Abstract
Objectives: To determine the frequency of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) in a group of patients with a diversity of rheumatic diseases.
Methods: 249 consecutive sera from an arthritis clinic sent for rheumatology testing were selected for testing with the anti-CCP2 assays and for the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF). Patient charts were reviewed for demographic information, clinical diagnosis, radiographic information, and other laboratory data.
Results: The sensitivity and specificity of anti-CCP reactivity for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were 66.0% and 90.4%, respectively. This compared with the sensitivity and specificity of RF for RA at 71.6% and 80.3%. Furthermore, 10/29 (34%) RF- patients with RA demonstrated reactivity to CCP. The presence of either anti-CCP or RF increased testing sensitivity for diagnosis of RA to 81.4%; the presence of both RF and anti-CCP demonstrated a testing specificity similar to that of anti-CCP reactivity alone for the diagnosis of RA (91.1%).
Conclusions: The detection of anti-CCP is useful for the diagnosis of RA, in fact even more so than RF, because of its higher specificity.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (120.5 KB).
Figure 1.
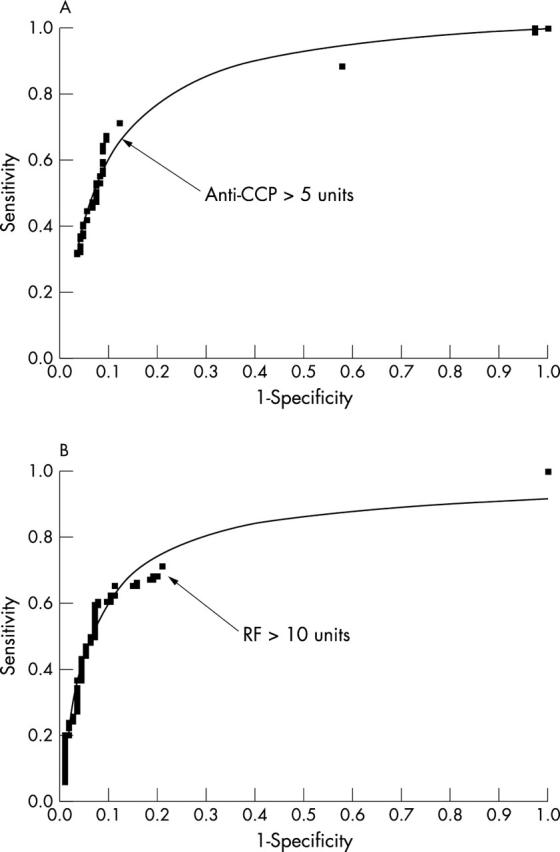
ROC curves for anti-CCP (A) and RF (B) assays. Individual datapoints are represented as small squares. A best fit curve was generated by non-linear regression calculation. Arrows mark the cut off values used for this study.
Figure 2.
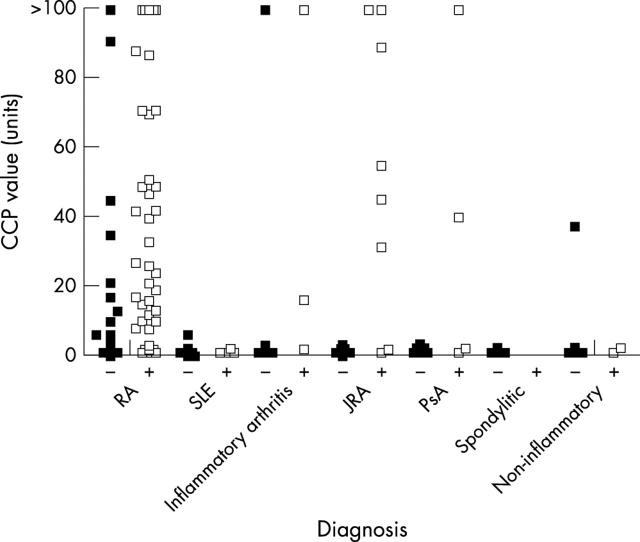
CCP reactivity in rheumatic disease subsets. Shown are the levels of anti-CCP reactivity in sera from patients with labelled rheumatic diagnoses. Closed squares RF-; open squares RF+.
Figure 3.
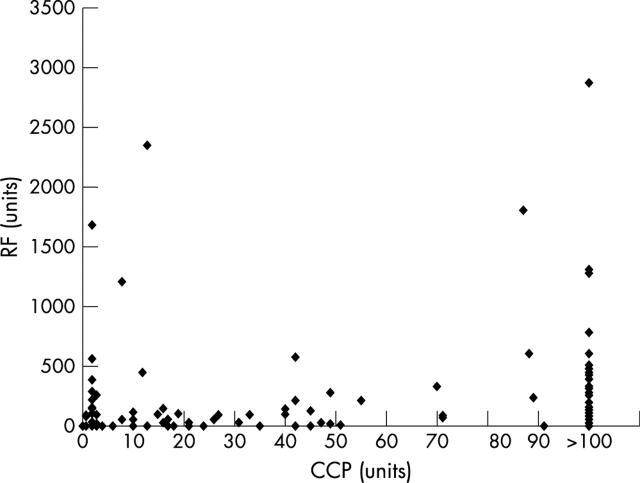
RF v CCP values. The values in units of RF and CCP activity in 214 rheumatic disease patients are shown. Correlation coefficient (R)=0.34.
Figure 4.
