Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the use of ultrasound, including quantitative Doppler analysis of synovial vascularisation, before and after intra-articular treatment with glucocorticosteroids in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: 51 patients with RA were followed prospectively after an intra-articular glucocorticosteroid injection. Disease modifying antirheumatic drug treatment was kept unchanged and no further injections given in this observation period. At baseline, disease activity was estimated clinically by target join pain on a 100 mm visual analogue scale, on which the target joint was scored 0–3 for swelling and tenderness, and by ultrasound measurements of grey scale pixels, colour Doppler pixels, and the spectral Doppler resistive index (RI) as indicators of synovial swelling and inflammation. After four weeks, the measurements were repeated on the same joint. An observer unaware of the sequence and patient number evaluated the ultrasound images.
Results: At one month follow up after the glucocorticosteroid injection, a marked decrease in the fraction of colour pixels was seen in 41/51 patients (Student's t test p<0.001). Correspondingly, the RI increased indicating a diminished flow to the synovium (Student's t test p<0.01). Both the fraction of colour pixels and the RI values corresponded with the clinical evaluation and with the subjective effect of the treatment. The synovial membrane volume estimated by total amount of pixels showed a significant decrease by 31% after treatment.
Conclusion: Ultrasound-Doppler seems to be a promising tool for the estimation of synovial activity in arthritis. After intra-articular glucocorticosteroid, changes in RI and fraction of colour pixels may both be used as quantitative measurements of the blood flow.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (619.5 KB).
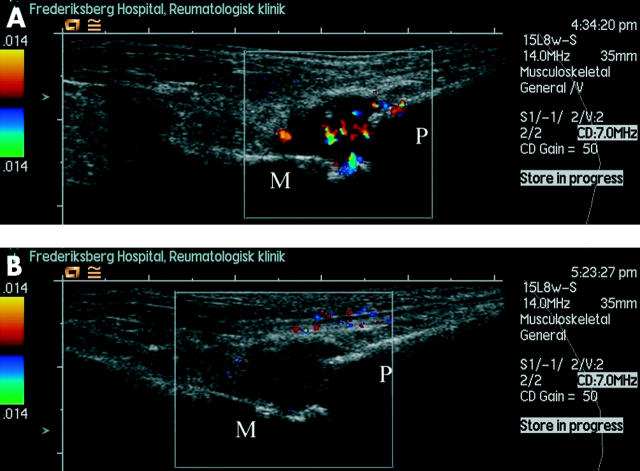
Figure 1 .
Longitudinal scan of the dorsal side of the right second metatarsophalangeal joint (A) before and (B) four weeks after intra-articular injection with 40 mg methylprednisolone. The synovial tissue is seen as a hypoechoic (dark) mass swelling from the joint. The metacarpal bone is marked "M" and the phalangeal bone "P". The phalangeal bone is subluxated dorsally. In the bottom image the coloured pixels have completely disappeared — a sign of reduced flow in the treated region. The few scattered extrasynovial colour pixels in the bottom image are generated by noise.
Figure 2 .
