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger N., Zuckerman A. A framework for studying personality in the stress process. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1995 Nov;69(5):890–902. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.69.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brief A. P., Butcher A. H., George J. M., Link K. E. Integrating bottom-up and top-down theories of subjective well-being: the case of health. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1993 Apr;64(4):646–653. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.64.4.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buescher K. L., Johnston J. A., Parker J. C., Smarr K. L., Buckelew S. P., Anderson S. K., Walker S. E. Relationship of self-efficacy to pain behavior. J Rheumatol. 1991 Jul;18(7):968–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassileth B. R., Lusk E. J., Strouse T. B., Miller D. S., Brown L. L., Cross P. A., Tenaglia A. N. Psychosocial status in chronic illness. A comparative analysis of six diagnostic groups. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 23;311(8):506–511. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408233110805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L. A., Watson D., Mineka S. Temperament, personality, and the mood and anxiety disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 1994 Feb;103(1):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. T., Jr, McCrae R. R. Influence of extraversion and neuroticism on subjective well-being: happy and unhappy people. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1980 Apr;38(4):668–678. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.38.4.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa P. T., Jr, McCrae R. R. Neuroticism, somatic complaints, and disease: is the bark worse than the bite? J Pers. 1987 Jun;55(2):299–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.1987.tb00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekdahl C., Eberhardt K., Andersson S. I., Svensson B. Assessing disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Use of a Swedish version of the Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Scand J Rheumatol. 1988;17(4):263–271. doi: 10.3109/03009748809098795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor H., Turk D. C. Chronic back pain and rheumatoid arthritis: predicting pain and disability from cognitive variables. J Behav Med. 1988 Jun;11(3):251–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00844431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Spitz P., Kraines R. G., Holman H. R. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Feb;23(2):137–145. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagglund K. J., Haley W. E., Reveille J. D., Alarcón G. S. Predicting individual differences in pain and functional impairment among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):851–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkins S. W., Price D. D., Braith J. Effects of extraversion and neuroticism on experimental pain, clinical pain, and illness behavior. Pain. 1989 Feb;36(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(89)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. J., Wolfe F. Anxiety and depression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study of 400 patients. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jun;15(6):932–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefe F. J., Brown G. K., Wallston K. A., Caldwell D. S. Coping with rheumatoid arthritis pain: catastrophizing as a maladaptive strategy. Pain. 1989 Apr;37(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(89)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen R. J. Neuroticism and selective encoding and recall of symptoms: evidence from a combined concurrent-retrospective study. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1992 Mar;62(3):480–488. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.62.3.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorig K., Chastain R. L., Ung E., Shoor S., Holman H. R. Development and evaluation of a scale to measure perceived self-efficacy in people with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jan;32(1):37–44. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundqvist C., Siösteen A., Blomstrand C., Lind B., Sullivan M. Spinal cord injuries. Clinical, functional, and emotional status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991 Jan;16(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manne S. L., Zautra A. J. Couples coping with chronic illness: women with rheumatoid arthritis and their healthy husbands. J Behav Med. 1990 Aug;13(4):327–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00844882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. C., Brooks P. M. An analysis of the relationship between psychological morbidity and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jun;15(6):926–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery H., Persson L. O., Rydén A. Importance and attainment of life values among disabled and non-disabled people. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1996 Dec;28(4):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicassio P. M., Wallston K. A., Callahan L. F., Herbert M., Pincus T. The measurement of helplessness in rheumatoid arthritis. The development of the arthritis helplessness index. J Rheumatol. 1985 Jun;12(3):462–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary A., Shoor S., Lorig K., Holman H. R. A cognitive-behavioral treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Health Psychol. 1988;7(6):527–544. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.7.6.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormel J., Wohlfarth T. How neuroticism, long-term difficulties, and life situation change influence psychological distress: a longitudinal model. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1991 May;60(5):744–755. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.60.5.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Smarr K. L., Buescher K. L., Phillips L. R., Frank R. G., Beck N. C., Anderson S. K., Walker S. E. Pain control and rational thinking. Implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Aug;32(8):984–990. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J., McRae C., Smarr K., Beck N., Frank R., Anderson S., Walker S. Coping strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Sep;15(9):1376–1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson L. O., Berglund K., Sahlberg D. A structure of self-conceptions and illness conceptions in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). J Psychosom Res. 1996 May;40(5):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(95)00618-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raykov T., Tomer A., Nesselroade J. R. Reporting structural equation modeling results in Psychology and Aging: some proposed guidelines. Psychol Aging. 1991 Dec;6(4):499–503. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.6.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revenson T. A., Felton B. J. Disability and coping as predictors of psychological adjustment to rheumatoid arthritis. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1989 Jun;57(3):344–348. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.57.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstiel A. K., Keefe F. J. The use of coping strategies in chronic low back pain patients: relationship to patient characteristics and current adjustment. Pain. 1983 Sep;17(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(83)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg L., Svensson E., Persson L. O. The measurement of mood. Scand J Psychol. 1979;20(1):1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9450.1979.tb00677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Peck J. R., Milano R. A., Ward J. R. Cognitive distortion in rheumatoid arthritis: relation to depression and disability. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988 Jun;56(3):412–416. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.56.3.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Peck J. R., Ward J. R. Helplessness and depression in rheumatoid arthritis. Health Psychol. 1990;9(4):377–389. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.9.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M. J., Wallston K. A., Nicassio P. M., Castner N. M. Correlates of a clinical classification schema for the arthritis helplessness subscale. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jul;31(7):876–881. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M. J., Wallston K. A., Nicassio P. M. Factor structure of the Arthritis Helplessness Index. J Rheumatol. 1988 Mar;15(3):427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stensman R. Severely mobility-disabled people assess the quality of their lives. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1985;17(2):87–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. E. Asymmetrical effects of positive and negative events: the mobilization-minimization hypothesis. Psychol Bull. 1991 Jul;110(1):67–85. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.110.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D., Pennebaker J. W. Health complaints, stress, and distress: exploring the central role of negative affectivity. Psychol Rev. 1989 Apr;96(2):234–254. doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.96.2.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. D. Psychological factors in rheumatoid arthritis. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1992 Aug;60(4):619–627. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.60.4.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]