Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the functional response of the kidney to an amino acid challenge (the so called renal functional reserve (RFR)) in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) with no clinical sign of renal involvement.
Methods: Before and after an intravenous amino acid load (Freamine III Baxter, 8.5% solution, 4.16 ml/min for two hours), glomerular filtration rate (GFR, as creatinine clearance), effective renal plasma flow (ERPF, as para-aminohyppurate clearance), and calculated total renal vascular resistance (TRVR) were measured in 21 patients with SSc with apparently normal renal function and 10 normal controls.
Results: In basal conditions, patients had lower ERPF (403.5 (SD 43.8) v 496.4 (SD 71.3) ml/min, p<0.0002) and higher TRVR (10 822 (SD 2044) v 8874 (SD 1639) dyne/sxcm-5, p<0.014) than controls. The RFR, evaluated as the percentage increase of GFR after the amino acid load, was significantly reduced in patients with SSc (SSc +1.9 (SD18.6)%, controls +34.8 (SD 13.9)%; p<0.0002). However, the response of patients was not uniform. Multiple regression analysis showed that the RFR was inversely dependent on the patients' mean arterial pressure at admission and basal GFR (R2=65%, p<0.0001).
Conclusions: Most patients with SSc cannot increase renal filtration under the challenge of a protein overload. This defective renal response to the amino acid load test sustains the concept of the prevalence of vasoconstrictor over vasodilating factors in the kidney of these patients.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (126.9 KB).
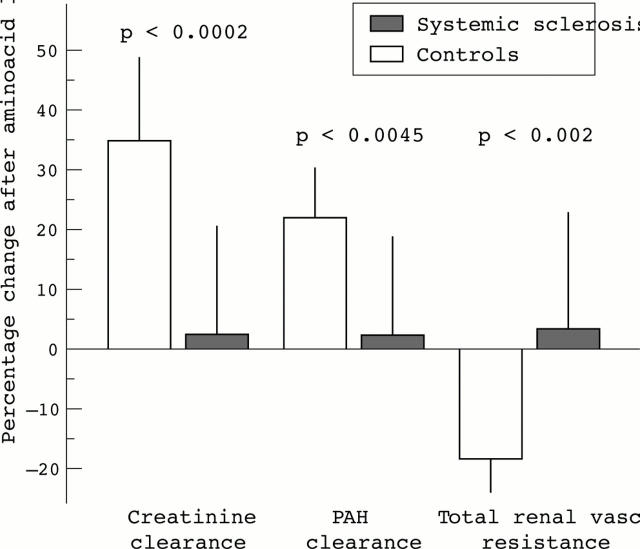
Figure 1 .
Effects of the amino acid load on glomerular filtration rate (creatinine clearance), effective renal plasma flow (PAH clearance), and calculated total renal vascular resistance in SSc patients and controls. Changes are expressed as percentage variation with respect to basal values.
Figure 2 .
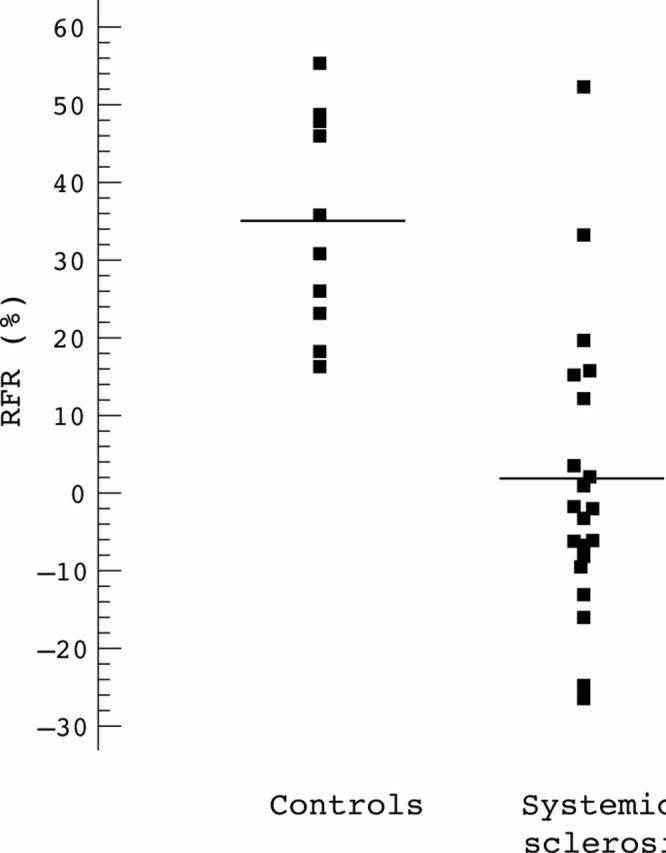
Distribution of the individual renal functional reserve (RFR) values obtained in SSc patients and controls. For each group, the horizontal line indicates the mean value.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosch J. P., Saccaggi A., Lauer A., Ronco C., Belledonne M., Glabman S. Renal functional reserve in humans. Effect of protein intake on glomerular filtration rate. Am J Med. 1983 Dec;75(6):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhler J., Glöer D., Reetze-Bonorden P., Keller E., Schollmeyer P. J. Renal functional reserve in elderly patients. Clin Nephrol. 1993 Mar;39(3):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cailes J., Winter S., du Bois R. M., Evans T. W. Defective endothelially mediated pulmonary vasodilation in systemic sclerosis. Chest. 1998 Jul;114(1):178–184. doi: 10.1378/chest.114.1.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon P. J., Hassar M., Case D. B., Casarella W. J., Sommers S. C., LeRoy E. C. The relationship of hypertension and renal failure in scleroderma (progressive systemic sclerosis) to structural and functional abnormalities of the renal cortical circulation. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Jan;53(1):1–46. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197401000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. Y., Cheng M. L., Keil L. C., Myers B. D. Functional response of healthy and diseased glomeruli to a large, protein-rich meal. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):245–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI113302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. J., Lachenbruch P. A., Furst D. E., Maxwell M., Danovitch G., Paulus H. E. Abnormalities of renal physiology in systemic sclerosis. A prospective study with 10-year followup. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jan;37(1):67–74. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottone S., Vadalà A., Contorno A., Mangano M. T., Zagarrigo C., Panepinto N., Cerasola G. The renal functional reserve in recently diagnosed essential hypertension. Clin Nephrol. 1994 Apr;41(4):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Nicola L., Blantz R. C., Gabbai F. B. Nitric oxide and angiotensin II. Glomerular and tubular interaction in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1248–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI115709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Nicola L., Blantz R. C., Gabbai F. B. Renal functional reserve in the early stage of experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 1992 Mar;41(3):267–273. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Nicola L., Keiser J. A., Blantz R. C., Gabbai F. B. Angiotensin II and renal functional reserve in rats with Goldblatt hypertension. Hypertension. 1992 Jun;19(6 Pt 2):790–794. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.6.