Abstract
Background: Recent studies with infliximab indicate the therapeutic potential of tumour necrosis factor α blockade in spondyloarthropathy (SpA). Because defective host defence is implicated in the pathogenesis of SpA, the potential side effects of this treatment due to impact on the antimicrobial defence are a major concern.
Objective: To report systematically the adverse events seen in a large cohort of patients with SpA treated with infliximab, with special attention to bacterial infections.
Patients and methods: 107 patients with SpA were treated with infliximab for a total of 191.5 patient years. All serious and/or treatment related adverse events were reported.
Results: Eight severe infections occurred, including two reactivations of tuberculosis and three retropharyngeal abscesses, and six minor infections with clear bacterial focus. One patient developed a spinocellular carcinoma of the skin. No cases of demyelinating disease or lupus-like syndrome were seen. Two patients had an infusion reaction, which, however, did not relapse during the next infusion. Finally, three patients with ankylosing spondylitis developed palmoplantar pustulosis. All patients recovered completely with adequate treatment, and infliximab treatment had to be stopped in only five patients with severe infections.
Conclusions: Although the global safety of infliximab in SpA is good compared with previous reports in rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease, the occurrence of infections such as tuberculosis and retropharyngeal abscesses highlights the importance of careful screening and follow up. Focal nasopharyngeal infections and infection related symptoms, possibly induced by streptococci, occurred frequently, suggesting an impairment of specific host defence mechanisms in SpA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (90.5 KB).
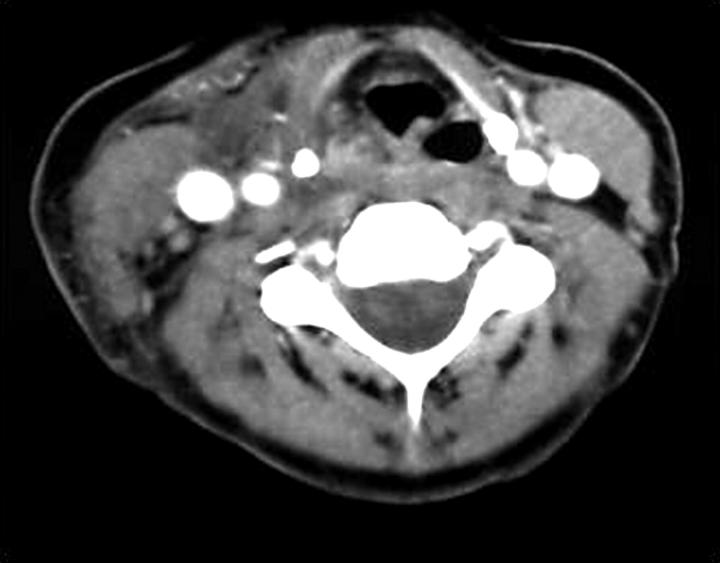
Figure 1.
CT scan of the neck in a patient with PsA developing a retropharyngeal abscess during infliximab treatment: flegmonal myositis of the left m. sternocleidomastoideus with an abscess in the retropharynx and anterior of the large blood vessels. The myositis extends to the m. sternohyoideus, m. sternothyroideus, and m. omohyoideus of the left and right neck region and even to the right m. sternocleidomastoideus.
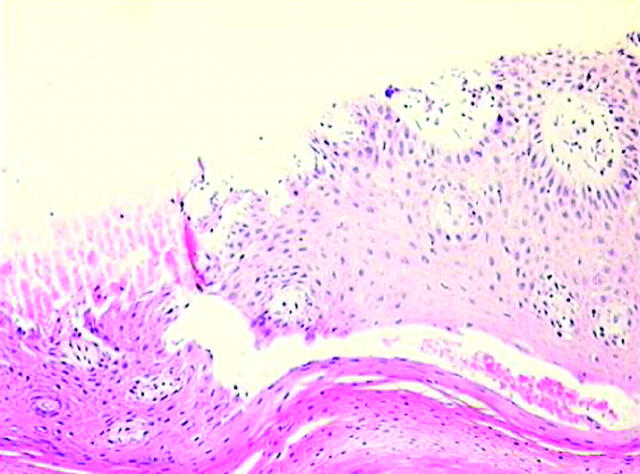
Figure 2.
