Abstract
Objective: To determine matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) serum levels in patients with rheumatic diseases and to study the relation between MMP-3 and C reactive protein (CRP) levels.
Methods: MMP-3 serum levels were determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in (a) patients with active inflammatory rheumatic diseases: rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, acute crystal arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis; (b) patients with active inflammatory systemic diseases: cutaneo-articular or renal systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), systemic sclerosis, and vasculitides; (c) patients with non-inflammatory rheumatic diseases: osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia; (d) critically ill patients without rheumatic diseases, representing an acute inflammatory control group; (e) healthy controls.
Results: MMP-3 serum levels were significantly increased in patients with active RA, psoriatic arthritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica, whether treated or not by corticosteroids, and in female patients with acute crystal arthritis. MMP-3 serum levels were normal in steroid-free patients with active cutaneo-articular or renal SLE, systemic sclerosis, and vasculitides but were significantly increased in steroid treated patients. MMP-3 levels were normal in fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and acute inflammatory controls. MMP-3 was significantly correlated with CRP in RA (r=0.5, p=0.0004) but not in any of the other disease groups.
Conclusions: MMP-3 serum levels are increased in inflammatory rheumatic diseases characterised by joint synovitis, such as RA, polymyalgia rheumatica, psoriatic arthritis, and acute crystal arthritis—that is, whether the diseases are acute or chronic, erosive or not. They are normal in SLE, systemic sclerosis, and vasculitides as well as in non-rheumatic inflammatory controls, but are significantly increased by steroids. These data strongly suggest that serum MMP-3 reflects synovial inflammation.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (188.4 KB).
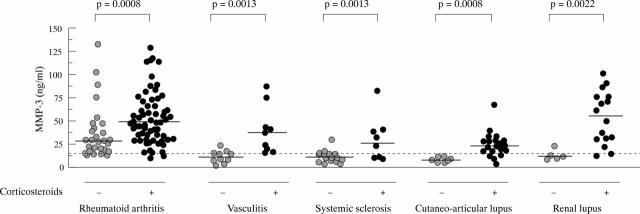
Figure 1 .
MMP-3 serum levels in female patients with various systemic diseases treated or not with corticosteroids. The horizontal line represents the median level of each group. The dotted line represents the upper normal limit of female healthy controls—that is, 14 ng/ml. Patients treated with steroids and those not treated were compared by the Mann-Whitney U test.
Figure 2 .
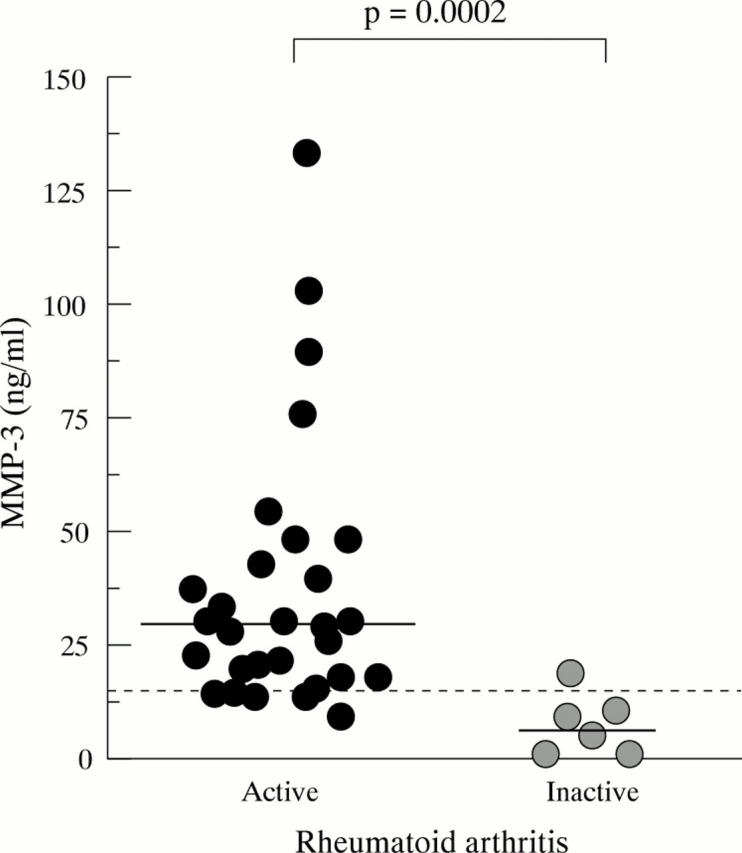
MMP-3 serum levels in female patients with active or inactive RA not treated with steroids. The horizontal line represents the median level. The dotted line represents the upper normal limit of female healthy controls—that is, 14 ng/ml. The two groups were compared by the Mann-Whitney U test.
