Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the possible association of interleukin 1α autoantibodies (IL1α aAb) with the long term course of joint erosion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Serum samples from 176 patients with RA included in a prospective study over 30 years were analysed for IL1α aAb by binding to human [125I]IL1α. Erosions of 19 diarthrodial joints were radiographically scored by the Larsen method.
Results: The relative risk (RR) of early IL1α aAb positive patients developing at least 30% of maximum radiographic joint destruction was significantly lower than for IL1α aAb negative patients, RR=0.29 (p=0.04). In rheumatoid factor positive patients RR was only 0.18 (p=0.02). Patients who seroconverted more than two years after the onset of RA showed the most aggressive development of joint erosion, with a relative risk of at least 40% of maximum radiographic joint destruction of 2.56 (p=0.048)
Conclusions: The progression of radiographic joint destruction in patients with RA is associated with, and perhaps modified by, circulating IL1α aAb, suggesting that IL1α or IL1α aAb, or both, have a role in the erosive processes. IL1α aAb appear to be of prognostic significance in RA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (93.6 KB).
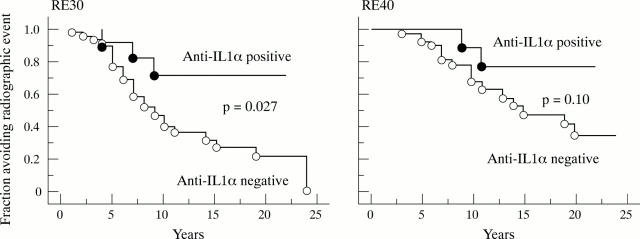
Figure 1 .
Effect of early IL1α aAb positivity on joint erosions in patients with RA. Kaplan-Meier plots of radiographic events defined as 30% and 40% of maximal radiographic destruction (RE30, RE40). The two patient groups are defined by the presence and absence of IL1α aAb during the first two years after onset of the disease. p Value: log rank test.
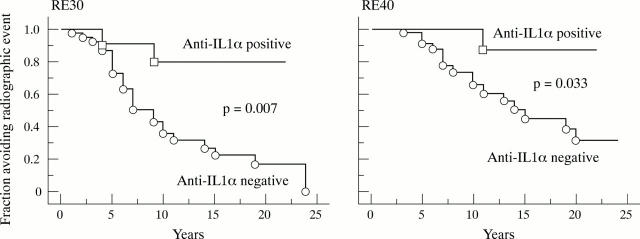
Figure 2 .
Effect of early IL1α aAb positivity on joint erosions in rheumatoid factor positive patients with RA. Kaplan-Meier plots are as in fig 1. The two patient groups are defined by the presence and absence of IL1α aAb during the first two years after onset of the disease. p Value: log rank test.
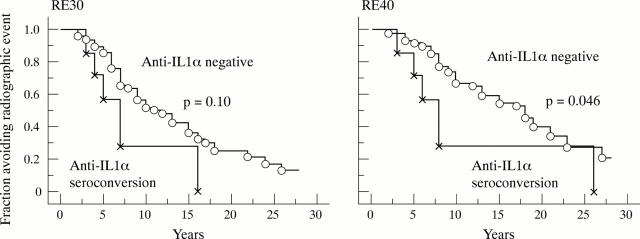
Figure 3 .
Effect of late IL1α aAb seroconversion on joint erosions. Kaplan-Meier plots are as in fig 1. The two patient groups are defined as those permanently negative for IL1α aAb and those initially negative who seroconverted more than two years after onset of the disease. p Value: log rank test.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 1958 REVISION of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1959 Feb;2(1):16–20. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(195902)2:1<16::aid-art1780020104>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Dayer J. M. Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Feb;38(2):151–160. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend W. P., Malyak M., Guthridge C. J., Gabay C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: role in biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:27–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K., Hansen M. B., Ross C., Svenson M. High-avidity autoantibodies to cytokines. Immunol Today. 1998 May;19(5):209–211. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(98)01252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Cobby M., Doherty M., Domljan Z., Emery P., Nuki G., Pavelka K., Rau R., Rozman B. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Dec;41(12):2196–2204. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199812)41:12<2196::AID-ART15>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikanza I. C., Kingsley G., Panayi G. S. Peripheral blood and synovial fluid monocyte expression of interleukin 1 alpha and 1 beta during active rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1995 Apr;22(4):600–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cominelli F., Nast C. C., Clark B. D., Schindler R., Lierena R., Eysselein V. E., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) gene expression, synthesis, and effect of specific IL-1 receptor blockade in rabbit immune complex colitis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):972–980. doi: 10.1172/JCI114799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A., Camp N. J., Cannings C., di Giovine F. S., Dale M., Worthington J., John S., Ollier W. E., Silman A. J., Duff G. W. Combined sib-TDT and TDT provide evidence for linkage of the interleukin-1 gene cluster to erosive rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Sep;8(9):1707–1713. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.9.1707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastgate J. A., Symons J. A., Wood N. C., Capper S. J., Duff G. W. Plasma levels of interleukin-1-alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1991 Aug;30(4):295–297. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/30.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastgate J. A., Symons J. A., Wood N. C., Grinlinton F. M., di Giovine F. S., Duff G. W. Correlation of plasma interleukin 1 levels with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1988 Sep 24;2(8613):706–709. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Kalden J. R., Antoni C., Smolen J. S., Leeb B., Breedveld F. C., Macfarlane J. D., Bijl H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1105–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feige U., Karbowski A., Rordorf-Adam C., Pataki A. Arthritis induced by continuous infusion of hr-interleukin-1 alpha into the rabbit knee-joint. Int J Tissue React. 1989;11(5):225–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison L., McDonnell N. D. Etanercept: therapeutic use in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Nov;58 (Suppl 1):I65–I69. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.2008.i65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrone P., Djossou O., Fossiez F., Reyes J., Ait-Yahia S., Maat C., Ho S., Hauser T., Dayer J. M., Greffe J. Generation and characterization of a human monoclonal autoantibody that acts as a high affinity interleukin-1 alpha specific inhibitor. Mol Immunol. 1996 May-Jun;33(7-8):649–658. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(96)00017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graudal N. A., Jurik A. G., de Carvalho A., Graudal H. K. Radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a long-term prospective study of 109 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Aug;41(8):1470–1480. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199808)41:8<1470::AID-ART18>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graudal N., Tarp U., Jurik A. G., Galløe A. M., Garred P., Milman N., Graudal H. K. Inflammatory patterns in rheumatoid arthritis estimated by the number of swollen and tender joints, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and hemoglobin: longterm course and association to radiographic progression. J Rheumatol. 