Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the biodistribution and specific targeting for tumour necrosis factor (TNF) of a fully human, radiolabelled anti-TNF monoclonal antibody (anti-TNF mAb) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To assess whether this agent is suitable for visualisation of synovitis.
Methods: Ten patients with RA underwent whole body scintigraphy after administration of a tracer—subtherapeutic dose of 100 µg 99mTc human anti-TNF mAb. After two weeks, the procedure was repeated to assess the specificity of the radiolabelled antibody for TNF and its sensitivity for changes in inflammation. Therefore, a competition study was performed in five patients, who received excess unlabelled anti-TNF mAb before the tracer dose of 99mTc-anti-TNF. Another five patients received 120 mg methylprednisolone two days before the second scintigraphy.
Results: Radiolabelled anti-TNF mAb allowed clear visualisation of inflamed joints in patients with active RA with a high specificity. Concomitant administration of excess unlabelled anti-TNF reduced the joint uptake of 99mTc-anti-TNF mAb by a median of 25% as a percentage of the injected dose after 24 hours, whereas uptake in liver and spleen remained unchanged. Systemic corticosteroids reduced the disease activity, which was mirrored by a decreased joint uptake of the tracer. The anti-TNF mAb retained its high affinity for TNFα after labelling and was cleared from the circulation with an elimination half life of 48 hours. The procedure was well tolerated.
Conclusions: Radiolabelled human anti-TNF mAb allows visualisation of synovitis in patients with RA. Joint accumulation of this agent is partly due to specific TNF targeting and is highly predictive for inflammation.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (80.7 KB).
Figure 1.
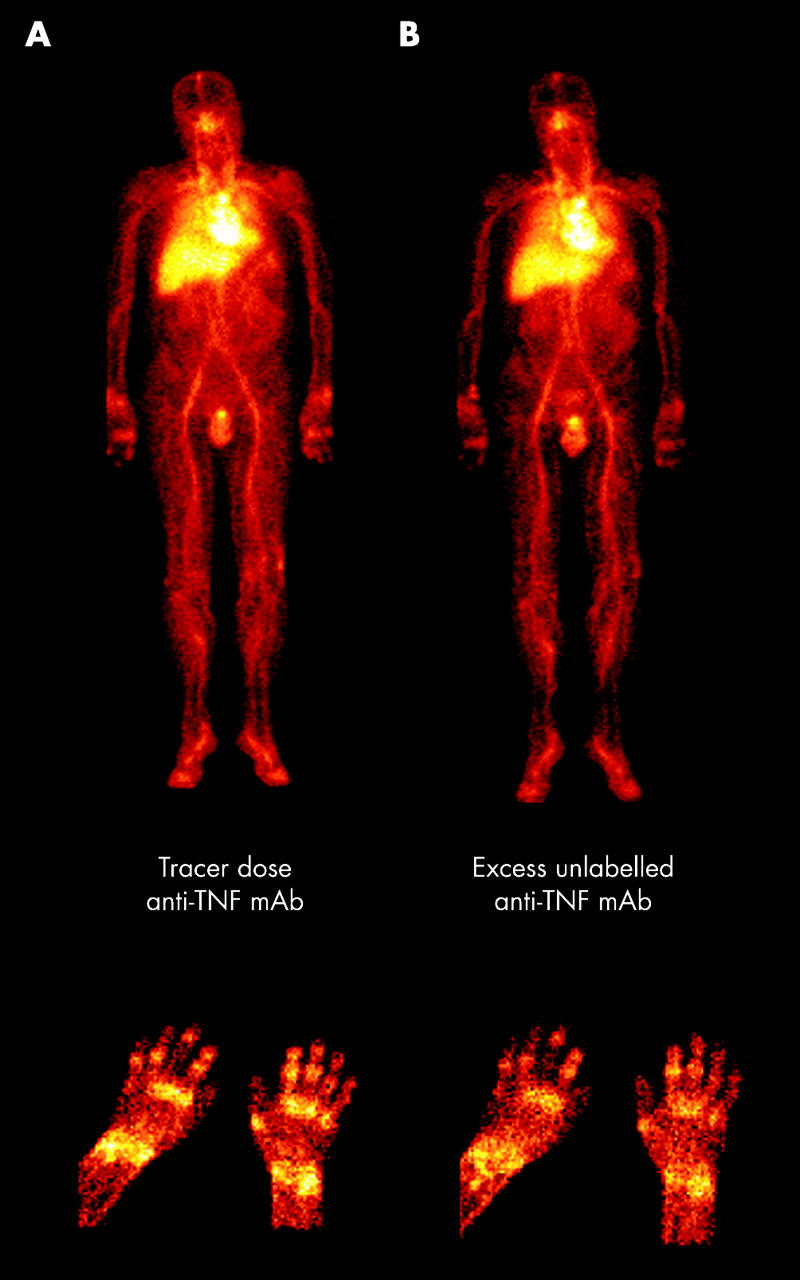
Scintigraphic images of the whole body and hands of a patient with active RA after injection of 99mTc human anti-TNF mAb. (A) The first imaging session. (B) Decreased uptake in joints after administration of an excess unlabelled anti-TNF mAb (hands detail), whereas the uptake in the reticuloendothelial organs remains unchanged (whole body).
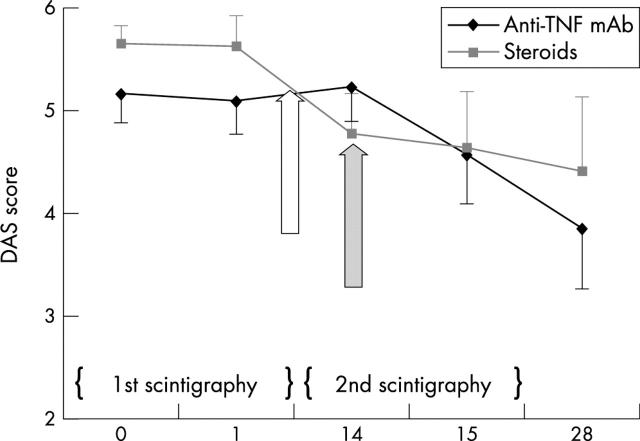
Figure 2.