Figure 3 .
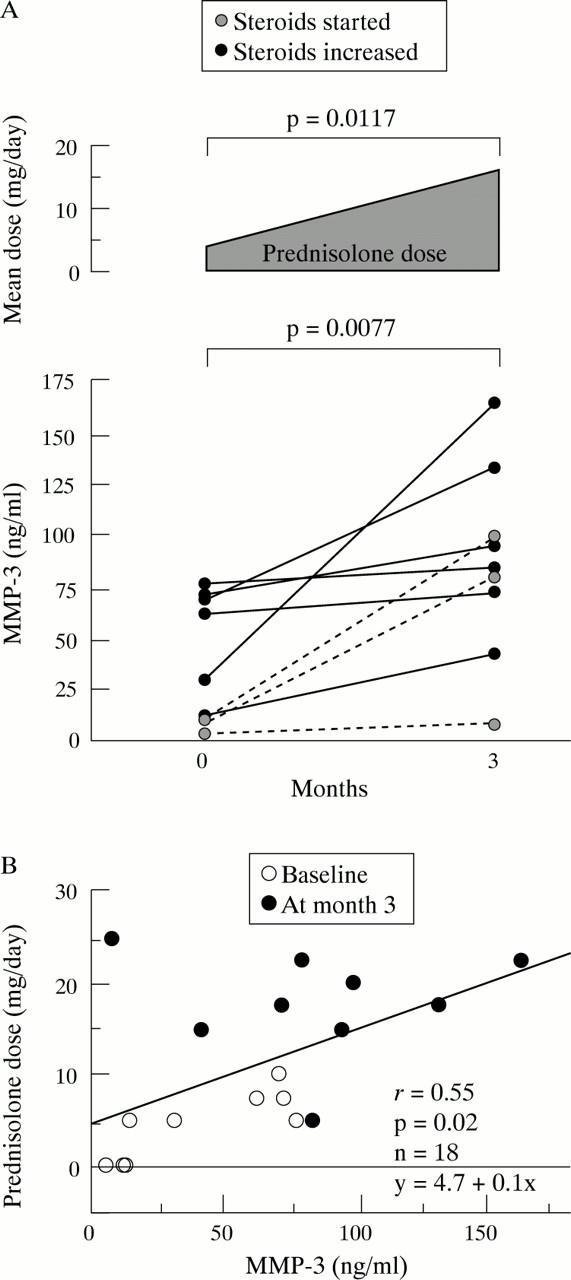
(A) MMP-3 serum levels in nine patients with an active lupus nephritis at the time of the renal biopsy (month 0) and after three months' treatment. Steroids were started in three patients (grey symbols, dotted line) or increased in six patients treated at baseline with low dose prednisolone (black symbols, continuous line, mean dose 4.4 mg/day). The prednisolone dose was significantly higher at three months (mean dose 17.8 mg/day). Paired samples of MMP-3 and of prednisolone were compared using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. (B) Positive linear correlation between MMP-3 levels and mean prednisolone dose in the nine lupus patients at baseline (white symbols) and at month 3 (black symbols).
