Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether rheumatoid factors (RFs), measured as continuous variables by time resolved fluoroimmunoassay, reflect disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Further, to study the association of RFs and other disease activity parameters with radiological joint damage, especially in individual patients.
Methods: In active, early RA, IgM and IgA RFs, as well as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C reactive protein (CRP), tender joint score, and swollen joint score were assessed regularly. At the study start and at 56 and 80 weeks, radiographs of hands and feet were assessed by the Sharp score (van der Heijde modification). Associations between RFs and disease activity parameters were studied. In addition, associations between radiographic damage and disease activity parameters (baseline and time integrated) were analysed by non-parametric tests and multiple regression analysis. The relation between time integrated disease activity parameters and radiological damage in individual patients was analysed and visualised.
Results: 155 patients were included. RF levels were strongly associated with the disease activity parameters (especially ESR and CRP) and with each other. All disease activity parameters, at baseline as well as time integrated parameters, were associated with (the progression of) radiographic damage. Moreover, in individual patients, a linear relationship between time integrated disease activity parameters and progression of radiological damage was seen.
Conclusion: RFs, measured as continuous variables, can be considered as disease activity parameters in patients with RA. The level of RF at baseline and the exposure to RF over time is associated with radiological damage. In individual patients, there is a constant relation between disease activity and radiological damage.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (131.1 KB).
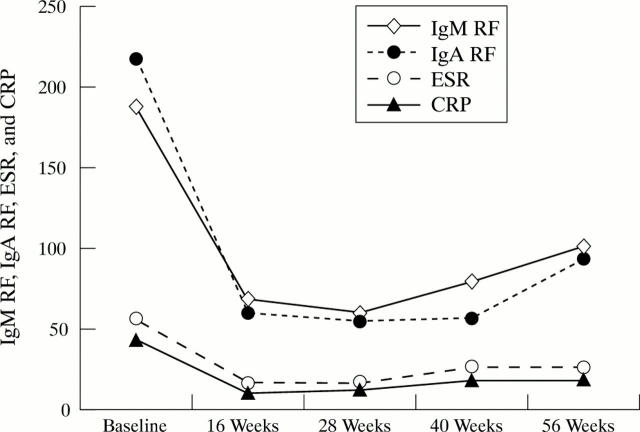
Figure 1 .
Pattern of changes over time of laboratory based disease activity parameters. Aggregated result of all patients receiving combination treatment (sulfasalazine, methotrexate, and prednisolone). IgM and IgA RF, IgM and IgA rheumatoid factor; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C reactive protein.
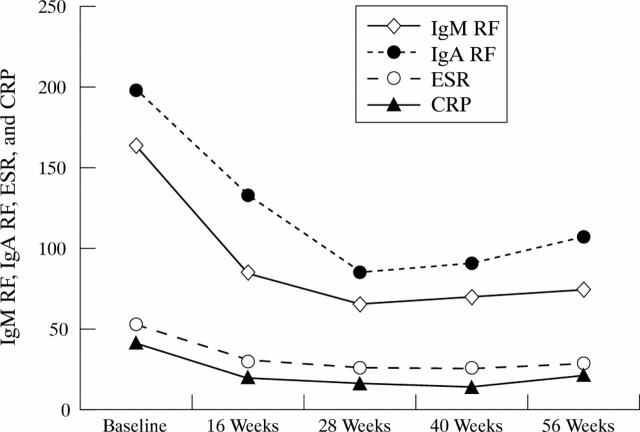
Figure 2 .
Pattern of changes over time of laboratory based disease activity parameters. Aggregated result of all patients receiving sulfasalazine treatment. IgM and IgA RF, IgM and IgA rheumatoid factor; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C reactive protein.
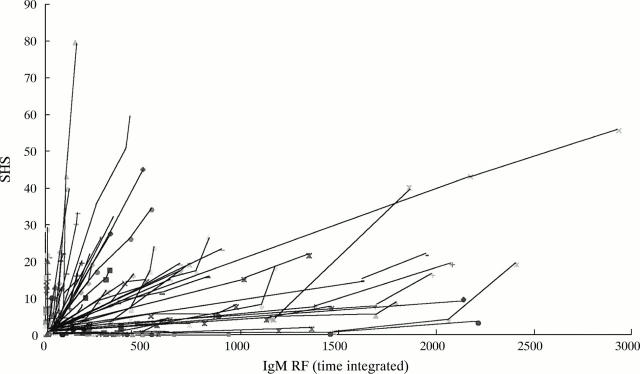
Figure 3 .
