Abstract
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 16 patients and from eight normal controls were cultured in the presence of phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), ß-casein, ß-lactoglobulin, or chicken egg albumin. Interferon γ (IFNγ) and interleukin 4 (IL4) were measured in the culture supernatants by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Serum samples from 46 patients with Behçet's disease and from 37 healthy subjects were also studied for antibody detection. Antibodies to ß-casein, ß-lactoglobulin, and chicken egg albumin were determined by ELISA.
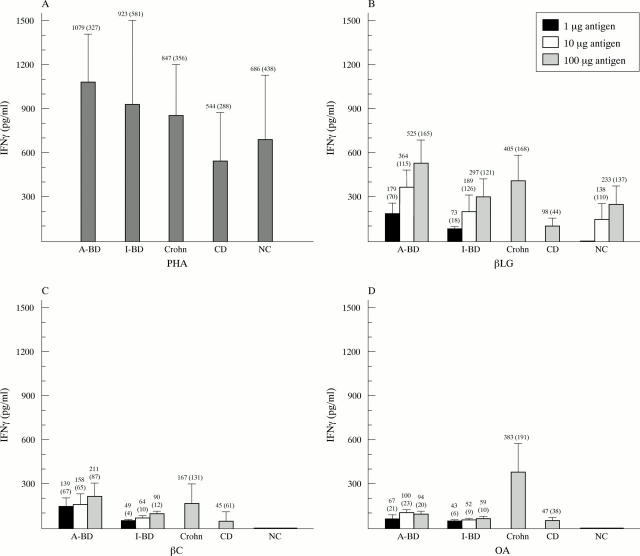
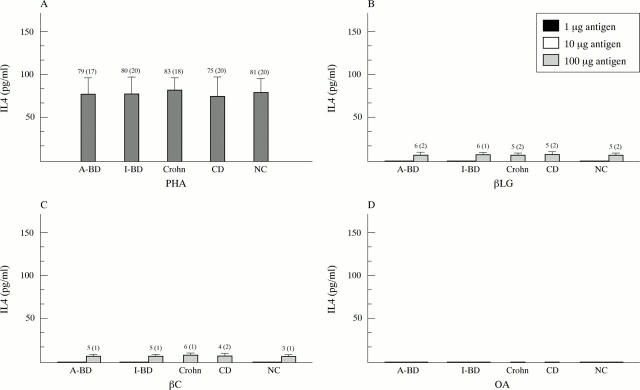
Results: High IFNγ but not IL4 levels were found in the supernatants of lymphocytes from patients with active disease cultured in the presence of cow's milk proteins. Levels were comparable with those obtained in cultures stimulated with PHA. A significantly higher level of anti-ß-casein and anti-ß-lactoglobulin IgG and IgA antibodies was found in patients with active Behçet's disease. No relation was found between their occurrence and the age of the patients, the duration of disease, or the presence of gastrointestinal abnormalities. Antibodies to chicken albumin were detected at low levels and with a prevalence similar to that of healthy subjects.
Conclusion: The results indicate that an active immune response occurs in Behçet's disease. This response involves an increased frequency of antibodies to cow's milk protein and a strong Th1 polarisation after exposure to these antigens. The occurrence of these abnormalities supports a putative role for cow's milk proteins immune response in the pathogenesis of Behçet's disease.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (106.6 KB).
Figure 1 .
IFNγ levels in supernatants of PBMC from patients with active or inactive Behçet's disease (A-BD, I-BD), from patients with Crohn's disease and coeliac disease (CD), and from normal controls (NC) cultured in the presence of (A) PHA or of increasing amounts of (B) ß-lactoglobulin (ßLG), (C) ß-casein (ßC), and (D) chicken egg albumin (OA).
Figure 2 .
IL4 levels in supernatants of PBMC from patients with active or inactive Behçet's disease (A-BD, I-BD), from patients with Crohn's disease and coeliac disease (CD), and from normal controls (NC) cultured in the presence of (A) PHA or of increasing amounts of (B) ß-lactoglobulin (ßLG), (C) ß-casein (ßC), and (D) chicken egg albumin (OA).