Correlation of anti-CCP activity and radiographic joint destruction. The percentage of patients with anti-CCP reactivity and RF relative to the presence of erosions in patients with available radiographs (n=129) is shown.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bas S., Perneger T. V., Kunzle E., Vischer T. L. Comparative study of different enzyme immunoassays for measurement of IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Jun;61(6):505–510. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bas S., Perneger T. V., Mikhnevitch E., Seitz M., Tiercy J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Guerne P. A. Association of rheumatoid factors and anti-filaggrin antibodies with severity of erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Oct;39(10):1082–1088. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.10.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bas S., Perneger T. V., Seitz M., Tiercy J-M, Roux-Lombard P., Guerne P. A. Diagnostic tests for rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, anti-keratin antibodies and IgM rheumatoid factors. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002 Jul;41(7):809–814. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.7.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläss S., Specker C., Lakomek H. J., Schneider E. M., Schwochau M. Novel 68 kDa autoantigen detected by rheumatoid arthritis specific antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 May;54(5):355–360. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.5.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P., Harrison B., Barrett E., Chakravarty K., Scott D., Silman A., Symmons D. A simple algorithm to predict the development of radiological erosions in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 1996 Aug 24;313(7055):471–476. doi: 10.1136/bmj.313.7055.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigall V. M., Bodman-Smith M. D., Fife M. S., Canas B., Myers L. K., Wooley P., Soh C., Staines N. A., Pappin D. J., Berlo S. E. The human endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone BiP is an autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis and prevents the induction of experimental arthritis. J Immunol. 2001 Feb 1;166(3):1492–1498. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.3.1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Després N., Boire G., Lopez-Longo F. J., Ménard H. A. The Sa system: a novel antigen-antibody system specific for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1994 Jun;21(6):1027–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassfeld W., Steiner G., Hartmuth K., Kolarz G., Scherak O., Graninger W., Thumb N., Smolen J. S. Demonstration of a new antinuclear antibody (anti-RA33) that is highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1515–1520. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassahn Daniela, Kolb Cornelia, Solomon Samuel, Bochtler Petra, Illges Harald. Few human autoimmune sera detect GPI. Nat Immunol. 2002 May;3(5):411–413. doi: 10.1038/ni0502-411b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroot E. J., de Jong B. A., van Leeuwen M. A., Swinkels H., van den Hoogen F. H., van't Hof M., van de Putte L. B., van Rijswijk M. H., van Venrooij W. J., van Riel P. L. The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1831–1835. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200008)43:8<1831::AID-ANR19>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M., Franklin E. C., Elias K., McCluskey R. T., Cooper N. Cryoglobulinemia--a clinical and laboratory study. II. Cryoglobulins with rheumatoid factor activity. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):837–856. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz C. E. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin Nucl Med. 1978 Oct;8(4):283–298. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(78)80014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen W. M., Dodge H. J., Duff I. F., Kato H. Estimates of the prevalence of rheumatic diseases in the population of Tecumseh, Michigan, 1959-60. J Chronic Dis. 1967 Jun;20(6):351–369. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(67)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möttönen Timo, Hannonen Pekka, Korpela Markku, Nissilä Martti, Kautiainen Hannu, Ilonen Jorma, Laasonen Leena, Kaipiainen-Seppänen Oili, Franzen Per, Helve Tapani. Delay to institution of therapy and induction of remission using single-drug or combination-disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Apr;46(4):894–898. doi: 10.1002/art.10135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIENHUIS R. L., MANDEMA E. A NEW SERUM FACTOR IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS; THE ANTIPERINUCLEAR FACTOR. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Jul;23:302–305. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.4.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell James R. Treating rheumatoid arthritis early: a window of opportunity? Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):283–285. doi: 10.1002/art.10092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraux Alain, Berthelot Jean M., Chalès Gérard, Le Henaff Catherine, Mary Jean Y., Thorel Jean B., Hoang Sylvie, Dueymes Maryvonne, Allain Jérôme, Devauchelle Valerie. Value of laboratory tests in early prediction of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Apr 15;47(2):155–165. doi: 10.1002/art.10241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M., Burton D. R., Ditzel H. J. Autoantibodies to GPI in rheumatoid arthritis: linkage between an animal model and human disease. Nat Immunol. 2001 Aug;2(8):746–753. doi: 10.1038/90696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens G. A., Visser H., de Jong B. A., van den Hoogen F. H., Hazes J. M., Breedveld F. C., van Venrooij W. J. The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):155–163. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<155::AID-ANR20>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens G. A., de Jong B. A., van den Hoogen F. H., van de Putte L. B., van Venrooij W. J. Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1998 Jan 1;101(1):273–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert David, Schmidt Monika, Zaiss Dietmar, Jungblut Peter R., Kamradt Thomas. Autoantibodies to GPI and creatine kinase in RA. Nat Immunol. 2002 May;3(5):411–413. doi: 10.1038/ni0502-411a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L. Prognostic factors in early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Jun;39 (Suppl 1):24–29. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rheumatology.a031490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmerling R. H., Delbanco T. L. The rheumatoid factor: an analysis of clinical utility. Am J Med. 1991 Nov;91(5):528–534. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser Henk, le Cessie Saskia, Vos Koen, Breedveld Ferdinand C., Hazes Johanna M. W. How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: a prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):357–365. doi: 10.1002/art.10117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Schur P. H. Rheumatoid factor detection by nephelometry. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jun;23(6):777–779. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. J., Mallya R. K., Leslie R. D., Clark C. J., Hamblin T. J. Anti-keratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1979 Jul 14;2(6182):97–99. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6182.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boekel Martinus A. M., Vossenaar Erik R., van den Hoogen Frank H. J., van Venrooij Walther J. Autoantibody systems in rheumatoid arthritis: specificity, sensitivity and diagnostic value. Arthritis Res. 2001 Nov 6;4(2):87–93. doi: 10.1186/ar395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Vandenbroucke J. P., Breedveld F. C. Factors predicting outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: results of a followup study. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1288–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]