Abstract
Objective: To study the prevalence of IgA antiphospholipid antibodies, particularly anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL) and anti-ß2-glycoprotein I (aß2GPI), in a cohort of patients with pregnancy morbidity.
Patients and methods: Serum samples from four groups of patients were studied by an in house enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Group I: 28 patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS) (median age 32.5 years, range 25–34). Twelve patients had a history of thrombosis. All were positive for IgG/M aCL or lupus anticoagulant (LA), or both. Group II: 28 patients with unexplained pregnancy morbidity (median age 35 years, range 23–48). Seven had history of thrombosis. Nine patients were positive for IgG/M aCL. None from this group fulfilled Sapporo criteria for APS. Group III: 28 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (median age 34 years, range 25–52). Eleven had a history of thrombosis. Twenty one patients had IgG/M aCL and/or LA, but only 19 fulfilled Sapporo criteria for APS.
Results: IgA aCL were found in 12, 6, and 14 patients from the groups with PAPS, unexplained pregnancy morbidity, and SLE, respectively. Most patients had these antibodies together with IgG/IgM aCL. Three patients from the group with unexplained pregnancy morbidity and two with SLE had IgA aCL alone. IgA aß2GPI was present in one patient from each group. All IgA aß2GPI were present together with IgG and/or IgM aß2GPI.
Conclusions: The prevalence of IgA aCL is high in patients with pregnancy morbidity, although IgA aCL are usually present together with IgG and/or IgM aCL. IgA aß2GPI are not useful in identifying additional women with APS and pregnancy morbidity.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (109.5 KB).
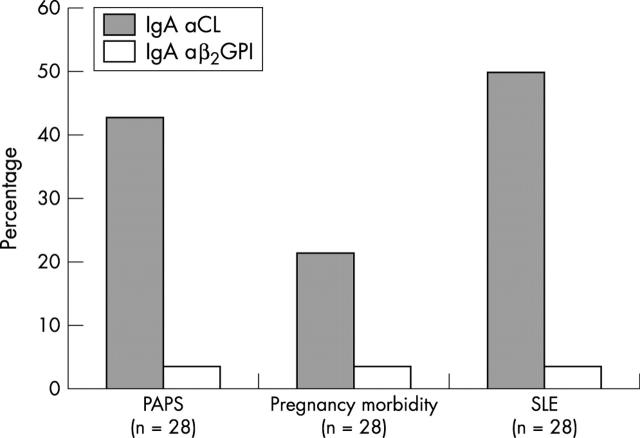
Figure 1.
Prevalence of IgA aCL and IgA aß2GPI in patients from the groups with PAPS, unexplained pregnancy morbidity, and SLE.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amengual O., Atsumi T., Khamashta M. A., Koike T., Hughes G. R. Specificity of ELISA for antibody to beta 2-glycoprotein I in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Dec;35(12):1239–1243. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.12.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolaccini M. L., Atsumi T., Escudero Contreras A., Khamashta M. A., Hughes G. R. The value of IgA antiphospholipid testing for diagnosis of antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001 Dec;28(12):2637–2643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevers E. M., Galli M., Barbui T., Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. Lupus anticoagulant IgG's (LA) are not directed to phospholipids only, but to a complex of lipid-bound human prothrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Dec 2;66(6):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J. T., Triplett D. A., Alving B., Scharrer I. Criteria for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants: an update. On behalf of the Subcommittee on Lupus Anticoagulant/Antiphospholipid Antibody of the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the ISTH. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Oct;74(4):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Papa N., Guidali L., Sala A., Buccellati C., Khamashta M. A., Ichikawa K., Koike T., Balestrieri G., Tincani A., Hughes G. R. Endothelial cells as target for antiphospholipid antibodies. Human polyclonal and monoclonal anti-beta 2-glycoprotein I antibodies react in vitro with endothelial cells through adherent beta 2-glycoprotein I and induce endothelial activation. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Mar;40(3):551–561. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanopoulos D., Teodorescu M. R., Varga J., Teodorescu M. High frequency of abnormal levels of IgA anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1998 Apr;25(4):675–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M. Non beta 2-glycoprotein I cofactors for antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus. 1996 Oct;5(5):388–392. doi: 10.1177/096120339600500511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: isotype distribution and phospholipid specificity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. Antiphospholipid antibodies and thrombosis. Lancet. 1999 Apr 17;353(9161):1348–1353. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)10362-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Pierangeli S., Birch D. Anticardiolipin wet workshop report. Fifth International Symposium on antiphospholipid antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;101(5):616–624. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalunian K. C., Peter J. B., Middlekauff H. R., Sayre J., Ando D. G., Mangotich M., Hahn B. H. Clinical significance of a single test for anti-cardiolipin antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1988 Nov;85(5):602–608. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. M., Branch D. W., Silver R. M. Immunoglobulin A anti-beta2-glycoprotein antibodies in women who experience unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion and unexplained fetal death. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001 Sep;185(3):748–753. doi: 10.1067/mob.2001.117659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. M., Emlen W., Scott J. R., Branch D. W., Silver R. M. Anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion, unexplained fetal death, and antiphospholipid syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Sep;181(3):642–648. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Yasuda T., Triplett D. A., Koike T. Anticardiolipin antibodies recognize beta 2-glycoprotein I structure altered by interacting with an oxygen modified solid phase surface. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):457–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosting J. D., Derksen R. H., Bobbink I. W., Hackeng T. M., Bouma B. N., de Groot P. G. Antiphospholipid antibodies directed against a combination of phospholipids with prothrombin, protein C, or protein S: an explanation for their pathogenic mechanism? Blood. 1993 May 15;81(10):2618–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Out H. J., Kooijman C. D., Bruinse H. W., Derksen R. H. Histopathological findings in placentae from patients with intra-uterine fetal death and anti-phospholipid antibodies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1991 Oct 8;41(3):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(91)90021-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierangeli S. S., Liu X. W., Barker J. H., Anderson G., Harris E. N. Induction of thrombosis in a mouse model by IgG, IgM and IgA immunoglobulins from patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Nov;74(5):1361–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selva-O'Callaghan A., Ordi-Ros J., Monegal-Ferran F., Martinez N., Cortes-Hernandez F., Vilardell-Tarres M. IgA anticardiolipin antibodies--relation with other antiphospholipid antibodies and clinical significance. Thromb Haemost. 1998 Feb;79(2):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi A., Matsuura E., Ichikawa K., Fujisaku A., Mukai M., Koike T. IgA class anti-beta2-glycoprotein I in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1998 Jan;25(1):74–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Gharavi A. E., Koike T., Lockshin M. D., Branch D. W., Piette J. C., Brey R., Derksen R., Harris E. N., Hughes G. R. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jul;42(7):1309–1311. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199907)42:7<1309::AID-ANR1>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Tsutsumi A., Ichikawa K., Kato E. H., Koike T., Fujimoto S. IgA-class anti-beta2-glycoprotein I in women with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Dec;42(12):2727–2728. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199912)42:12<2727::AID-ANR33>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]