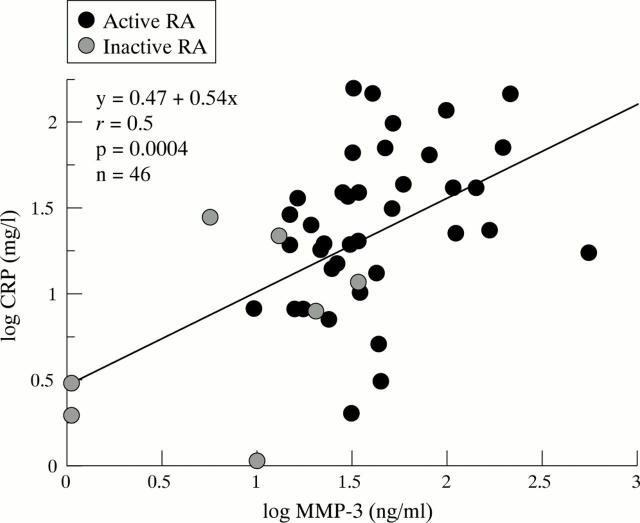
Figure 4 .
Positive linear correlation between MMP-3 and CRP serum levels in non-steroid treated female and male patients with active (n=39) or inactive (n=7) rheumatoid arthritis.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama K., Shikata K., Sugimoto H., Matsuda M., Shikata Y., Fujimoto N., Obata K., Matsui H., Makino H. Changes in serum concentrations of matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases and type IV collagen in patients with various types of glomerulonephritis. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1997 Feb;95(2):115–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R. D. Criteria for classification of clinical osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991 Feb;27:10–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Moore W. G., Bodden M. K., Windsor L. J., Birkedal-Hansen B., DeCarlo A., Engler J. A. Matrix metalloproteinases: a review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4(2):197–250. doi: 10.1177/10454411930040020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Browne K. A., Green P. A., Jaspar J. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Reduction of serum matrix metalloproteinase 1 and matrix metalloproteinase 3 in rheumatoid arthritis patients following anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha (cA2) therapy. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Jun;36(6):643–650. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.6.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese L. H., Michel B. A., Bloch D. A., Arend W. P., Edworthy S. M., Fauci A. S., Fries J. F., Hunder G. G., Leavitt R. Y., Lie J. T. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of hypersensitivity vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1108–1113. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs: properties and implications for the rheumatic diseases. Mol Med Today. 1998 Mar;4(3):130–137. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(97)01192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung N. T., Dawes P. T., Poulton K. V., Ollier W. E., Taylor D. J., Mattey D. L. High serum levels of pro-matrix metalloproteinase-3 are associated with greater radiographic damage and the presence of the shared epitope in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000 Apr;27(4):882–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabay C., Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1999 Feb 11;340(6):448–454. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199902113400607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanemaaijer R., Koolwijk P., le Clercq L., de Vree W. J., van Hinsbergh V. W. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in human vein and microvascular endothelial cells. Effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1 and phorbol ester. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):803–809. doi: 10.1042/bj2960803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunder G. G., Bloch D. A., Michel B. A., Stevens M. B., Arend W. P., Calabrese L. H., Edworthy S. M., Fauci A. S., Leavitt R. Y., Lie J. T. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1122–1128. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Ito T., Obata K., Fujimoto N., Iwata H. Determination of stromelysin-1, 72 and 92 kDa type IV collagenase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), and TIMP-2 in synovial fluid and serum from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996 Sep;23(9):1599–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyszer G., Lambiri I., Nagel R., Keysser C., Keysser M., Gromnica-Ihle E., Franz J., Burmester G. R., Jung K. Circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-3 and MMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1), and MMP-1/TIMP-1 complex in rheumatic disease. Correlation with clinical activity of rheumatoid arthritis versus other surrogate markers. J Rheumatol. 1999 Feb;26(2):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M. Ultrasonographic evidence of synovitis in axial joints in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;31(3):201–203. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotajima L., Aotsuka S., Fujimani M., Okawa-Takatsuji M., Kinoshita M., Sumiya M., Obata K. Increased levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in sera from patients with active lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 Jul-Aug;16(4):409–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R. Y., Fauci A. S., Bloch D. A., Michel B. A., Hunder G. G., Arend W. P., Calabrese L. H., Fries J. F., Lie J. T., Lightfoot R. W., Jr The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1101–1107. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot R. W., Jr, Michel B. A., Bloch D. A., Hunder G. G., Zvaifler N. J., McShane D. J., Arend W. P., Calabrese L. H., Leavitt R. Y., Lie J. T. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1088–1093. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malide D., Russo P., Bendayan M. Presence of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in renal mesangial cells of lupus nephritis patients. Hum Pathol. 