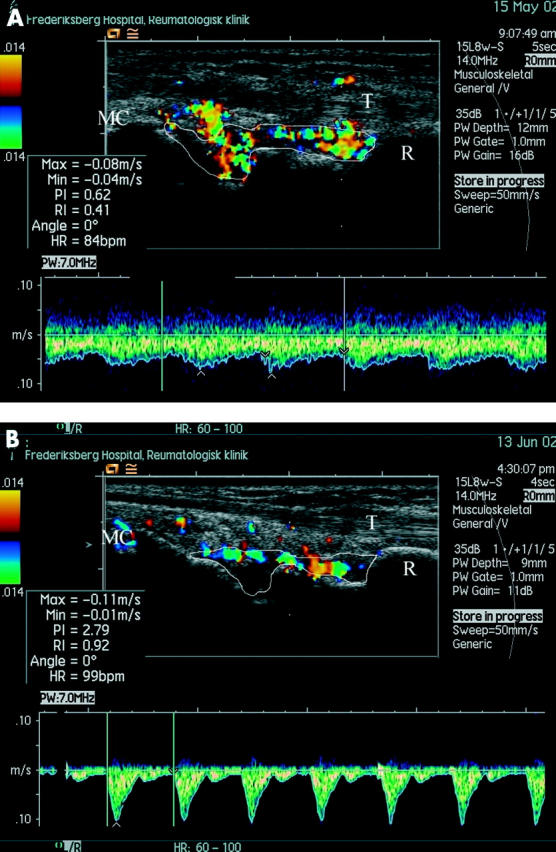
Longitudinal scan on the radial side of the left wrist showing the area with most activity (A) before and (B) four weeks after intra-articular injection with 40 mg methylprednisolone. The radial bone (R) is seen at the right side of the image and the metacarpus (MC) at the left. The extensor carpi radialis tendon is marked "T". The synovium has been traced defining the ROI for the calculation of the colour fraction. The trace was made with the help of an extra image (not shown) where the colour had been removed, thereby allowing for definition of the border between synovium and extrasynovial tissue in the areas where it is covered with colour. In both images the Doppler gate (the space between the two horizontal lines on the dotted vertical Doppler line) has been placed over an intrasynovial artery and the resulting spectral curve is shown beneath. The ultrasound unit has traced the spectrum, defined maximum systolic value and end diastolic value, and displayed RI (0.41 and 0.92) in the data boxes. There is a reduction in colour fraction and an increase in peripheral resistance (increase in RI) as signs of reduced flow to the treated region.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson S. L. Arterial pressure, vascular input impedance, and resistance as determinants of pulsatile blood flow in the umbilical artery. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1999 Jun;84(2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/s0301-2115(98)00320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus M., Kamradt T., Sandrock D., Loreck D., Fritz J., Wolf K. J., Raber H., Hamm B., Burmester G. R., Bollow M. Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1232–1245. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1232::AID-ANR21>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bude R. O., Rubin J. M. Effect of downstream cross-sectional area of an arterial bed on the resistive index and the early systolic acceleration. Radiology. 1999 Sep;212(3):732–738. doi: 10.1148/radiology.212.3.r99se13732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardinal E., Lafortune M., Burns P. Power Doppler US in synovitis: reality or artifact? Radiology. 1996 Sep;200(3):868–869. doi: 10.1148/radiology.200.3.8756948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emkey R. D., Lindsay R., Lyssy J., Weisberg J. S., Dempster D. W., Shen V. The systemic effect of intraarticular administration of corticosteroid on markers of bone formation and bone resorption in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Feb;39(2):277–282. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER J. L., BROWN E. M., Jr, JESSAR R. A., BROWN C. Y. Hydrocortisone and cortisone injected into arthritic joints; comparative effects of and use of hydrocortisone as a local antiarthritic agent. J Am Med Assoc. 1951 Dec 22;147(17):1629–1635. doi: 10.1001/jama.1951.03670340019005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hau M., Kneitz C., Tony H-P, Keberle M., Jahns R., Jenett M. High resolution ultrasound detects a decrease in pannus vascularisation of small finger joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving treatment with soluble tumour necrosis factor alpha receptor (etanercept). Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Jan;61(1):55–58. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Chiang C. D., Chen C. Y., Kwan P. C., Hsu J. Y., Hsu C. P., Ho W. L. Color Doppler ultrasound pulsatile flow signals of thoracic lesions: comparison of lung cancers and benign lesions. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1998 Oct;24(8):1087–1095. doi: 10.1016/s0301-5629(98)00088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund M., Ostergaard M., Gideon P., Sørensen K., Jensen K. E., Lorenzen I. Wrist and finger joint MR imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Radiol. 1999 Jul;40(4):400–409. doi: 10.3109/02841859909177754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M., Hermunen H. Intra-articular glucocorticoid treatment of the rheumatoid wrist. An ultrasonographic study. Scand J Rheumatol. 2001;30(5):268–270. doi: 10.1080/030097401753180336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. J. Treatment of rheumatoid joint inflammation with triamcinolone hexacetonide. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):157–173. