Abstract
Methods: SF and serum IL13 levels were determined in 35 patients with PsA, 36 with RA, and 15 with OA. The main clinical and laboratory variables, including number of painful and/or swollen joints, Ritchie index, morning stiffness, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, level of C reactive protein, level of rheumatoid factor, and SF analysis, were also evaluated.
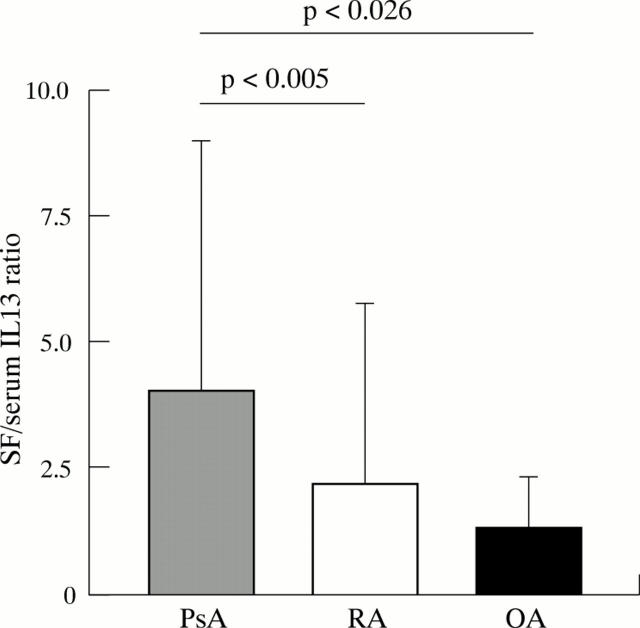
Results: SF IL13 levels were significantly higher in patients with PsA (p<0.02) or RA (p<0.012) than in patients with OA, with no significant difference between the former two. SF IL12 levels were significantly higher in patients with PsA (p<0.023) than in those with OA. Serum IL13 (p<0.0001) and IL12 (p<0.02) levels were lower in patients with PsA than in those affected by RA. Only patients with PsA had higher IL13 levels in SF than in serum (p<0.002). The IL13 SF/serum ratio was higher in the PsA group than in the group with RA (p<0.005) or OA (p<0.026). SF IL13 levels correlated with serum IL13 levels (p<0.0001) in RA and with SF IL12 levels (p<0.03) in PsA.
Conclusions: In PsA, there appears to be localised production of IL13, in balance with IL12, in the inflamed joints. The distinct IL13 secretion profiles in PsA, RA, and OA may be related to the clinical pictures, reflecting the different pathogenic mechanisms involved in inflammatory and degenerative joint diseases.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (95.1 KB).
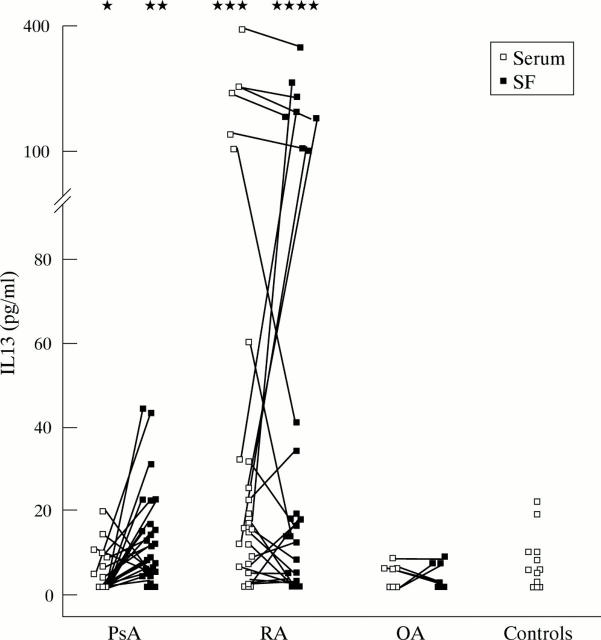
Figure 1 .
Synovial fluid (SF) and serum levels of interleukin (IL) 13 in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) (n=35), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n=36), or osteoarthritis (OA) (n=15) and healthy controls (n=22). Lines connect the corresponding samples (SF and serum) of each patient. *Significantly different from SF of patients with PsA (p<0.002); **significantly different from SF of patients with OA (p<0.02); ***significantly different from serum of patients with PsA (p<0.0001) or OA (p<0.003) and controls (p<0.017); ****significantly different from SF of patients with OA (p<0.012).
Figure 2 .
Interleukin (IL) 13 SF/serum ratio (mean (SD)) in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) (n=35), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n=36), or osteoarthritis (OA) (n=15).