1995 May;26(5):558–564. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manicourt D. H., Fujimoto N., Obata K., Thonar E. J. Levels of circulating collagenase, stromelysin-1, and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Relationship to serum levels of antigenic keratan sulfate and systemic parameters of inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Aug;38(8):1031–1039. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Stephens P. E., Smith B. J., Docherty A. J. Stromelysin is an activator of procollagenase. A study with natural and recombinant enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):265–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2480265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata Y., Enghild J. J., Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) activates the precursor for the human matrix metalloproteinase 9. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3581–3584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partsch G., Wagner E., Leeb B. F., Dunky A., Steiner G., Smolen J. S. Upregulation of cytokine receptors sTNF-R55, sTNF-R75, and sIL-2R in psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid. J Rheumatol. 1998 Jan;25(1):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):581–590. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbens C., Andre B., Jaspar J. M., Kaye O., Kaiser M. J., De Groote D., Malaise M. G. Matrix metalloproteinase-3 serum levels are correlated with disease activity and predict clinical response in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000 Apr;27(4):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbens C., Andre B., Kaye O., Kaiser M. J., Bonnet V., Jaspar J. M., de Groote D., Franchimont N., Malaise M. G. Synovial fluid matrix metalloproteinase-3 levels are increased in inflammatory arthritides whether erosive or not. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Dec;39(12):1357–1365. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.12.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Iwata H., Ishiguro N., Obata K., Miura T. Detection of stromelysin in synovial fluid and serum from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1994 Jun;13(2):228–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02249017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif M., Salisbury C., Taylor D. J., Kirwan J. R. Changes in biochemical markers of joint tissue metabolism in a randomized controlled trial of glucocorticoid in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jul;41(7):1203–1209. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1203::AID-ART9>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki D., Miyazaki M., Jinde K., Koji T., Yagame M., Endoh M., Nomoto Y., Sakai H. In situ hybridization studies of matrix metalloproteinase-3, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and type IV collagen in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1997 Jul;52(1):111–119. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Cheung N. T., Dawes P. T. Increased serum proMMP-3 in inflammatory arthritides: a potential indicator of synovial inflammatory monokine activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Nov;53(11):768–772. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.11.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincenti M. P., Clark I. M., Brinckerhoff C. E. Using inhibitors of metalloproteinases to treat arthritis. Easier said than done? Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Aug;37(8):1115–1126. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe F., Smythe H. A., Yunus M. B., Bennett R. M., Bombardier C., Goldenberg D. L., Tugwell P., Campbell S. M., Abeles M., Clark P. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Feb;33(2):160–172. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka H., Matsuda Y., Tanaka M., Sendo W., Nakajima H., Taniguchi A., Kamatani N. Serum matrix metalloproteinase 3 as a predictor of the degree of joint destruction during the six months after measurement, in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Apr;43(4):852–858. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<852::AID-ANR16>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara Y., Obata K., Fujimoto N., Yamashita K., Hayakawa T., Shimmei M. Increased levels of stromelysin-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jul;38(7):969–975. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker S., Lysik R. M., Zarrabi M. H., Greenwald R. A., Gruber B., Tickle S. P., Baker T. S., Docherty A. J. Elevated plasma stromelysin levels in arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2329–2333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker S., Mian N., Drews M., Conner C., Davidson A., Miller F., Birembaut P., Nawrocki B., Docherty A. J., Greenwald R. A. Increased serum stromelysin-1 levels in systemic lupus erythematosus: lack of correlation with disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1999 Jan;26(1):78–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]