Abstract
Background: Receptors for IgG play an important part in immune complex clearance. Several studies have identified polymorphisms of receptors for the Fc fragment of IgG (FcγR) as genetic factors influencing susceptibility to disease or disease course of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Objective: To examine these possibilities by evaluating a panel of clinical parameters in a cohort of 140 German patients with SLE for correlations with the FcγRIIa, IIIa, and IIIb polymorphisms in an explorative study.
Methods: 140 German patients with SLE according to American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria and 187 German controls were genotyped for the FcγRIIa, IIIa, and IIIb polymorphisms. Associations between FcγR genotypes, combined genotypes and clinical as well as laboratory features were analysed.
Results: No significant skewing of any of the three FcγR polymorphisms was seen in the German SLE cohort studied. Various clinical and serological parameters were found more frequently and at younger age in homozygous patients with the genotypes IIA-R/R131 or IIIA-F/F158 than in patients with IIA-H/H131 or IIIA-V/V158. These effects were even more pronounced in patients with the low binding combined phenotypes of the FcγRIIa, IIIa (double negative phenotypes) and FcγRIIa, IIIa, and IIIb (triple negative phenotypes). In patients with the double negative IIA and IIIA genotypes significantly higher frequencies of nephritis (63% v 33%) and proteinuria according to ACR criteria (58% v 11%), anaemia (84% v 55%), and anticardiolipin antibodies (63% v 22%) were found than in patients with the double positive genotypes. Patients with the IIA-R/R131 genotype and the double negative homozygous genotype had an earlier incidence of clinical symptoms, haematological and immunological abnormalities. Accordingly, SLE is diagnosed earlier in these patients, the difference reaching statistical significance only in the double negative v the double positive genotype (26.3 v 39.5 years) and the IIIA-F/F158 genotype v the rest (26.7 v 32.0 years). Most relevant is the fact that a higher median disease activity (ECLAM score) was demonstrated, both in the IIA-R/R131 homozygous (3.3 v 2.7) and the double negative (3.4 v 2.3) patients, reaching statistical significance in the first group.
Conclusion: The results of this explorative study support the view that the FcγRIIa/IIIa and IIIb polymorphisms constitute factors influencing clinical manifestations and the disease course of SLE but do not represent genetic risk factors for the occurrence of SLE. Higher frequencies of clinical symptoms, haematological and immunological abnormalities as well as an earlier onset of clinical symptoms, haematological and immunological markers of active disease were found in patients with the IIA-R/R131 genotype and the double negative and triple negative genotypes.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (116.1 KB).
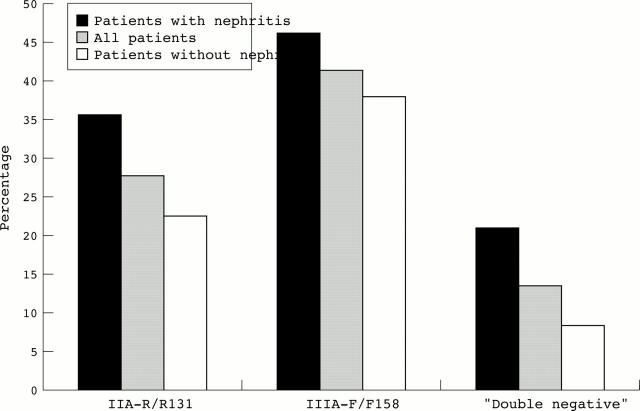
Figure 1 .
Overrepresentation of the homozygous low binding genotypes FcγRIIA-R/R131, FcγRIIIA-F/F158, and FcγRIIA/IIIA-R/R131, F/F158 (double negative) in patients with SLE and nephritis. Differences are not significant. n=57 for patients with nephritis, n=140 for all patients, n=83 for patients without nephritis.
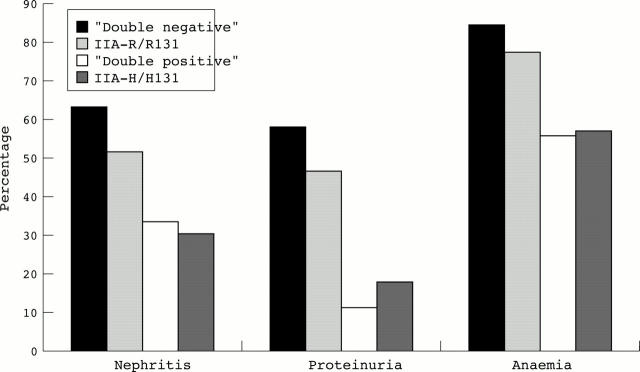
Figure 2 .