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midiri M., Iovane A., Finazzo M., Brancatelli G., Gallo C., Lagalla R. L'eco color Doppler nell'artrite reumatoide con localizzazione extra-articolare. Esperienza preliminare. Radiol Med. 1999 Sep;98(3):123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidel Jasper, Boehnke Martina, Küster R. Michael. The efficacy and safety of intraarticular corticosteroid therapy for coxitis in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jun;46(6):1620–1628. doi: 10.1002/art.10313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. S., Adler R. S., Bude R. O., Rubin J. M. Detection of soft-tissue hyperemia: value of power Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994 Aug;163(2):385–389. doi: 10.2214/ajr.163.2.8037037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. S., Laing T. J., McCarthy C. J., Adler R. S. Power Doppler sonography of synovitis: assessment of therapeutic response--preliminary observations. Radiology. 1996 Feb;198(2):582–584. doi: 10.1148/radiology.198.2.8596870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Stoltenberg M., Gideon P., Sørensen K., Henriksen O., Lorenzen I. Changes in synovial membrane and joint effusion volumes after intraarticular methylprednisolone. Quantitative assessment of inflammatory and destructive changes in arthritis by MRI. J Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;23(7):1151–1161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvistgaard E., Røgind H., Torp-Pedersen S., Terslev L., Danneskiold-Samsøe B., Bliddal H. Quantitative ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of inflammation by Doppler technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Jul;60(7):690–693. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.7.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D. Common disorders of synovium-lined joints: pathogenesis, imaging abnormalities, and complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Dec;151(6):1079–1093. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.6.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. M., Adler R. S., Fowlkes J. B., Spratt S., Pallister J. E., Chen J. F., Carson P. L. Fractional moving blood volume: estimation with power Doppler US. Radiology. 1995 Oct;197(1):183–190. doi: 10.1148/radiology.197.1.7568820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. M., Bude R. O., Carson P. L., Bree R. L., Adler R. S. Power Doppler US: a potentially useful alternative to mean frequency-based color Doppler US. Radiology. 1994 Mar;190(3):853–856. doi: 10.1148/radiology.190.3.8115639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. A., Völker L., Zacher J., Schläfke M., Ruhnke M., Gromnica-Ihle E. Colour Doppler ultrasonography to detect pannus in knee joint synovitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000 Jul-Aug;18(4):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri E., Martinoli C., Onetto F., Neumaier C. E., Cimmino M. A., Derchi L. E. Valutazione dell'artrite reumatoide del ginocchio con color Doppler. Radiol Med. 1994 Oct;88(4):364–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjoldbye B., Nielsen A. H., Court-Payen M., Nørgaard N., Rasmussen F., Løkkegaard H., Lorentzen T., Holm H. H. Perioperative Doppler ultrasonography: renal detection of renal graft perfusion. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1998 Sep;32(5):345–349. doi: 10.1080/003655998750015313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M., Bergin D., Whelan B., Maher M., Murray J., McCarthy C. Power Doppler ultrasound assessment of rheumatoid hand synovitis. J Rheumatol. 2001 Sep;28(9):1979–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struijk P. C., Ursem N. T., Mathews J., Clark E. B., Keller B. B., Wladimiroff J. W. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate and blood flow velocity variability measured in the umbilical and uterine arteries in early pregnancy: a comparative study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001 Apr;17(4):316–321. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2001.00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szkudlarek M., Court-Payen M., Strandberg C., Klarlund M., Klausen T., Ostergaard M. Power Doppler ultrasonography for assessment of synovitis in the metacarpophalangeal joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):2018–2023. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2018::AID-ART350>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terslev L., Torp-Pedersen S., Qvistgaard E., Kristoffersen H., Røgind H., Danneskiold-Samsøe B., Bliddal H. Effects of treatment with etanercept (Enbrel, TNRF:Fc) on rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by Doppler ultrasonography. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Feb;62(2):178–181. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.2.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther M., Harms H., Krenn V., Radke S., Faehndrich T. P., Gohlke F. Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):331–338. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<331::AID-ANR50>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]