Course of the DAS during the study. Patients with active RA underwent a first scintigraphy with a tracer dose of a fully human anti-TNF mAb radiolabelled with 99mTc. Two weeks thereafter, a subset of patients (n=5, rhomboids) received a therapeutic dose of the same antibody (grey arrow) before the second imaging session to assess the TNF targeting in the joints. Another patient subset (n=5, squares) was treated with systemic steroids two days before the second scintigraphy (white arrow).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams M. J., Juweid M., tenKate C. I., Schwartz D. A., Hauser M. M., Gaul F. E., Fuccello A. J., Rubin R. H., Strauss H. W., Fischman A. J. Technetium-99m-human polyclonal IgG radiolabeled via the hydrazino nicotinamide derivative for imaging focal sites of infection in rats. J Nucl Med. 1990 Dec;31(12):2022–2028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera P., Joosten L. A., den Broeder A. A., van de Putte L. B., van Riel P. L., van den Berg W. B. Effects of treatment with a fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody on the local and systemic homeostasis of interleukin 1 and TNFalpha in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Jul;60(7):660–669. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.7.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buijs W. C., Oyen W. J., Dams E. T., Boerman O. C., Siegel J. A., Claessens R. A., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Dynamic distribution and dosimetric evaluation of human non-specific immunoglobulin G labelled with 111In or 99Tcm. Nucl Med Commun. 1998 Aug;19(8):743–751. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199808000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. T., Jamar F., Keelan E. T., Peters A. M., Haskard D. O. Use of a radiolabeled monoclonal antibody against E-selectin for imaging of endothelial activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Aug;39(8):1371–1375. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. Q., Field M., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Localization of tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial tissues and at the cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1125–1132. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dams E. T., Oyen W. J., Boerman O. C., Claessens R. A., Wymenga A. B., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Technetium-99m labeled to human immunoglobulin G through the nicotinyl hydrazine derivative: a clinical study. J Nucl Med. 1998 Jan;39(1):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleuran B. W., Chu C. Q., Field M., Brennan F. M., Mitchell T., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Localization of tumor necrosis factor receptors in the synovial tissue and cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Implications for local actions of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Oct;35(10):1170–1178. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hnatowich D. J., Qu T., Chang F., Ley A. C., Ladner R. C., Rusckowski M. Labeling peptides with technetium-99m using a bifunctional chelator of a N-hydroxysuccinimide ester of mercaptoacetyltriglycine. J Nucl Med. 1998 Jan;39(1):56–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamar F., Chapman P. T., Manicourt D. H., Glass D. M., Haskard D. O., Peters A. M. A comparison between 111In-anti-E-selectin mAb and 99Tcm-labelled human non-specific immunoglobulin in radionuclide imaging of rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Radiol. 1997 May;70(833):473–481. doi: 10.1259/bjr.70.833.9227228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempeni J. Update on D2E7: a fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Nov;59 (Suppl 1):i44–i45. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyen W. J., Boerman O. C., van der Laken C. J., Claessens R. A., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. The uptake mechanisms of inflammation- and infection-localizing agents. Eur J Nucl Med. 1996 Apr;23(4):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF01247377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau R. Adalimumab (a fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis: the initial results of five trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Nov;61 (Suppl 2):ii70–ii73. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.suppl_2.ii70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santora L. C., Krull I. S., Grant K. Characterization of recombinant human monoclonal tissue necrosis factor-alpha antibody using cation-exchange HPLC and capillary isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1999 Nov 1;275(1):98–108. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens M. G., Oosterwijk E., Kranenborg M. H., Manders J. M., Debruyne F. M., Corstens F. H., Boerman O. C. In vivo and in vitro characterizations of three 99mTc-labeled monoclonal antibody G250 preparations. J Nucl Med. 1999 May;40(5):829–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfgren A. K., Gröndal L., Lindblad S., Khademi M., Johnell O., Klareskog L., Andersson U. Interindividual and intra-articular variation of proinflammatory cytokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: potential implications for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):439–447. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Laken C. J., Boerman O. C., Oyen W. J., Van de Ven M. T., Ven der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. The kinetics of radiolabelled interleukin-8 in infection and sterile inflammation. Nucl Med Commun. 1998 Mar;19(3):271–281. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199803000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Broeder A. A., Joosten L. A. B., Saxne T., Heinegård D., Fenner H., Miltenburg A. M. M., Frasa W. L. H., van Tits L. J., Buurman W. A., van Riel P. L. C. M. Long term anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: effect on radiological course and prognostic value of markers of cartilage turnover and endothelial activation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Apr;61(4):311–318. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., Theunisse L. A., Lubberts E. W., van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Nov;49(11):916–920. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.11.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laken C. J., Boerman O. C., Oyen W. J., van de Ven M. T., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Imaging of infection in rabbits with radioiodinated interleukin-1 (alpha and beta), its receptor antagonist and a chemotactic peptide: a comparative study. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998 Apr;25(4):347–352. doi: 10.1007/s002590050231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laken C. J., Boerman O. C., Oyen W. J., van de Ven M. T., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Scintigraphic detection of infection and inflammation: new developments with special emphasis on receptor interaction. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998 May;25(5):535–546. doi: 10.1007/s002590050255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]