Abstract
Objective: To evaluate biomechanical properties of skin in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) using the BTC-2000 suction device.
Methods: Twenty five patients with limited cutaneous SSc (lcSSc), 20 patients with diffuse disease (dcSSc), and 25 age matched healthy controls were evaluated. Viscoelastic deformation (VED, mm), elastic deformation (ED, mm), ultimate deformation (UD, mm), and pressure-deformation ratio (PDR, mm Hg/mm) were measured on the dorsal surface of the forearm, shoulder, and above the trapezius muscle on the back.
Results: Indices of skin extensibility (VED, ED, UD) were reduced and resistance to stress (PDR) increased in patients with dcSSc compared with healthy controls, or patients with lcSSc, at all three sites (p<0.001). At all sites, and overall, UD, ED, and VED were lower and PDR was higher at skin score above grade 2, compared with clinically normal skin. For both lcSSc and dcSSc biomechanical differences from controls were found even at sites of clinically normal skin.
Conclusion: BTC-2000 is a sensitive tool for clinical evaluation of skin involvement in SSc and may be a valuable adjunct to skin sclerosis score in disease monitoring.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (88.2 KB).
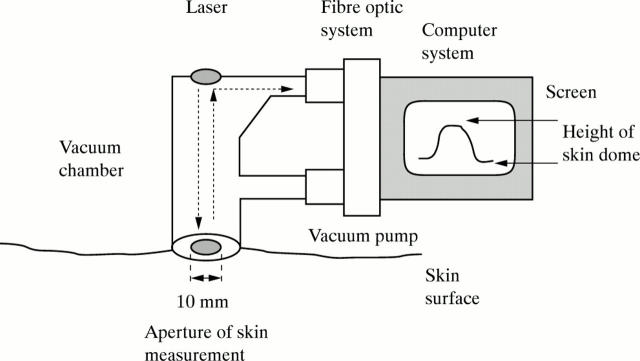
Figure 1 .
Schematic representation of the BTC-2000 suction device. Simple schematic representation of the suction chamber, laser for measuring the skin dome height, and the arrangement of computerised analysis hardware for the BTC-2000.
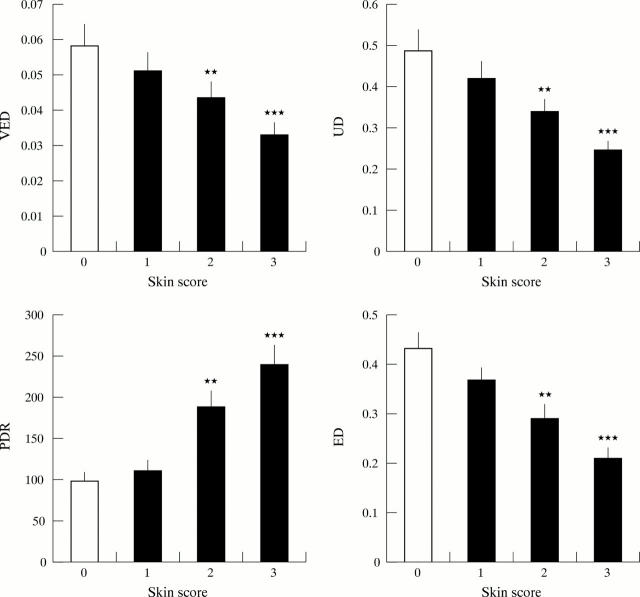
Figure 2 .