2000 Jan;27(1):47–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Andersen V., Rohde K., Florescu A., Ross C., Svenson M., Bendtzen K. Cytokine autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1995;24(4):197–203. doi: 10.3109/03009749509100873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. B., Svenson M., Abell K., Varming K., Nielsen H. P., Bertelsen A., Bendtzen K. Sex- and age-dependency of IgG auto-antibodies against IL-1 alpha in healthy humans. Eur J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;24(3):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1994.tb00991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harriman G., Harper L. K., Schaible T. F. Summary of clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis using infliximab, an anti-TNFalpha treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Nov;58 (Suppl 1):I61–I64. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.2008.i61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Bendele A. M., Carlson D. G. In vivo administration with IL-1 accelerates the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Cole H., Bendele A. M. Interleukin 1 enhances the development of spontaneous arthritis in MRL/lpr mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Apr;55(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai R., Saijo S., Tanioka H., Nakae S., Sudo K., Okahara A., Ikuse T., Asano M., Iwakura Y. Development of chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in interleukin 1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 2000 Jan 17;191(2):313–320. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Genant H. K., Watt I., Cobby M., Bresnihan B., Aitchison R., McCabe D. A multicenter, double-blind, dose-ranging, randomized, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: radiologic progression and correlation of Genant and Larsen scores. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 May;43(5):1001–1009. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200005)43:5<1001::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joosten L. A., Helsen M. M., Saxne T., van De Loo F. A., Heinegard D., van Den Berg W. B. IL-1 alpha beta blockade prevents cartilage and bone destruction in murine type II collagen-induced arthritis, whereas TNF-alpha blockade only ameliorates joint inflammation. J Immunol. 1999 Nov 1;163(9):5049–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joosten L. A., Helsen M. M., van de Loo F. A., van den Berg W. B. Anticytokine treatment of established type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. A comparative study using anti-TNF alpha, anti-IL-1 alpha/beta, and IL-1Ra. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 May;39(5):797–809. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvenne P., Fossiez F., Banchereau J., Miossec P. High levels of neutralizing autoantibodies against IL-1 alpha are associated with a better prognosis in chronic polyarthritis: a follow-up study. Scand J Immunol. 1997 Oct;46(4):413–418. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1997.d01-139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvenne P., Vannier E., Dinarello C. A., Miossec P. Elevated levels of soluble interleukin-1 receptor type II and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with chronic arthritis: correlations with markers of inflammation and joint destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jun;41(6):1083–1089. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199806)41:6<1083::AID-ART15>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Dale K., Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1977 Jul;18(4):481–491. doi: 10.1177/028418517701800415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malyak M., Swaney R. E., Arend W. P. Levels of synovial fluid interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Potential contribution from synovial fluid neutrophils. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jun;36(6):781–789. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniwa K., Ogushi F., Tani K., Ohmoto Y., Muraguchi M., Sone S. Increased incidence of autoantibodies to interleukin-1a in rheumatoid arthritis with interstitial lung disease. Respirology. 2000 Dec;5(4):315–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Thompson R. C. Pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-1 in recurrence of bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4436–4442. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4436-4442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Loetscher P., Dewald B., Towbin H., Rordorf C., Gallati H., Gerber N. J. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors, IL-1 beta, and IL-8--markers of remission in rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with methotrexate. J Rheumatol. 1996 Sep;23(9):1512–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingu M., Fujikawa Y., Wada T., Nonaka S., Nobunaga M. Increased IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) production and decreased IL-1 beta/IL-1ra ratio in mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Jan;34(1):24–30. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Akama T., Okane M., Kono I., Matsui Y., Yamane K., Kashiwagi H. Interleukin-1-inhibitory IgG in sera from some patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1528–1538. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Ayabe T., Kamimura J., Kashiwagi H. Anti-IL-1 alpha autoantibodies in patients with rheumatic diseases and in healthy subjects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Sep;85(3):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Bagge Hansen M., Bendtzen K. Distribution and characterization of autoantibodies to interleukin 1 alpha in normal human sera. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Dec;32(6):695–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Hansen M. B., Kayser L., Rasmussen A. K., Reimert C. M., Bendtzen K. Effects of human anti-IL-1 alpha autoantibodies on receptor binding and biological activities of IL-1. Cytokine. 1992 Mar;4(2):125–133. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(92)90047-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson M., Poulsen L. K., Fomsgaard A., Bendtzen K. IgG autoantibodies against interleukin 1 alpha in sera of normal individuals. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Apr;29(4):489–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekanecz Z., Koch A. E., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Potential targets for pharmacological intervention. Drugs Aging. 1998 May;12(5):377–390. doi: 10.2165/00002512-199812050-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B. Joint inflammation and cartilage destruction may occur uncoupled. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1998;20(1-2):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00832004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]