Abstract
Patients and methods: 120 patients with active RA, rheumatoid factor positive and/or erosive, were randomly allocated to receive CsA with MTX (n=60) or CsA with placebo (n=60). Treatment with CsA was started in all patients at 2.5 mg/kg/day and increased to a maximum of 5 mg/kg/day in 16 weeks. MTX was started at 7.5 mg/week and increased to a maximal dose of 15 mg/week at week 16. Primary outcomes were clinical remission (Pinals criteria) and radiological damage (Larsen score), at week 48.
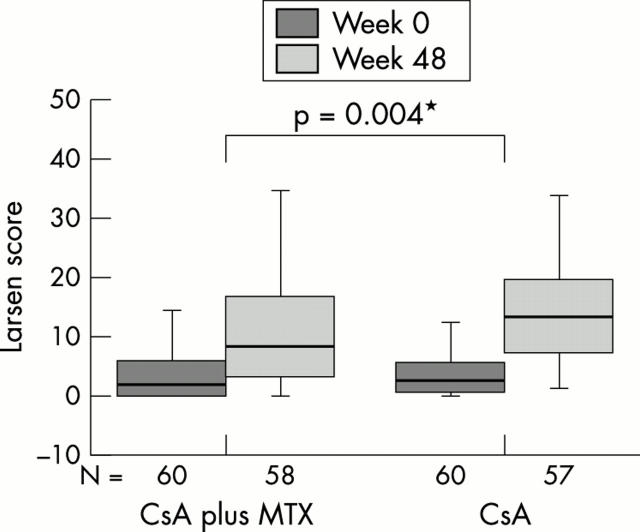
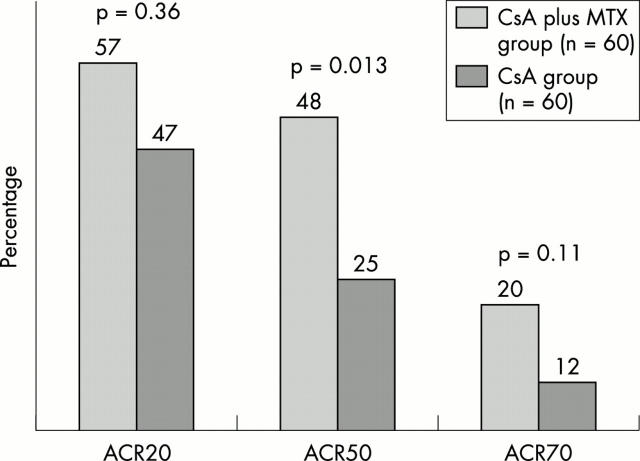
Results: Treatment was discontinued prematurely in 27 patients in the monotherapy group (21 because of inefficacy, and six because of toxicity) and in 26 patients in the combination therapy group (14 and 12, respectively). At week 48, clinical remission was achieved in four patients in the monotherapy group and in six patients in the combination therapy group (p=0.5). The median Larsen score increased to 10 (25th, 75th centiles: 3.5; 13.3) points in the monotherapy group and to 4 (1.0; 10.5) points in the combination therapy group (p=0.004). 28/60 (47%) of patients in the monotherapy group v 34/60 (57%) of patients in the combination therapy group had reached an American college of Rheumatology 20% (ACR20) response (p=0.36) at week 48; 15/60 (25%) v 29/60 (48%) of patients had reached an ACR50 response (p=0.013); and 7 (12%) v 12 (20%) of patients had reached an ACR70 response (p=0.11).Their was a tendency towards more toxicity in the combination therapy group.
Conclusions: In patients with early RA, neither CsA plus MTX combination therapy nor CsA monotherapy is very effective in inducing clinical remission. Combination therapy is probably better at improving clinical disease activity, and definitely better at slowing radiological progression. Combination therapy should still be compared with methotrexate monotherapy.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (158.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
Radiological progression. Median Larsen scores (25th, 75th centiles) at baseline and after 48 weeks of treatment are given in each group. The p value refers to the between-group difference in change after 48 weeks. Numbers are the number of patients on which the analyses were based.
