Abstract
Objective: To assess the intrarater and interrater reliability among rheumatologists of a standardised protocol for measurement of shoulder movements using a gravity inclinometer.
Methods: After instruction, six rheumatologists independently assessed eight movements of the shoulder, including total and glenohumeral flexion, total and glenohumeral abduction, external rotation in neutral and in abduction, internal rotation in abduction and hand behind back, in random order in six patients with shoulder pain and stiffness according to a 6x6 Latin square design using a standardised protocol. These assessments were then repeated. Analysis of variance was used to partition total variability into components of variance in order to calculate intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs).
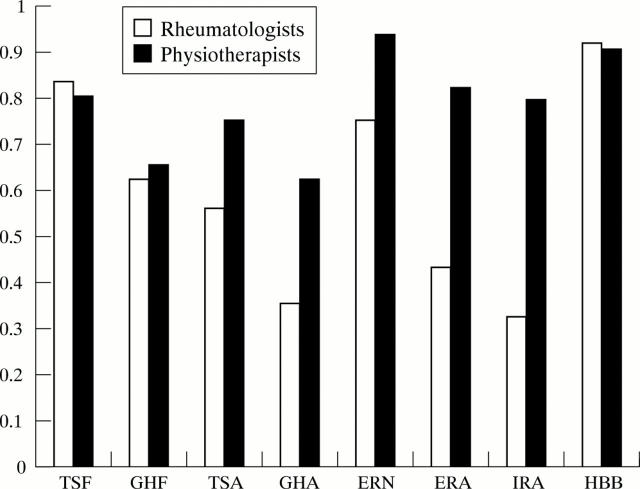
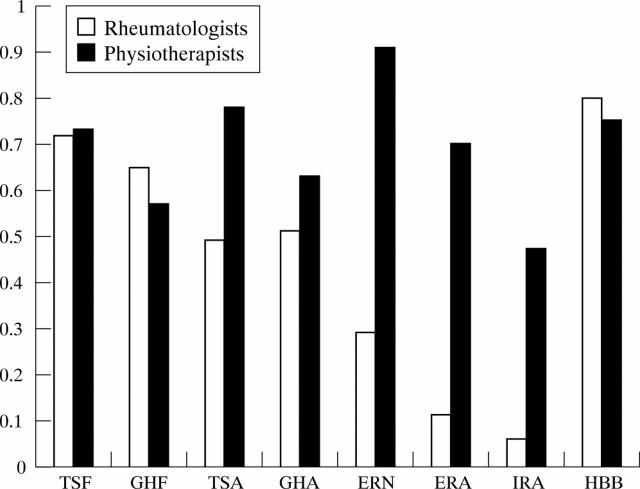
Results: The intrarater and interrater reliability of different shoulder movements varied widely. The movement of hand behind back and total shoulder flexion yielded the highest ICC scores for both intrarater reliability (0.91 and 0.83, respectively) and interrater reliability (0.80 and 0.72, respectively). Low ICC scores were found for the movements of glenohumeral abduction, external rotation in abduction, and internal rotation in abduction (intrarater ICCs 0.35, 0.43, and 0.32, respectively), and external rotation in neutral, external rotation in abduction, and internal rotation in abduction (interrater ICCs 0.29, 0.11, and 0.06, respectively).
Conclusions: The measurement of shoulder movements using a standardised protocol by rheumatologists produced variable intrarater and interrater reliability. Reasonable reliability was obtained only for the movement of hand behind back and total shoulder flexion.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (131.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
Intrarater reliability of rheumatologists and physiotherapists for each movement. TSF, total shoulder flexion; GHF, glenohumeral flexion; TSA, total shoulder abduction; GHA, glenohumeral abduction; ERN, external rotation in neutral; ERA, external rotation in abduction; IRA, internal rotation in abduction; HBB, hand behind back.
Figure 2 .
Interrater reliability of rheumatologists and physiotherapists for each movement. TSF, total shoulder flexion; GHF, glenohumeral flexion; TSA, total shoulder abduction; GHA, glenohumeral abduction; ERN, external rotation in neutral; ERA, external rotation in abduction; IRA, internal rotation in abduction; HBB, hand behind back.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews A. W., Bohannon R. W. Decreased shoulder range of motion on paretic side after stroke. Phys Ther. 1989 Sep;69(9):768–772. doi: 10.1093/ptj/69.9.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassey E. J., Morgan K., Dallosso H. M., Ebrahim S. B. Flexibility of the shoulder joint measured as range of abduction in a large representative sample of men and women over 65 years of age. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1989;58(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00643509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovens A. M., van Baak M. A., Vrencken J. G., Wijnen J. A., Verstappen F. T. Variability and reliability of joint measurements. Am J Sports Med. 1990 Jan-Feb;18(1):58–63. doi: 10.1177/036354659001800110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty K., Webley M. Shoulder joint movement and its relationship to disability in the elderly. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1359–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft P., Pope D., Boswell R., Rigby A., Silman A. Observer variability in measuring elevation and external rotation of the shoulder. Primary Care Rheumatology Society Shoulder Study Group. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Oct;33(10):942–946. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.10.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft P., Pope D., Silman A. The clinical course of shoulder pain: prospective cohort study in primary care. Primary Care Rheumatology Society Shoulder Study Group. BMJ. 1996 Sep 7;313(7057):601–602. doi: 10.1136/bmj.313.7057.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Buchbinder R., Forbes A., Bellamy N. A standardized protocol for measurement of range of movement of the shoulder using the Plurimeter-V inclinometer and assessment of its intrarater and interrater reliability. Arthritis Care Res. 1998 Feb;11(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/art.1790110108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Buchbinder R., Glazier R., Forbes A. Interventions for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001156–CD001156. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan K., Dziedzic K., Jones P. W., Ong B. N., Dawes P. T. The reliability of the three-dimensional FASTRAK measurement system in measuring cervical spine and shoulder range of motion in healthy subjects. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Apr;39(4):382–388. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.4.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermid J. C., Chesworth B. M., Patterson S., Roth J. H. Intratester and intertester reliability of goniometric measurement of passive lateral shoulder rotation. J Hand Ther. 1999 Jul-Sep;12(3):187–192. doi: 10.1016/s0894-1130(99)80045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandya S., Florence J. M., King W. M., Robison J. D., Oxman M., Province M. A. Reliability of goniometric measurements in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Phys Ther. 1985 Sep;65(9):1339–1342. doi: 10.1093/ptj/65.9.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope D. P., Croft P. R., Pritchard C. M., Macfarlane G. J., Silman A. J. The frequency of restricted range of movement in individuals with self-reported shoulder pain: results from a population-based survey. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;35(11):1137–1141. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.11.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle D. L., Rothstein J. M., Lamb R. L. Goniometric reliability in a clinical setting. Shoulder measurements. Phys Ther. 1987 May;67(5):668–673. doi: 10.1093/ptj/67.5.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triffitt P. D., Wildin C., Hajioff D. The reproducibility of measurement of shoulder movement. Acta Orthop Scand. 1999 Aug;70(4):322–324. doi: 10.3109/17453679908997817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Windt D. A., Koes B. W., de Jong B. A., Bouter L. M. Shoulder disorders in general practice: incidence, patient characteristics, and management. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Dec;54(12):959–964. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.12.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]