Abstract
Objective: To present the management and follow up of two patients with limited PAN localised to the male and female reproductive system.
Case reports: A 26 year old man presented with an "acute scrotum". He was afebrile and had no other sign or symptom. Laboratory tests, including complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, liver and renal function tests, C reactive protein, antinuclear antibody, cryoglobulins, complement levels, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, and hepatitis B surface antigen, were all normal. His left testis was excised. Histopathology disclosed PAN of medium sized arteries with testicular infarction but no signs of torsion or infection. The other patient was a 51 year old woman who had had a total hysterectomy for a uterine myoma; incidentally PAN of the uterus and fallopian tubes was discovered. Neither patient received any immunosuppressive treatment after surgical removal of the affected organ. On prolonged follow up (clinical and laboratory evaluation) both patients are healthy with no sign of local recurrence or systemic PAN.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (136.3 KB).
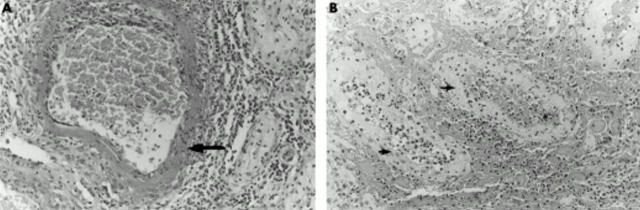
Figure 1 .
(A) Histopathological examination of the testis showed fibrinoid necrosis affecting a medium sized artery within the testicular parenchyma with acute transmural inflammation. The arrow indicates the affected medium sized artery. Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain; x150. (B) Testicular necrosis. The arrows indicate necrotic testicular tubuli. H&E stain; x150.
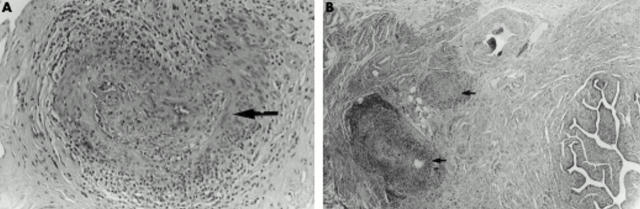
Figure 2 .
(A) Histopathological examination of the uteri cervix showing fibrinoid necrosis of a medium sized artery with mural lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and obstruction of the arterial lumen. The arrow indicates the affected arterial wall. H&E stain; x75. (B) Medium sized arteries around the fallopian tubes (arrows) showing fibrinoid necrosis, transmural inflammation, and thrombus within the arterial lumen. H&E stain; x150.