Abstract
Objective: To examine the serum levels of IL15 in KD and to evaluate the role of IL15 in estimating the severity of inflammation in KD.
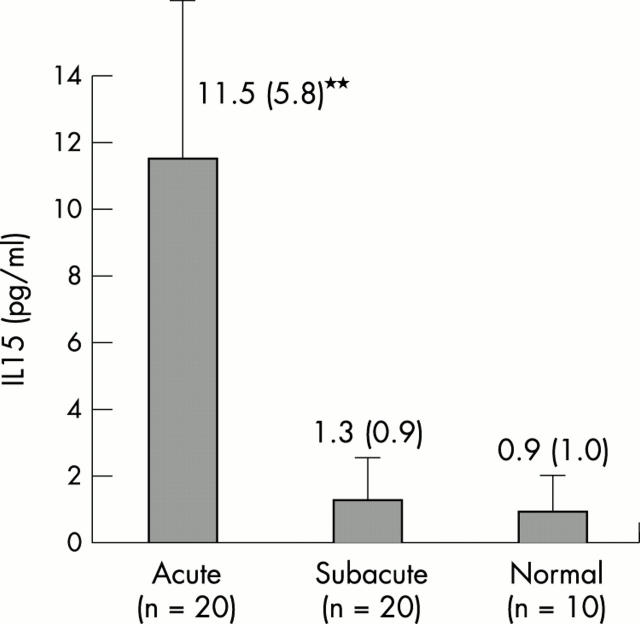
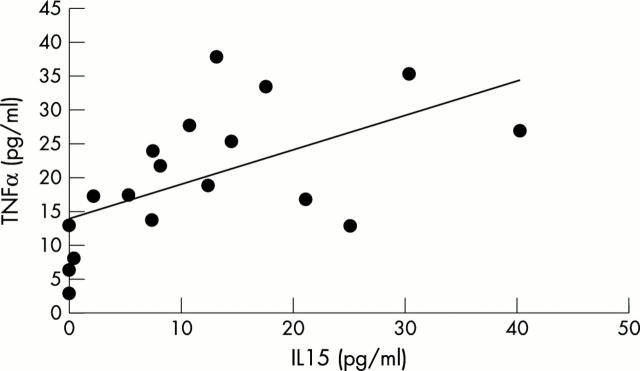
Results and conclusion: There was a significant increase in the mean (SD) serum levels of IL15 measured in the acute stage of KD (11.5 (5.8) pg/ml) compared with those in the subacute stage (1.3 (0.9) pg/ml) (p<0.01) and normal controls (0.9 (1.0) pg/ml) (p<0.01). The increase in IL15 correlated with the increase in TNFα (rs=0.66, p<0.01); however it did not correlate with the levels of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C reactive protein, suggesting that IL15 may not be a useful marker in estimating the severity of inflammation in KD.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (133.8 KB).
Figure 1.
Serum levels of IL15 in patients in the acute phase of KD. compared with the subacute phase and normal controls **p<0.01.
Figure 2.
Correlation between IL15 and TNFα levels in patients with KD.