Individual relation between exposure to disease activity (time integrated IgM rheumatoid factor (IgM RF)) and radiological damage (Sharp score, modification van der Heijde (SHS)). Every patient has his/her own line, composed of the consecutive six month values for time integrated IgM RF in relation to the SHS.
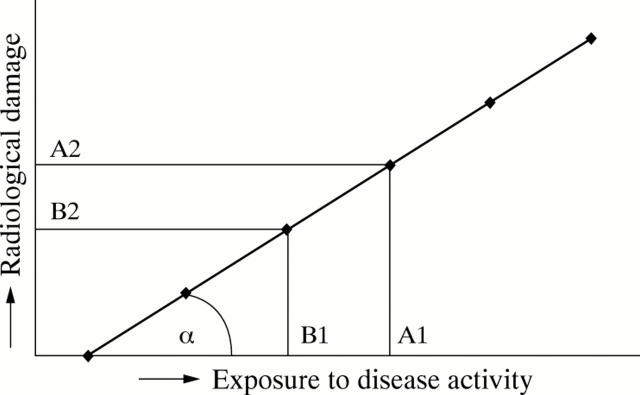
Figure 4 .
Relation between exposure to disease activity and radiological damage in the individual patient. The slope of the curve (α ) is individually constant but can vary between patients.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt K. B., Truedsson L., Pettersson H., Svensson B., Stigsson L., Eberhardt J. L., Wollheim F. A. Disease activity and joint damage progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: relation to IgG, IgA, and IgM rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Nov;49(11):906–909. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.11.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggelmeijer F., Otten H. G., de Rooy H. H., Daha M. R., Breedveld F. C. Significance of rheumatoid factor isotypes in seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(1):43–46. doi: 10.1007/BF02274780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioud-Paquet M., Auvinet M., Raffin T., Girard P., Bouvier M., Lejeune E., Monier J. C. IgM rheumatoid factor (RF), IgA RF, IgE RF, and IgG RF detected by ELISA in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):65–71. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssien D. A., Jonsson T., Davies E., Scott D. L. Clinical significance of IgA rheumatoid factor subclasses in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997 Nov;24(11):2119–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssien D. A., Jónsson T., Davies E., Scott D. L. Rheumatoid factor isotypes, disease activity and the outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: comparative effects of different antigens. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(1):46–53. doi: 10.1080/030097498441173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päi S., Päi L., Birkenfeldt R. Correlation of serum IgA rheumatoid factor levels with disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(4):252–256. doi: 10.1080/030097498442352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Nilsson L. A. Isotype-specific measurement of rheumatoid factor with reference to clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1983 Nov;12(3):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winska Wiloch H., Thompson K., Young A., Corbett M., Shipley M., Hay F. IgA and IgM rheumatoid factors as markers of later erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:238–243. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withrington R. H., Teitsson I., Valdimarsson H., Seifert M. H. Prospective study of early rheumatoid arthritis. II. Association of rheumatoid factor isotypes with fluctuations in disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Oct;43(5):679–685. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.5.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen M. A., Westra J., van Riel P. L., Limburg P. C., van Rijswijk M. H. IgM, IgA, and IgG rheumatoid factors in early rheumatoid arthritis predictive of radiological progression? Scand J Rheumatol. 1995;24(3):146–153. doi: 10.3109/03009749509099303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., Sluiter W. J., van Riel P. L., Kuper I. H., van de Putte L. B., Pepys M. B., Limburg P. C. Individual relationship between progression of radiological damage and the acute phase response in early rheumatoid arthritis. Towards development of a decision support system. J Rheumatol. 1997 Jan;24(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van der Heijde D. M., Te Meerman G. J., van Riel P. L., Houtman P. M., van De Putte L. B., Limburg P. C. The acute-phase response in relation to radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study during the first three years of the disease. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Jun;32 (Suppl 3):9–13. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.suppl_3.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., van der Voort E. A., Breedveld F. C. Clinical significance of rheumatoid factors in early rheumatoid arthritis: results of a follow up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Sep;51(9):1029–1035. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.9.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., Nuver-Zwart I. H., Gribnau F. W., vad de Putte L. B. Effects of hydroxychloroquine and sulphasalazine on progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1036–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluijs Veer G., Soons J. W. A time-resolved fluoroimmuno assay of the IgM-rheumatoid factor. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1992 May;30(5):301–305. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1992.30.5.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]