Abstract
Objectives: To compare receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) production in the synovial tissue from patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inactive RA, spondyloarthropathies (SpA), osteoarthritis, and from normal subjects. In addition, to establish the cell lineages expressing RANKL in these tissues.
Methods: Immunohistological analysis of frozen synovial tissue biopsy specimens was performed using a monoclonal antibody (mAb) to detect RANKL. Sections were evaluated by computer assisted image analysis and semiquantitative analysis to compare RANKL expression between groups. Dual and sequential labelling with mAb RANKL and cell lineage specific monoclonal antibodies were used to determine the types of cells expressing RANKL.
Results: Higher levels of RANKL were expressed in tissues from patients with active RA and SpA than in tissues from patients with inactive RA, osteoarthritis, and from normal subjects. RANKL protein was associated with CD3 antigen-positive lymphocytes and some macrophages. RANKL was predominantly associated with activated, memory T cells (CD45Ro positive cells) in patients with active RA and spondyloarthropathy (SpA).
Conclusions: The highest levels of RANKL were detected in patients with RA with active synovitis and in some patients with SpA. An increase in RANKL in the inflamed joint of patients with RA, produced by infiltrating activated T cells and macrophages, is likely to be an important cause of joint erosions in RA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (282.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
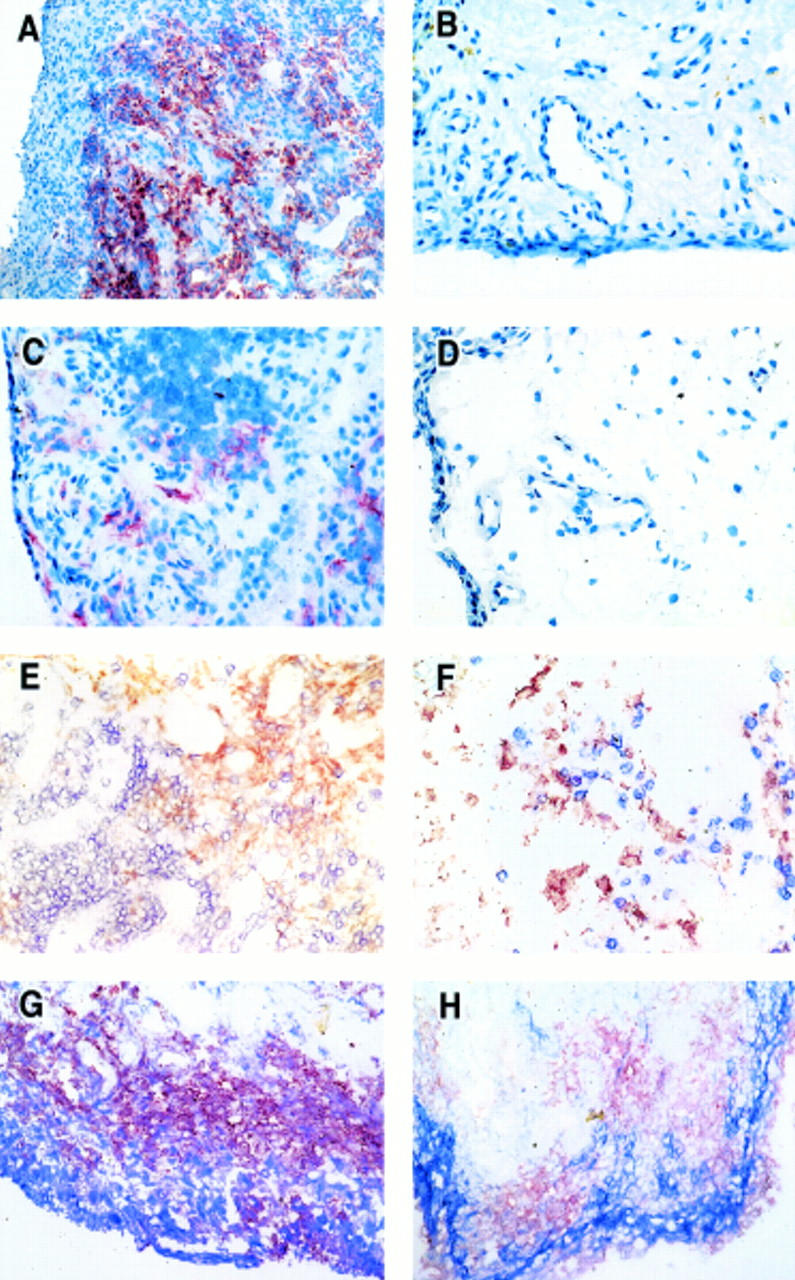
RANKL detected with mAb 626/immunoperoxidase and AEC (red), in synovial tissue from a patient with RA with (A) active disease and (B) inactive disease, (C) a patient with SpA, and (D) a patient with OA. (E) to (H) identify cell lineages expressing RANKL (mAb 626/immunoperoxidase (red)) using dual immunohistochemical labelling on serial synovial biopsy sections from a patient with RA with active disease. RANKL expression is identified by mAb 626 using an AEC/immunoperoxidase technique combined with an immunohistochemical alkaline phosphatase technique using fast blue to identify cell surface markers. (E) Dual labelling with anti-CD3 (blue) and both (purple), (F) B cell antibody anti-CD22 (blue), (G) monocyte/macrophage lineage anti-CD68 (blue) and both (purple), (H) FLS with anti- CD55/fast blue (blue). All magnifications taken at x20.
Figure 2 .
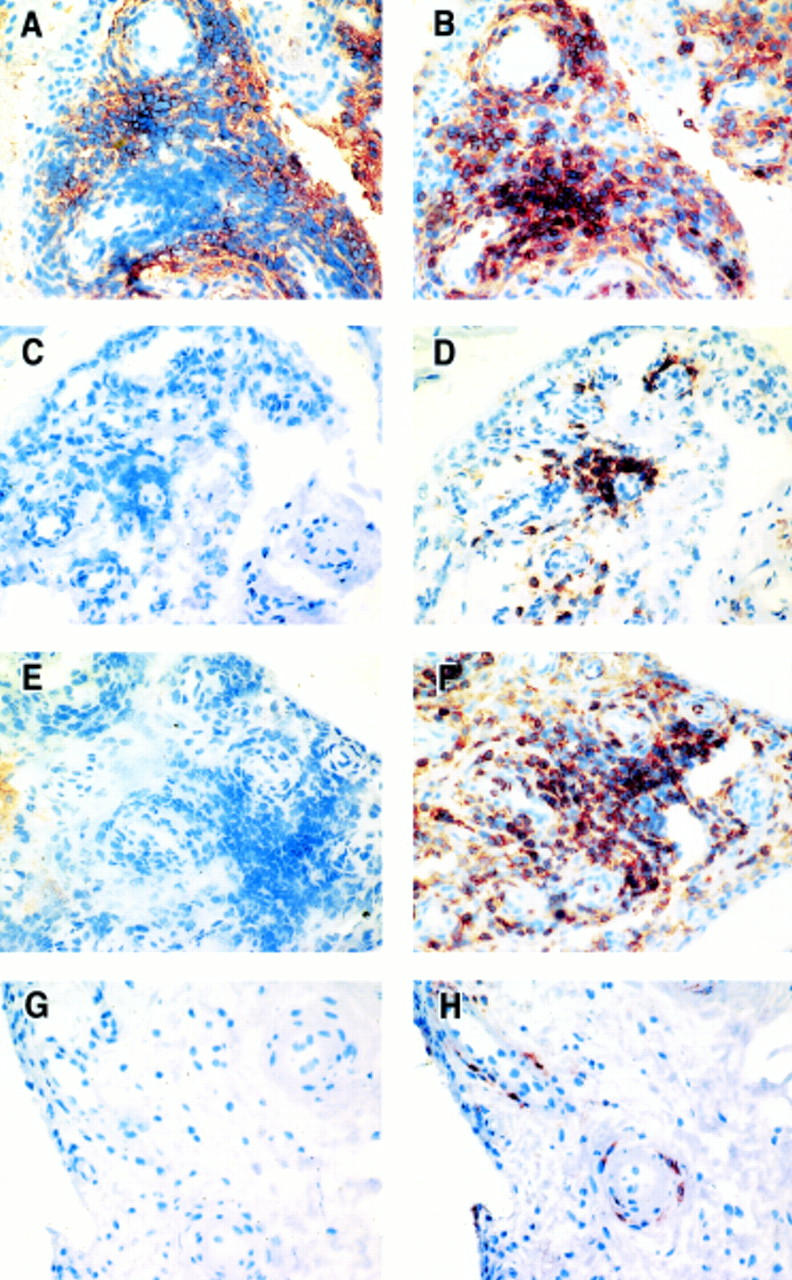
Panels (A), (C), (E), (G) demonstrate RANKL expression, detected with mAb 626/ immunoperoxidase and AEC (red), in synovial tissue from a patient with RA with active disease (A), inactive disease (C), SpA (E), and from a normal subject (G). Panels (B), (D), (F), (H) show sequential sections where CD45Ro is detected with immunoperoxidase and AEC (red) in synovial tissue from patients with active RA (B), inactive RA (D), SpA (F), and from a normal subject (H). All magnifications taken at x20.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., Christy W., Cooke T. D., Greenwald R., Hochberg M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. M., Maraskovsky E., Billingsley W. L., Dougall W. C., Tometsko M. E., Roux E. R., Teepe M. C., DuBose R. F., Cosman D., Galibert L. A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature. 