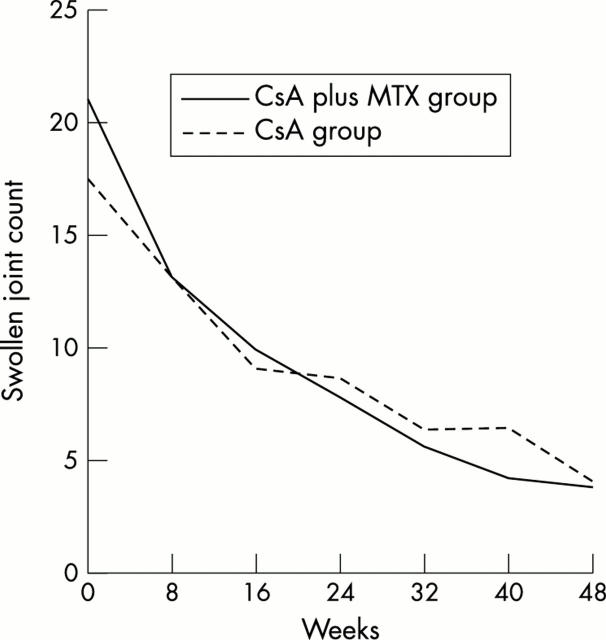
Figure 2 .
Swollen joint count. Course of swollen joint count over time. Mean numbers of swollen joints in each group at different times are shown.
Figure 3 .
Improvement according to ACR criteria. Percentages of patients fulfilling ACR criteria for 20%, 50% and 70% improvement at week 48. p Values refer to between-group differences.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón G. S., López-Méndez A., Walter J., Boerbooms A. M., Russell A. S., Furst D. E., Rau R., Drosos A. A., Bartolucci A. A. Radiographic evidence of disease progression in methotrexate treated and nonmethotrexate disease modifying antirheumatic drug treated rheumatoid arthritis patients: a meta-analysis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Dec;19(12):1868–1873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Tugwell P., Felson D. T., van Riel P. L., Kirwan J. R., Edmonds J. P., Smolen J. S., Khaltaev N., Muirden K. D. World Health Organization and International League of Associations for Rheumatology core endpoints for symptom modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1994 Sep;41:86–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drossaers-Bakker K. W., Kroon H. M., Zwinderman A. H., Breedveld F. C., Hazes J. M. Radiographic damage of large joints in long-term rheumatoid arthritis and its relation to function. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Sep;39(9):998–1003. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.9.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Katz L. M., Lightfoot R., Jr, Paulus H., Strand V. American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jun;38(6):727–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Meenan R. F. The efficacy and toxicity of combination therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Oct;37(10):1487–1491. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraccioli G. F., Della Casa-Alberighi O., Marubini E., Priolo F., Mathieu A., Fantini F., Cutolo M., Pasero G. Is the control of disease progression within our grasp? Review of the GRISAR study. (Gruppo Reumatologi Italiani Studio Artrite Reumatoide). Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Sep;35 (Suppl 2):8–13. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_2.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F. Reevaluating the therapeutic approach to rheumatoid arthritis: the "sawtooth" strategy. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1990 May;22:12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furst D. E. Clinical pharmacology of combination DMARD therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1996 Mar;44:86–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Førre O. Radiologic evidence of disease modification in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with cyclosporine. Results of a 48-week multicenter study comparing low-dose cyclosporine with placebo. Norwegian Arthritis Study Group. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Oct;37(10):1506–1512. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagsma C. J., van Riel P. L., de Jong A. J., van de Putte L. B. Combination of sulphasalazine and methotrexate versus the single components in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled, double-blind, 52 week clinical trial. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Oct;36(10):1082–1088. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.10.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsmans H. M., Jacobs J. W., van der Heijde D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., Schenk Y., Bijlsma J. W. The course of radiologic damage during the first six years of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Sep;43(9):1927–1940. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<1927::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger K., Schattenkirchner M. Comparison of cyclosporin A and azathioprine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis--results of a double-blind multicentre study. Clin Rheumatol. 1994 Jun;13(2):248–255. doi: 10.1007/BF02249021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landewe R. B., Goei The H. S., van Rijthoven A. W., Rietveld J. R., Breedveld F. C., Dijkmans B. A. Cyclosporine in common clinical practice: an estimation of the benefit/risk ratio in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;21(9):1631–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landewé R. B., Goei Thè H. S., van Rijthoven A. W., Breedveld F. C., Dijkmans B. A. A randomized, double-blind, 24-week controlled study of low-dose cyclosporine versus chloroquine for early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 May;37(5):637–643. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. How to apply Larsen score in evaluating radiographs of rheumatoid arthritis in long-term studies. J Rheumatol. 1995 Oct;22(10):1974–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. J. Suppress rheumatoid inflammation early and leave the pyramid to the Egyptians. J Rheumatol. 1990 Sep;17(9):1115–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell J. R., Haire C. E., Erikson N., Drymalski W., Palmer W., Eckhoff P. J., Garwood V., Maloley P., Klassen L. W., Wees S. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate alone, sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine, or a combination of all three medications. N Engl J Med. 1996 May 16;334(20):1287–1291. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199605163342002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paimela L., Laasonen L., Helve T., Leirisalo-Repo M. Comparison of the original and the modified Larsen methods and the Sharp method in scoring radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1998 Jun;25(6):1063–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinals R. S., Masi A. T., Larsen R. A. Preliminary criteria for clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1308–1315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Breedveld F. C., Emery P. Does partial control of inflammation prevent long-term joint damage? Clinical rationale for combination therapy with multiple disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999 Nov-Dec;17(6 Suppl 18):S2–S7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Callahan L. F. Reassessment of twelve traditional paradigms concerning the diagnosis, prevalence, morbidity and mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1989;79:67–96. doi: 10.3109/03009748909092614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau R., Herborn G., Karger T., Werdier D. Retardation of radiologic progression in rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate therapy. A controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1236–1244. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez F., Krayenbühl J. C., Harrison W. B., Førre O., Dijkmans B. A., Tugwell P., Miescher P. A., Mihatsch M. J. Renal biopsy findings and followup of renal function in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with cyclosporin A. An update from the International Kidney Biopsy Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Sep;39(9):1491–1498. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwell P., Baker P. Guidelines for the use of cyclosporine in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;14 (Suppl 2):37–41. doi: 10.1007/BF02215857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwell P., Bombardier C., Gent M., Bennett K. J., Bensen W. G., Carette S., Chalmers A., Esdaile J. M., Klinkhoff A. V., Kraag G. R. Low-dose cyclosporin versus placebo in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1990 May 5;335(8697):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92630-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwell P., Pincus T., Yocum D., Stein M., Gluck O., Kraag G., McKendry R., Tesser J., Baker P., Wells G. Combination therapy with cyclosporine and methotrexate in severe rheumatoid arthritis. The Methotrexate-Cyclosporine Combination Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jul 20;333(3):137–141. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507203330301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven A. C., Boers M., Tugwell P. Combination therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: updated systematic review. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Jun;37(6):612–619. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.6.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E. Efficacy of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Nov;34 (Suppl 2):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske K. R., Healey L. A. Remodeling the pyramid--a concept whose time has come. J Rheumatol. 1989 May;16(5):565–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Riel P. L., van der Heijde D. M., Nuver-Zwart I. H., van de Putte L. B. Radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: results of 3 comparative trials. J Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;22(9):1797–1799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijthoven A. W., Dijkmans B. A., Goei The H. S., Hermans J., Montnor-Beckers Z. L., Jacobs P. C., Cats A. Cyclosporin treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: a placebo controlled, double blind, multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Sep;45(9):726–731. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.9.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijthoven A. W., Dijkmans B. A., Thè H. S., Meijers K. A., Montnor-Beckers Z. L., Moolenburgh J. D., Boers M., Cats A. Comparison of cyclosporine and D-penicillamine for rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double blind, multicenter study. J Rheumatol. 1991 Jun;18(6):815–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Vandenbroucke J. P., Breedveld F. C. Factors predicting outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: results of a followup study. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1288–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Borne B. E., Landewé R. B., Goei The H. S., Breedveld F. C., Dijkmans B. A. Cyclosporin A therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: only strict application of the guidelines for safe use can prevent irreversible renal function loss. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Mar;38(3):254–259. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide A., Jacobs J. W., Bijlsma J. W., Heurkens A. H., van Booma-Frankfort C., van der Veen M. J., Haanen H. C., Hofman D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., ter Borg E. J. The effectiveness of early treatment with "second-line" antirheumatic drugs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Apr 15;124(8):699–707. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-8-199604150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Leeuwen M. A., van Riel P. L., Koster A. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Biannual radiographic assessments of hands and feet in a three-year prospective followup of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jan;35(1):26–34. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.