Relation between sclerosis score and biomechanical properties of skin. For each of the three skin areas assessed (forearm, shoulder, and back) the VED, UD, PDR and ED were compared for areas scored between 0 and 3. Representative histograms summarise data from forearm skin sites scored 0 (n=14), 0 (n=24), 2 (n=15), or 3 (n=8). Indices of skin deformity were lower at higher skin scores, whereas the PDR, reflecting stiffness, was increased. Data show means (SEM) and comparison is by Student's unpaired t test. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agache P. G., Monneur C., Leveque J. L., De Rigal J. Mechanical properties and Young's modulus of human skin in vivo. Arch Dermatol Res. 1980;269(3):221–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00406415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akesson A., Forsberg L., Hederström E., Wollheim F. Ultrasound examination of skin thickness in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1986 Jan-Feb;27(1):91–94. doi: 10.1177/028418518602700117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. M. Measurement of skin involvement in scleroderma. J Rheumatol. 1995 Jul;22(7):1217–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P., Silman A., Black C., Bernstein R., Coppock J., Maddison P., Sheeran T., Stevens C., Wollheim F. Reliability of skin involvement measures in scleroderma. The UK Scleroderma Study Group. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Jul;31(7):457–460. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.7.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald D., Wener M. H., Komaroff A. L. Anti-neuronal antibody levels in chronic fatigue syndrome patients with neurologic abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Nov;34(11):1485–1486. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn C. C., Denton C. P., Shi-Wen X., Knight C., Black C. M. Anti-RNA polymerases and other autoantibody specificities in systemic sclerosis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Jan;37(1):15–20. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles D., Williams K., 3rd, Perry L. C., Fisher J., Rees R. S. An improved method of in vivo wound disruption and measurement. J Surg Res. 1992 Mar;52(3):214–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(92)90076-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. J., Lachenbruch P. A., Ng S. C., Simmons M., Sterz M., Furst D. E. Skin score. A semiquantitative measure of cutaneous involvement that improves prediction of prognosis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1256–1263. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleixhe-Mauhin F., Piérard-Franchimont C., Rorive G., Piérard G. E. Influence of chronic haemodialysis on the mechanical properties of skin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1994 Mar;19(2):130–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1994.tb01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escoffier C., de Rigal J., Rochefort A., Vasselet R., Lévêque J. L., Agache P. G. Age-related mechanical properties of human skin: an in vivo study. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Sep;93(3):353–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Kenedi R. M. Biomechanical properties of skin. Surg Clin North Am. 1967 Apr;47(2):279–294. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)38180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame R. A method for measuring human skin elasticity in vivo with observations of the effects of age, sex and pregnancy. Clin Sci. 1970 Aug;39(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/cs0390223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame R., Beighton P. The physical properties of skin in cutis laxa. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Apr;84(4):326–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb14227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B., Sultany G. L., Smith E. A., Huffstutter J. E., Loadholt C. B., LeRoy E. C. A modified scleroderma skin scoring method. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1986 Oct-Dec;4(4):367–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalis B., De Rigal J., Léonard F., le Lévêque J. L., De Riche O., Corre Y. L., Lacharriere O. D. In vivo study of scleroderma by non-invasive techniques. Br J Dermatol. 1990 Jun;122(6):785–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb06267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkels-Tassoudji N., Henry F., Letawe C., Pierard-Franchimont C., Lefebvre P., Pierard G. E. Mechanical properties of the diabetic waxy skin. Dermatology. 1996;192(1):19–22. doi: 10.1159/000246307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxlund H., Andreassen T. T. The roles of hyaluronic acid, collagen and elastin in the mechanical properties of connective tissues. J Anat. 1980 Dec;131(Pt 4):611–620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. C., Connors A. W., Matrisian L. M., Nanney L. B., Charles P. D., Reyes D. P., Kerr L. D., Fisher J. Role of transforming growth factor-beta and epidermal growth factor in the wound-healing process: an in vivo biomechanical evaluation. Wound Repair Regen. 1993 Jan;1(1):41–46. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-475X.1993.10109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierard G. E., Lapière C. M. Physiopathological variations in the mechanical properties of skin. Arch Dermatol Res. 1977 Dec 27;260(3):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00561418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheja A., Akesson A. Comparison of high frequency (20 MHz) ultrasound and palpation for the assessment of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997 May-Jun;15(3):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidenari S., Belletti B., Conti A. A quantitative description of echographic images of sclerotic skin in patients with systemic sclerosis, as assessed by computerized image analysis on 20 MHz B-scan recordings. Acta Derm Venereol. 1996 Sep;76(5):361–364. doi: 10.2340/0001555576361364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B., Bauer E. A., Goldsmith L. A., Hochberg M. C., Katz L. M., Korn J. H., Lachenbruch P. A., LeRoy E. C., Mitrane M. P., Paulus H. E. Guidelines for clinical trials in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). I. Disease-modifying interventions. The American College of Rheumatology Committee on Design and Outcomes in Clinical Trials in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Mar;38(3):351–360. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes G. L., Brown I. A., Wildnauer R. H. The biomechanical properties of skin. CRC Crit Rev Bioeng. 1973 Aug;1(4):453–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]