1997 Nov 13;390(6656):175–179. doi: 10.1038/36593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucay N., Sarosi I., Dunstan C. R., Morony S., Tarpley J., Capparelli C., Scully S., Tan H. L., Xu W., Lacey D. L. osteoprotegerin-deficient mice develop early onset osteoporosis and arterial calcification. Genes Dev. 1998 May 1;12(9):1260–1268. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.9.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Qian Y., Kaufman S., Ring B. D., Van G., Capparelli C., Kelley M., Hsu H., Boyle W. J., Dunstan C. R. The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 1999 May 3;145(3):527–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. Q., Field M., Allard S., Abney E., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Detection of cytokines at the cartilage/pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: implications for the role of cytokines in cartilage destruction and repair. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Oct;31(10):653–661. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.10.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. Q., Field M., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Localization of tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial tissues and at the cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1125–1132. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleuran B. W., Chu C. Q., Field M., Brennan F. M., Katsikis P., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Localization of interleukin-1 alpha, type 1 interleukin-1 receptor and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in the synovial membrane and cartilage/pannus junction in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Dec;31(12):801–809. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.12.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa Y., Sabokbar A., Neale S., Athanasou N. A. Human osteoclast formation and bone resorption by monocytes and synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996 Nov;55(11):816–822. doi: 10.1136/ard.55.11.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladman D. D., Farewell V. T. Progression in psoriatic arthritis: role of time varying clinical indicators. J Rheumatol. 1999 Nov;26(11):2409–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravallese E. M., Manning C., Tsay A., Naito A., Pan C., Amento E., Goldring S. R. Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):250–258. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<250::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Crotti T. N., Loric M., Bain G. I., Atkins G. J., Findlay D. M. Osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) regulate osteoclast formation by cells in the human rheumatoid arthritic joint. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Jun;40(6):623–630. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.6.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Crotti T. N., Potter A. E., Loric M., Atkins G. J., Howie D. W., Findlay D. M. The osteoclastogenic molecules RANKL and RANK are associated with periprosthetic osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001 Aug;83(6):902–911. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.83b6.10905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwood N. J., Kartsogiannis V., Quinn J. M., Romas E., Martin T. J., Gillespie M. T. Activated T lymphocytes support osteoclast formation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Nov;265(1):144–150. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itonaga I., Fujikawa Y., Sabokbar A., Murray D. W., Athanasou N. A. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial macrophage-osteoclast differentiation is osteoprotegerin ligand-dependent. J Pathol. 2000 Sep;192(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/1096-9896(2000)9999:9999<::AID-PATH672>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Takahashi N., Jimi E., Udagawa N., Takami M., Kotake S., Nakagawa N., Kinosaki M., Yamaguchi K., Shima N. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction. J Exp Med. 2000 Jan 17;191(2):275–286. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong Y. Y., Feige U., Sarosi I., Bolon B., Tafuri A., Morony S., Capparelli C., Li J., Elliott R., McCabe S. Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature. 1999 Nov 18;402(6759):304–309. doi: 10.1038/46303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong Y. Y., Yoshida H., Sarosi I., Tan H. L., Timms E., Capparelli C., Morony S., Oliveira-dos-Santos A. J., Van G., Itie A. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999 Jan 28;397(6717):315–323. doi: 10.1038/16852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotake S., Sato K., Kim K. J., Takahashi N., Udagawa N., Nakamura I., Yamaguchi A., Kishimoto T., Suda T., Kashiwazaki S. Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res. 1996 Jan;11(1):88–95. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650110113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotake S., Udagawa N., Hakoda M., Mogi M., Yano K., Tsuda E., Takahashi K., Furuya T., Ishiyama S., Kim K. J. Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 May;44(5):1003–1012. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200105)44:5<1003::AID-ANR179>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotake S., Udagawa N., Takahashi N., Matsuzaki K., Itoh K., Ishiyama S., Saito S., Inoue K., Kamatani N., Gillespie M. T. IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1999 May;103(9):1345–1352. doi: 10.1172/JCI5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Haringman J. J., Ahern M. J., Breedveld F. C., Smith M. D., Tak P. P. Quantification of the cell infiltrate in synovial tissue by digital image analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Jan;39(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey D. L., Timms E., Tan H. L., Kelley M. J., Dunstan C. R., Burgess T., Elliott R., Colombero A., Elliott G., Scully S. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998 Apr 17;93(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manabe N., Kawaguchi H., Chikuda H., Miyaura C., Inada M., Nagai R., Nabeshima Y., Nakamura K., Sinclair A. M., Scheuermann R. H. Connection between B lymphocyte and osteoclast differentiation pathways. J Immunol. 2001 Sep 1;167(5):2625–2631. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.5.2625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno A., Amizuka N., Irie K., Murakami A., Fujise N., Kanno T., Sato Y., Nakagawa N., Yasuda H., Mochizuki S. Severe osteoporosis in mice lacking osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor/osteoprotegerin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Jun 29;247(3):610–615. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima T., Kobayashi Y., Yamasaki S., Kawakami A., Eguchi K., Sasaki H., Sakai H. Protein expression and functional difference of membrane-bound and soluble receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand: modulation of the expression by osteotropic factors and cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Sep 7;275(3):768–775. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker A., Smith M. D. Immunohistochemical detection of cytokines and cell adhesion molecules in the synovial membrane. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1999 Jun;21(5):311–319. doi: 10.1358/mf.1999.21.5.541907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. M., Horwood N. J., Elliott J., Gillespie M. T., Martin T. J. Fibroblastic stromal cells express receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand and support osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Aug;15(8):1459–1466. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.8.1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romas E., Bakharevski O., Hards D. K., Kartsogiannis V., Quinn J. M., Ryan P. F., Martin T. J., Gillespie M. T. Expression of osteoclast differentiation factor at sites of bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Apr;43(4):821–826. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<821::AID-ANR12>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakkas L. I., Scanzello C., Johanson N., Burkholder J., Mitra A., Salgame P., Katsetos C. D., Platsoucas C. D. T cells and T-cell cytokine transcripts in the synovial membrane in patients with osteoarthritis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1998 Jul;5(4):430–437. doi: 10.1128/cdli.5.4.430-437.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet W. S., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R., Kelley M., Chang M. S., Lüthy R., Nguyen H. Q., Wooden S., Bennett L., Boone T. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Chandran G., Youssef P. P., Darby T., Ahern M. J. Day case knee arthroscopy under regional anaesthesia, performed by rheumatologists. Aust N Z J Med. 1996 Feb;26(1):108–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1996.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Kraan M. C., Slavotinek J., Au V., Weedon H., Parker A., Coleman M., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Ahern M. J. Treatment-induced remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients is characterized by a reduction in macrophage content of synovial biopsies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Apr;40(4):367–374. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., O'Donnell J., Highton J., Palmer D. G., Rozenbilds M., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Immunohistochemical analysis of synovial membranes from inflammatory and non-inflammatory arthritides: scarcity of CD5 positive B cells and IL2 receptor bearing T cells. Pathology. 1992 Jan;24(1):19–26. doi: 10.3109/00313029209063615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., van der Lubbe P. A., Cauli A., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Yanni G., Panayi G. S., Breedveld F. C. Reduction of synovial inflammation after anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Oct;38(10):1457–1465. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi H., Iizuka H., Juji T., Nakagawa T., Yamamoto A., Miyazaki T., Koshihara Y., Oda H., Nakamura K., Tanaka S. Involvement of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand/osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis from synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):259–269. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<259::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetlow L. C., Woolley D. E. Mast cells, cytokines, and metalloproteinases at the rheumatoid lesion: dual immunolocalisation studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Nov;54(11):896–903. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.11.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trabandt A., Gay R. E., Fassbender H. G., Gay S. Cathepsin B in synovial cells at the site of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Nov;34(11):1444–1451. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikaningrum R., Highton J., Parker A., Coleman M., Hessian P. A., Roberts-Thompson P. J., Ahern M. J., Smith M. D. Pathogenic mechanisms in the rheumatoid nodule: comparison of proinflammatory cytokine production and cell adhesion molecule expression in rheumatoid nodules and synovial membranes from the same patient. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Oct;41(10):1783–1797. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199810)41:10<1783::AID-ART10>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. R., Josien R., Lee S. Y., Sauter B., Li H. L., Steinman R. M., Choi Y. TRANCE (tumor necrosis factor [TNF]-related activation-induced cytokine), a new TNF family member predominantly expressed in T cells, is a dendritic cell-specific survival factor. J Exp Med. 1997 Dec 15;186(12):2075–2080. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.12.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. R., Rho J., Arron J., Robinson E., Orlinick J., Chao M., Kalachikov S., Cayani E., Bartlett F. S., 3rd, Frankel W. N. TRANCE is a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family that activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in T cells. J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 3;272(40):25190–25194. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.40.25190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E., Crossley M. J., Evanson J. M. Collagenase at sites of cartilage erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(6):1231–1239. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Shima N., Nakagawa N., Mochizuki S. I., Yano K., Fujise N., Sato Y., Goto M., Yamaguchi K., Kuriyama M. Identity of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) and osteoprotegerin (OPG): a mechanism by which OPG/OCIF inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Endocrinology. 1998 Mar;139(3):1329–1337. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.3.5837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Shima N., Nakagawa N., Yamaguchi K., Kinosaki M., Mochizuki S., Tomoyasu A., Yano K., Goto M., Murakami A. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 31;95(7):3597–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssef P. P., Haynes D. R., Triantafillou S., Parker A., Gamble J. R., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Ahern M. J., Smith M. D. Effects of pulse methylprednisolone on inflammatory mediators in peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;40(8):1400–1408. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssef P. P., Triantafillou S., Parker A., Coleman M., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Ahern M. J., Smith M. D. Variability in cytokine and cell adhesion molecule staining in arthroscopic synovial biopsies: quantification using color video image analysis. J Rheumatol. 1997 Dec;24(12):2291–2298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Vandenbroucke J. P., Breedveld F. C. Factors predicting outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: results of a followup study. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1288–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