Prevalence of nephritis, proteinuria, and anaemia in patients with SLE with the homozygous genotypes FcγRIIA/IIIA-R/R131, F/F158 (double negative), FcγRIIA-R/R131, FcγRIIA/IIIA-H/H131, V/V158 (double positive), and FcγRIIA-H/H131. Statistical differences for the frequency of each symptom were calculated with a χ2 test. The differences between columns 1 and 3 and columns 2 and 4 were significant for nephritis, proteinuria, and anaemia (p<0.05).
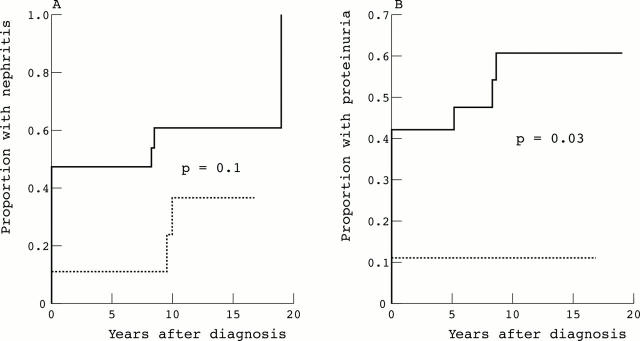
Figure 3 .
Kaplan Meier analysis of onset of (A) nephritis and (B) proteinuria according to the double negative (dashed line) versus double positive (solid line) homozygous FcγRIIA/IIIA genotypes. The difference between haplotypes was estimated with a log rank test; the p value indicates the level of significance.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasini A. M., Stekman I. L., Leon-Ponte M., Caldera D., Rodriguez M. A. Increased proportion of responders to a murine anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody of the IgG1 class in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Dec;94(3):423–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Chu J. L., Brot N., Elkon K. B. Lupus anti-ribosomal P peptide antibodies show limited heterogeneity and are predominantly of the IgG1 and IgG2 subclasses. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Oct;45(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros P., Muryoi T., Spiera H., Bona C., Unkeless J. C. Autoantibodies directed against different classes of Fc gamma R are found in sera of autoimmune patients. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):2018–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botto M., Theodoridis E., Thompson E. M., Beynon H. L., Briggs D., Isenberg D. A., Walport M. J., Davies K. A. Fc gamma RIIa polymorphism in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): no association with disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 May;104(2):264–268. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.33740.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredius R. G., Fijen C. A., De Haas M., Kuijper E. J., Weening R. S., Van de Winkel J. G., Out T. A. Role of neutrophil Fc gamma RIIa (CD32) and Fc gamma RIIIb (CD16) polymorphic forms in phagocytosis of human IgG1- and IgG3-opsonized bacteria and erythrocytes. Immunology. 1994 Dec;83(4):624–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L. E., Santoso S., Baurichter G., Kroll H., Papenberg S., Eichler P., Westerdaal N. A., Kiefel V., van de Winkel J. G., Greinacher A. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: new insights into the impact of the FcgammaRIIa-R-H131 polymorphism. Blood. 1998 Sep 1;92(5):1526–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alfonso S., Rampi M., Bocchio D., Colombo G., Scorza-Smeraldi R., Momigliano-Richardi P. Systemic lupus erythematosus candidate genes in the Italian population: evidence for a significant association with interleukin-10. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):120–128. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<120::AID-ANR15>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. A., Peters A. M., Beynon H. L., Walport M. J. Immune complex processing in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. In vivo imaging and clearance studies. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2075–2083. doi: 10.1172/JCI116090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijstelbloem H. M., Scheepers R. H., Oost W. W., Stegeman C. A., van der Pol W. L., Sluiter W. J., Kallenberg C. G., van de Winkel J. G., Tervaert J. W. Fcgamma receptor polymorphisms in Wegener's granulomatosis: risk factors for disease relapse. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Sep;42(9):1823–1827. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199909)42:9<1823::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duits A. J., Bootsma H., Derksen R. H., Spronk P. E., Kater L., Kallenberg C. G., Capel P. J., Westerdaal N. A., Spierenburg G. T., Gmelig-Meyling F. H. Skewed distribution of IgG Fc receptor IIa (CD32) polymorphism is associated with renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Dec;38(12):1832–1836. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Hamburger M. I., Lawley T. J., Kimberly R. P., Plotz P. H. Defective reticuloendothelial system Fc-receptor function in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 8;300(10):518–523. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903083001002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Hamburger M. I., Lawley T. J., Kimberly R. P., Plotz P. H. Fc-receptor dysfunction in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jun 28;300(26):1487–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzler E. M., Diamond H. S., Weiner M., Schlesinger M., Fries J. F., Wasner C., Medsger T. A., Jr, Ziegler G., Klippel J. H., Hadler N. M. A multicenter study of outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Entry variables as predictors of prognosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jun;25(6):601–611. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladman D., Ginzler E., Goldsmith C., Fortin P., Liang M., Urowitz M., Bacon P., Bombardieri S., Hanly J., Hay E. The development and initial validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Mar;39(3):363–369. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung K., Baur M. P., Coldewey R., Fricke M., Kalden J. R., Lakomek H. J., Peter H. H., Schendel D., Schneider P. M., Seuchter S. A. Major histocompatibility complex haplotypes and complement C4 alleles in systemic lupus erythematosus. Results of a multicenter study. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1346–1351. doi: 10.1172/JCI116000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta Y., Tsuchiya N., Ohashi J., Matsushita M., Fujiwara K., Hagiwara K., Juji T., Tokunaga K. Association of Fc gamma receptor IIIB, but not of Fc gamma receptor IIA and IIIA polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus in Japanese. Genes Immun. 1999 Sep;1(1):53–60. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg M. C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1725–1725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koene H. R., Kleijer M., Algra J., Roos D., von dem Borne A. E., de Haas M. Fc gammaRIIIa-158V/F polymorphism influences the binding of IgG by natural killer cell Fc gammaRIIIa, independently of the Fc gammaRIIIa-48L/R/H phenotype. Blood. 1997 Aug 1;90(3):1109–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koene H. R., Kleijer M., Swaak A. J., Sullivan K. E., Bijl M., Petri M. A., Kallenberg C. G., Roos D., von dem Borne A. E., de Haas M. The Fc gammaRIIIA-158F allele is a risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Oct;41(10):1813–1818. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199810)41:10<1813::AID-ART13>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppers-van de Straat F. G., van der Pol W. L., Jansen M. D., Sugita N., Yoshie H., Kobayashi T., van de Winkel J. G. A novel PCR-based method for direct Fc gamma receptor IIIa (CD16) allotyping. J Immunol Methods. 2000 Aug 28;242(1-2):127–132. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger K., Repp R., Spriewald B. M., Rascu A., Geiger A., Wassmuth R., Westerdaal N. A., Wentz B., Manger B., Kalden J. R. Fcgamma receptor IIa polymorphism in Caucasian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: association with clinical symptoms. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jul;41(7):1181–1189. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1181::AID-ART6>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norsworthy P., Theodoridis E., Botto M., Athanassiou P., Beynon H., Gordon C., Isenberg D., Walport M. J., Davies K. A. Overrepresentation of the Fcgamma receptor type IIA R131/R131 genotype in caucasoid systemic lupus erythematosus patients with autoantibodies to C1q and glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Sep;42(9):1828–1832. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199909)42:9<1828::AID-ANR6>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossent H. C., Henzen-Logmans S. C., Vroom T. M., Berden J. H., Swaak T. J. Contribution of renal biopsy data in predicting outcome in lupus nephritis. Analysis of 116 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jul;33(7):970–977. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh M., Petri M. A., Kim N. A., Sullivan K. E. Frequency of the Fc gamma RIIIA-158F allele in African American patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1999 Jul;26(7):1486–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parren P. W., Warmerdam P. A., Boeije L. C., Arts J., Westerdaal N. A., Vlug A., Capel P. J., Aarden L. A., van de Winkel J. G. On the interaction of IgG subclasses with the low affinity Fc gamma RIIa (CD32) on human monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets. Analysis of a functional polymorphism to human IgG2. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1537–1546. doi: 10.1172/JCI116022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rascu A., Repp R., Westerdaal N. A., Kalden J. R., van de Winkel J. G. Clinical relevance of Fc gamma receptor polymorphisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997 Apr 5;815:282–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb52070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Edberg J. C., Brogle N. L., Kimberly R. P. Allelic polymorphisms of human Fc gamma receptor IIA and Fc gamma receptor IIIB. Independent mechanisms for differences in human phagocyte function. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1274–1281. doi: 10.1172/JCI115712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Kimberly R. P., Gibofsky A., Fotino M. Defective mononuclear phagocyte function in systemic lupus erythematosus: dissociation of Fc receptor-ligand binding and internalization. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2525–2531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Millard S., Schachter L. A., Arnett F. C., Ginzler E. M., Gourley M. F., Ramsey-Goldman R., Peterson M. G., Kimberly R. P. Fc gamma RIIA alleles are heritable risk factors for lupus nephritis in African Americans. J Clin Invest. 1996 Mar 1;97(5):1348–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI118552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Ng S., Yoo D. H., Kim T. H., Kim S. Y., Song G. G. Altered distribution of Fcgamma receptor IIIA alleles in a cohort of Korean patients with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Apr;42(4):818–819. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199904)42:4<818::aid-anr28>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammaritano L. R., Ng S., Sobel R., Lo S. K., Simantov R., Furie R., Kaell A., Silverstein R., Salmon J. E. Anticardiolipin IgG subclasses: association of IgG2 with arterial and/or venous thrombosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Nov;40(11):1998–2006. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Iwano M., Akai Y., Nishino T., Fujimoto T., Shiiki H., Dohi K. FcgammaRIIa polymorphism in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2001;10(2):97–101. doi: 10.1191/096120301677569675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman V. A., Suarez C., Lum R., Inda S. E., Lin D., Li H., Olson J. L., Seldin M. F., Criswell L. A. The Fcgamma receptor IIIA-158F allele is a major risk factor for the development of lupus nephritis among Caucasians but not non-Caucasians. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Mar;44(3):618–625. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200103)44:3<618::AID-ANR110>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth L. J., Snowden N., Carthy D., Papasteriades C., Hajeer A., Ollier W. E. Fc gamma RIIa polymorphism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Dec;56(12):744–746. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.12.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Y. W., Han C. W., Kang S. W., Baek H. J., Lee E. B., Shin C. H., Hahn B. H., Tsao B. P. Abnormal distribution of Fc gamma receptor type IIa polymorphisms in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Mar;41(3):421–426. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199803)41:3<421::AID-ART7>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Cantor R. M., Kalunian K. C., Chen C. J., Badsha H., Singh R., Wallace D. J., Kitridou R. C., Chen S. L., Shen N. Evidence for linkage of a candidate chromosome 1 region to human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1997 Feb 15;99(4):725–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI119217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Wallace D. J. Genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1997 Sep;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199709000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bencivelli W., Isenberg D. A., Smolen J. S., Snaith M. L., Sciuto M., Neri R., Bombardieri S. Disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: report of the Consensus Study Group of the European Workshop for Rheumatology Research. II. Identification of the variables indicative of disease activity and their use in the development of an activity score. The European Consensus Study Group for Disease Activity in SLE. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Sep-Oct;10(5):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam P. A., van de Winkel J. G., Vlug A., Westerdaal N. A., Capel P. J. A single amino acid in the second Ig-like domain of the human Fc gamma receptor II is critical for human IgG2 binding. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1338–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Edberg J. C., Redecha P. B., Bansal V., Guyre P. M., Coleman K., Salmon J. E., Kimberly R. P. A novel polymorphism of FcgammaRIIIa (CD16) alters receptor function and predisposes to autoimmune disease. J Clin Invest. 1997 Sep 1;100(5):1059–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI119616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. N., Phipps M. E., Manivasagar M., Bosco J. J. Fc gamma receptor IIIB-NA gene frequencies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy individuals of Malay and Chinese ethnicity. Immunol Lett. 1999 Jun 1;68(2-3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(99)00061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. N., Phipps M. E., Manivasagar M., Tan S. Y., Bosco J. J. Human Fc gamma receptor IIA (FcgammaRIIA) genotyping and association with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in Chinese and Malays in Malaysia. Lupus. 1999;8(4):305–310. doi: 10.1191/096120399678847876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun H. R., Koh H. K., Kim S. S., Chung W. T., Kim D. W., Hong K. P., Song G. G., Chang H. K., Choe J. Y., Bae S. C. FcgammaRIIa/IIIa polymorphism and its association with clinical manifestations in Korean lupus patients. Lupus. 2001;10(7):466–472. doi: 10.1191/096120301678416015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuñiga R., Ng S., Peterson M. G., Reveille J. D., Baethge B. A., Alarcón G. S., Salmon J. E. Low-binding alleles of Fcgamma receptor types IIA and IIIA are inherited independently and are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hispanic patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):361–367. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<361::AID-ANR54>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas M., Kleijer M., van Zwieten R., Roos D., von dem Borne A. E. Neutrophil Fc gamma RIIIb deficiency, nature, and clinical consequences: a study of 21 individuals from 14 families. Blood. 1995 Sep 15;86(6):2403–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Capel P. J. Human IgG Fc receptor heterogeneity: molecular aspects and clinical implications. Immunol Today. 1993 May;14(5):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90166-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]