Skin biopsy of a patient with AS who developed palmoplantar pustulosis, showing enlarged epidermis with ortho- and parakeratosis and perivascular infiltration by lymphocytes. There is no clear spongiosis. Haematoxylin-eosin staining, magnification x160.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baert Filip, Noman Maja, Vermeire Severine, Van Assche Gert, D' Haens Geert, Carbonez An, Rutgeerts Paul. Influence of immunogenicity on the long-term efficacy of infliximab in Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003 Feb 13;348(7):601–608. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten Dominique, Demetter Pieter, Cuvelier Claude A., Kruithof Elli, Van Damme Nancy, De Vos Martine, Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip. Macrophages expressing the scavenger receptor CD163: a link between immune alterations of the gut and synovial inflammation in spondyloarthropathy. J Pathol. 2002 Mar;196(3):343–350. doi: 10.1002/path.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Haibel H., Cornely D., Golder W., Gonzalez J., Reddig J., Thriene W., Sieper J., Braun J. Successful treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jun;43(6):1346–1352. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200006)43:6<1346::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles P. J., Smeenk R. J., De Jong J., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Assessment of antibodies to double-stranded DNA induced in rheumatoid arthritis patients following treatment with infliximab, a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha: findings in open-label and randomized placebo-controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Nov;43(11):2383–2390. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200011)43:11<2383::AID-ANR2>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Dittrich K. A. Anti-TNF therapy and malignancy - a critical review. Can J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jun;15(6):376–384. doi: 10.1155/2001/403102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derrico C. A., Goodrum K. J. Interleukin-12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha mediate innate production of gamma interferon by group B Streptococcus-treated splenocytes of severe combined immunodeficiency mice. Infect Immun. 1996 Apr;64(4):1314–1320. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.4.1314-1320.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Kalden J. R., Antoni C., Smolen J. S., Leeb B., Breedveld F. C., Macfarlane J. D., Bijl H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1105–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster J. C., Lagier R., Livio J. J. Propionibacterium acnes in a spondylitis with palmoplantar pustulosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 May;49(5):337–338. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.5.337-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer Stephen B., Feagan Brian G., Lichtenstein Gary R., Mayer Lloyd F., Schreiber S., Colombel Jean Frederic, Rachmilewitz Daniel, Wolf Douglas C., Olson Allan, Bao Weihang. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002 May 4;359(9317):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08512-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashigucci K., Yokoyama M., Niizeki H., Yamasaki Y., Akiya K., Tojo T., Urushibara T., Yamazaki Y., Shimizu H., Nishikawa T. Polymorphism in the tumor necrosis factor B gene is associated with Palmoplantar pustulosis. Tissue Antigens. 1999 Sep;54(3):288–290. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.1999.540312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane J., Gershon S., Wise R. P., Mirabile-Levens E., Kasznica J., Schwieterman W. D., Siegel J. N., Braun M. M. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001 Oct 11;345(15):1098–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E., Van den Bosch F., Baeten D., Herssens A., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Repeated infusions of infliximab, a chimeric anti-TNFalpha monoclonal antibody, in patients with active spondyloarthropathy: one year follow up. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Mar;61(3):207–212. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Jong-Hoon, Slifman Nancy R., Gershon Sharon K., Edwards Evelyne T., Schwieterman William D., Siegel Jeffrey N., Wise Robert P., Brown S. Lori, Udall John N., Jr, Braun M. Miles. Life-threatening histoplasmosis complicating immunotherapy with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists infliximab and etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Oct;46(10):2565–2570. doi: 10.1002/art.10583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., van der Heijde D. M., St Clair E. W., Furst D. E., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Weisman M., Emery P., Feldmann M. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1594–1602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R., St Clair E. W., Breedveld F., Furst D., Kalden J., Weisman M., Smolen J., Emery P., Harriman G., Feldmann M. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)05246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan N., Edwards E. T., Cupps T. R., Oliverio P. J., Sandberg G., Crayton H., Richert J. R., Siegel J. N. Demyelination occurring during anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy for inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Dec;44(12):2862–2869. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200112)44:12<2862::aid-art474>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakata H., Harabuchi Y., Kukuminato Y., Yokoyama Y., Kataura A. Cytokine production by tonsillar lymphocytes stimulated with alpha-streptococci in patients with pustulosis palmaris et plantaris. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1996;523:201–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Kawaguchi M., Ishizawa S., Kaji T., Kitagawa K., Koizumi F. Histological features of palatine tonsils in pustulosis palmaris et plantaris: a morphometric study. Pathol Int. 1994 Mar;44(3):186–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1994.tb02591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeverbeke T., Lequen L., de Barbeyrac B., Labbé L., Bébéar C. M., Morrier Y., Bannwarth B., Bébéar C., Dehais J. Propionibacterium acnes isolated from synovial tissue and fluid in a patient with oligoarthritis associated with acne and pustulosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Oct;41(10):1889–1893. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199810)41:10<1889::AID-ART23>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seta N., Granfors K., Sahly H., Kuipers J. G., Song Y. W., Baeten D., Veys E. M., Maksymowych W., Märker-Hermann E., Gu J. Expression of host defense scavenger receptors in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Apr;44(4):931–939. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200104)44:4<931::AID-ANR150>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Hanauer S. B., van Deventer S. J., Mayer L., Present D. H., Braakman T., DeWoody K. L., Schaible T. F., Rutgeerts P. J. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor alpha for Crohn's disease. Crohn's Disease cA2 Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997 Oct 9;337(15):1029–1035. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199710093371502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teranishi Y., Mizutani H., Murata M., Shimizu M., Matsushima K. Increased spontaneous production of IL-8 in peripheral blood monocytes from the psoriatic patient: relation to focal infection and response to treatments. J Dermatol Sci. 1995 Jul;10(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0923-1811(95)00384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bosch Filip, Kruithof Elli, Baeten Dominique, Herssens Annemie, de Keyser Filip, Mielants Herman, Veys Eric M. Randomized double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) versus placebo in active spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):755–765. doi: 10.1002/art.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Baeten D., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Katayama I., Nishioka K. Restricted usage of the T-cell receptor V beta repertoire in tonsillitis in association with palmoplantar pustulosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998 May;78(3):161–163. doi: 10.1080/000155598441431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka N., Yamamoto Y., Kuki K. Engraftment of tonsillar mononuclear cells in human skin/SCID mouse chimera--validation of a novel xenogeneic transplantation model for autoimmune diseases. Microbiol Immunol. 2001;45(7):507–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2001.tb02651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dullemen H. M., van Deventer S. J., Hommes D. W., Bijl H. A., Jansen J., Tytgat G. N., Woody J. Treatment of Crohn's disease with anti-tumor necrosis factor chimeric monoclonal antibody (cA2). Gastroenterology. 1995 Jul;109(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]