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Nicola L., Peterson O. W., Obagi S., Kaiser J. A., Wilson C. B., Gabbai F. B. Renal functional reserve in experimental chronic glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1994;9(10):1383–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliser D., Ritz E., Franek E. Renal reserve in the elderly. Semin Nephrol. 1995 Sep;15(5):463–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbai F. B., De Nicola L., Garcia G. E., Blantz R. C. Role of angiotensin in the regulation of renal response to proteins. Semin Nephrol. 1995 Sep;15(5):396–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia G. E., Hammond T. C., Wead L. M., Mendonca M. M., Brown M. R., Gabbai F. B. Effect of angiotensin II on the renal response to amino acid in rats. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996 Jul;28(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(96)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras H., Gavras I., Cannon P. J., Brunner H. R., Laragh J. H. Is elevated plasma renin activity of prognostic importance in progressive systemic sclerosis? Arch Intern Med. 1977 Nov;137(11):1554–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf H., Stummvoll H. K., Luger A., Prager R. Effect of amino acid infusion on glomerular filtration rate. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 20;308(3):159–160. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301203080318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadj-Aïssa A., Bankir L., Fraysse M., Bichet D. G., Laville M., Zech P., Pozet N. Influence of the level of hydration on the renal response to a protein meal. Kidney Int. 1992 Nov;42(5):1207–1216. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. L., Viberti G. Renal functional reserve in subjects with diabetes mellitus. Semin Nephrol. 1995 Sep;15(5):475–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh B., Matucci-Cerinic M. Raynaud's phenomenon and scleroderma. Dysregulated neuroendothelial control of vascular tone. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):1–4. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovalchik M. T., Guggenheim S. J., Silverman M. H., Robertson J. S., Steigerwald J. C. The kidney in progressive systemic sclerosis: a prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Dec;89(6):881–887. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-6-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Civita L., Rossi M., Vagheggini G., Storino F. A., Credidio L., Pasero G., Giusti C., Ferri C. Microvascular involvement in systemic sclerosis: laser Doppler evaluation of reactivity to acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside by iontophoresis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Jan;57(1):52–55. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoy E. C., Black C., Fleischmajer R., Jablonska S., Krieg T., Medsger T. A., Jr, Rowell N., Wollheim F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Feb;15(2):202–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matucci-Cerinic M., Pietrini U., Marabini S. Local venomotor response to intravenous infusion of substance P and glyceryl trinitrate in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Nov-Dec;8(6):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. W., Ichikawa I., Zatz R., Brenner B. M. The renal hemodynamic response to amino acid infusion in the rat. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1983;96:76–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivolta R., Mascagni B., Berruti V., Quarto Di Palo F., Elli A., Scorza R., Castagnone D. Renal vascular damage in systemic sclerosis patients without clinical evidence of nephropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jun;39(6):1030–1034. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruilope L. M., Rodicio J., Garcia Robles R., Sancho J., Miranda B., Granger J. P., Romero J. C. Influence of a low sodium diet on the renal response to amino acid infusions in humans. Kidney Int. 1987 Apr;31(4):992–999. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolins J. P., Raij L. Effects of amino acid infusion on renal hemodynamics. Role of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):1045–1051. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trostle D. C., Bedetti C. D., Steen V. D., Al-Sabbagh M. R., Zee B., Medsger T. A., Jr Renal vascular histology and morphometry in systemic sclerosis. A case-control autopsy study. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):393–400. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URAI L., NAGY Z., SZINAY G., WILTNER W. Renal function in scleroderma. Br Med J. 1958 Nov 22;2(5107):1264–1266. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5107.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]