Abstract
Background: Glucocorticoids induce hypercholesterolaemia, a cardiovascular risk factor, in patients with diseases other than rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but the data in RA are contradictory.
Objective: To determine the effects of antirheumatic treatment, including prednisolone (combination) therapy on total and high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels in RA, taking disease activity into account.
Methods: HDL cholesterol and total cholesterol levels were determined in:(a) established RA (b) two cohorts with early active RA, (c) a previously conducted 56 week trial among patients with early RA comparing the value of intensive combination therapy (that included glucocorticoids) with sulfasalazine alone (COBRA trial).
Results: In established RA total cholesterol levels were only slightly raised, irrespective of disease activity. However, HDL cholesterol was significantly higher in patients in remission than in patients with active disease. In contrast, in active early RA at baseline total cholesterol was low normal: between 4.6 and 5.1 mmol/l in the different populations. The level of HDL cholesterol was highly dependent on the duration of storage. In both COBRA groups total cholesterol increased by a mean of 0.6 mmol/l. HDL cholesterol increased by more than 50% after treatment, leading to an improvement of the total cholesterol/HDL ratio (atherogenic index). This increase (and index improvement) was much more rapid in the group receiving combination treatment. A similar pattern was seen in the 2001 cohort with early RA. In all the groups with active disease HDL and total cholesterol levels correlated inversely with disease activity.
Conclusion: In established, but especially in early RA, disease activity is accompanied by atherogenic lipid levels. This dyslipidaemia can be rapidly reversed by aggressive antirheumatic treatment including glucocorticoids.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (103.4 KB).
Figure 1.
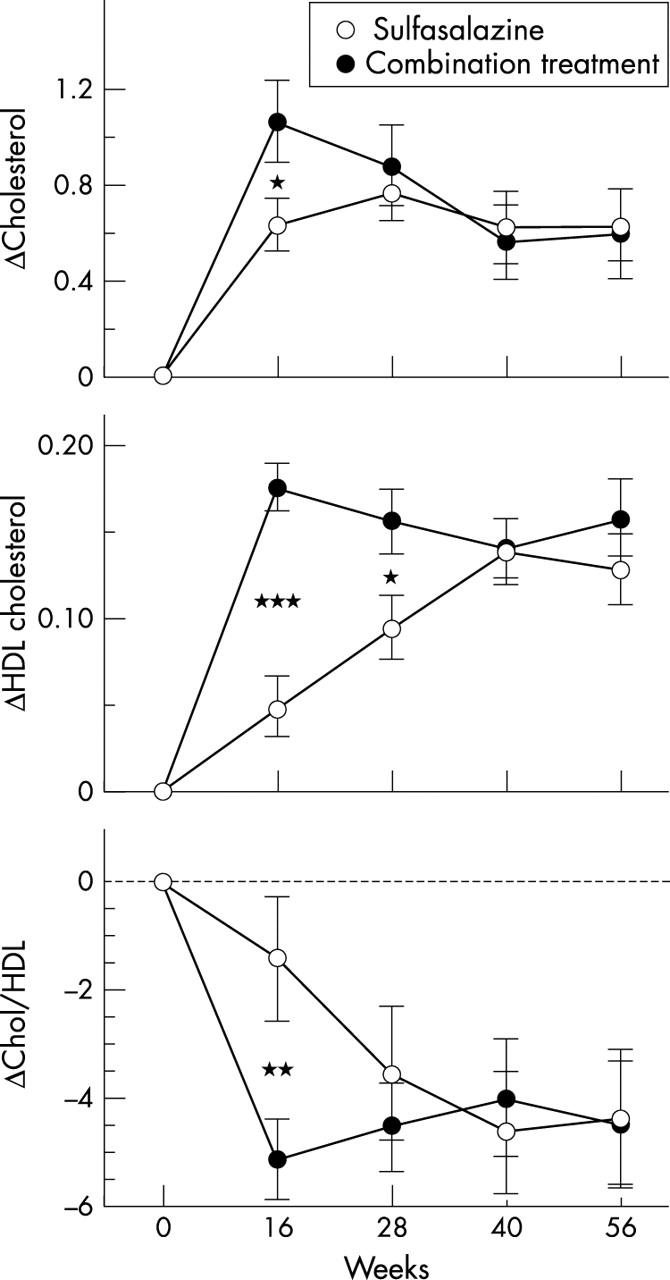
Changes in total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and the atherogenic index (chol/HDL) in the COBRA trial.
Figure 2.

HDL cholesterol levels at baseline related to storage duration.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. C., Walker B. R. Glucocorticoids and insulin resistance: old hormones, new targets. Clin Sci (Lond) 1999 May;96(5):513–523. doi: 10.1042/cs0960513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landewé Robert B. M., Boers Maarten, Verhoeven Arco C., Westhovens Rene, van de Laar Mart A. F. J., Markusse Harry M., van Denderen J. Christiaan, Westedt Marie Louise, Peeters Andre J., Dijkmans Ben A. C. COBRA combination therapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: long-term structural benefits of a brief intervention. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):347–356. doi: 10.1002/art.10083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux I., Lamarche B., Couillard C., Pascot A., Cantin B., Bergeron J., Dagenais G. R., Després J. P. Total cholesterol/HDL cholesterol ratio vs LDL cholesterol/HDL cholesterol ratio as indices of ischemic heart disease risk in men: the Quebec Cardiovascular Study. Arch Intern Med. 2001 Dec 10;161(22):2685–2692. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.22.2685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell S. R., Moots R. J., Kendall M. J. Corticosteroids: do they damage the cardiovascular system? Postgrad Med J. 1994 Dec;70(830):863–870. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.70.830.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar Esmeralda T. H., Voskuyl Alexandre E., Dijkmans Ben A. C. Functional disability in relation to radiological damage and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in remission. J Rheumatol. 2002 Feb;29(2):267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Yong-Beom, Choi Hyon K., Kim Min-Young, Lee Won-Ki, Song Jungsik, Kim Dong-Kee, Lee Soo-Kon. Effects of antirheumatic therapy on serum lipid levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Am J Med. 2002 Aug 15;113(3):188–193. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01186-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinals R. S., Masi A. T., Larsen R. A. Preliminary criteria for clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1308–1315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynauld J. P. Cardiovascular mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: how harmful are corticosteroids? J Rheumatol. 1997 Mar;24(3):415–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubenoff R., Roubenoff R. A., Ward L. M., Holland S. M., Hellmann D. B. Rheumatoid cachexia: depletion of lean body mass in rheumatoid arthritis. Possible association with tumor necrosis factor. J Rheumatol. 1992 Oct;19(10):1505–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doornum S., McColl G., Wicks I. P. Accelerated atherosclerosis: an extraarticular feature of rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Apr;46(4):862–873. doi: 10.1002/art.10089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Horst-Bruinsma I. E., Speyer I., Visser H., Breedveld F. C., Hazes J. M. Diagnosis and course of early-onset arthritis: results of a special early arthritis clinic compared to routine patient care. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Oct;37(10):1084–1088. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.10.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


