Abstract
Objective: To determine a value of serum human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC gp39) as a marker of arthritis associated with IBD.
Methods: Serum levels of HC gp39 and ultrasensitive C reactive protein (CRP) were determined in 121 patients with IBD: 58 without arthritis (IBD-nonA) and 63 with arthritis (IBD-A), and in 20 healthy controls. IBD was classified as active (aIBD) and non-active (naIBD), and patients with IBD-A were classified as type I, II, and III arthritis by clinical activity indices.
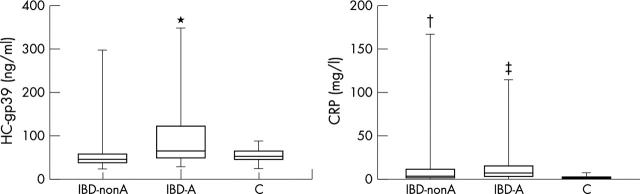
Results: HC gp39 was higher in IBD-A than in IBD-nonA (p<0.001) and controls (p<0.01), while no difference was found between IBD-nonA and controls. CRP was increased in both IBD-A and IBD-nonA compared with the controls (p<0.01 and <0.05, respectively) and in aIBD-nonA v naIBD-nonA (p<0.05), but no difference in CRP was found between aIBD-A and naIBD-A. Finally, a correlation was found between the number of affected joints (NAJ) and HC gp39 (r = 0.6, p<0.001).
Discussion: Increased serum levels of HC gp39, which were higher in IBD-A than in IBD-nonA, suggest that this substance might be a marker of arthropathy in IBD. HC gp39, because of its relationship with NAJ in IBD-A, may also be proposed as a disease activity marker in arthritis associated with IBD.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (225.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
Serum levels of HC gp39 and CRP in patients with IBD-A, IBD-nonA, and controls (C). Significant differences (Student's t test): *p<0.001 IBD-A v IBD-nonA; †p<0.05 IBD-nonA v controls; ‡p<0.01 IBD-A v controls.
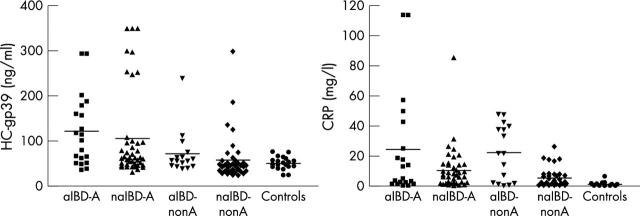
Figure 2 .
The Kruskal-Wallis analysis for HC gp39 and CRP in aIBD-A, naIBD-A, aIBD-nonA, naIBD-nonA, and controls.