Abstract
Methods: Isolated synovial cells, treated or not with TGFß1, were cultured in the presence or absence of anti-Fas IgM, proteasome inhibitor Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-aldehyde (LLL-CHO), etoposide, or C2-ceramide. After cultivation, apoptosis of synovial cells was examined by the presence of hypodiploid DNA+ cells, the presence of terminal deoxy (d)-UTP nick end labelling+ cells (TUNEL+ cells), activation of caspases, and disruption of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨm).
Results: Activation of caspase-9 and ΔΨm was found in anti-Fas IgM treated synovial cells. The increment of both hypodiploid DNA+ cells and TUNEL+ cells accompanied by the activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 was also determined in anti-Fas IgM treated synovial cells. These hallmarks for apoptosis induced by anti-Fas IgM were significantly suppressed in TGFß1 treated synovial cells. LLL-CHO, etoposide, and C2-ceramide also caused ΔΨm, the increment of both hypodiploid DNA+ cells and TUNEL+ cells, and the activation of both Leu-Glu-His-Asp ase (LEHDase; caspase-9 like activity) and Asp-Glu-Val-Asp ase (DEVDase; caspase-3 like activity) in synovial cells. As determined in anti-Fas IgM treatment, TGFß1 significantly reduced apoptotic cell death of synovial cells induced by the above chemicals.
Conclusions: The protective effect of TGFß1 for mitochondrial homoeostasis may be important in the anti-apoptogenic function of TGFß1 for synovial cells.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (228.0 KB).
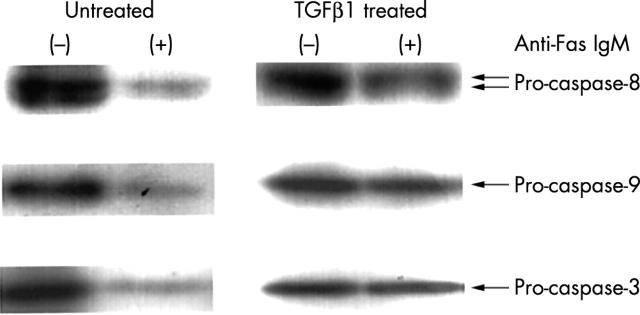
Figure 1 .
Western blot analysis for the activation of caspase-3/-8/-9 in synovial cells induced by anti-Fas IgM, which is inhibited by TGFß1. Synovial cells isolated from the rheumatoid synovial tissues were cultured with or without TGFß1 for 48 hours, washed, and further incubated with control mouse IgM or anti-Fas IgM for 12 hours. After cultivation, the expression of procaspase-3/-8/-9 in synovial cells was examined by western blotting as described in the text. Note that the disappearance of procaspase-3/-8/-9 in anti-Fas IgM treated synovial cells, which indicates the activation of each caspase, was significantly inhibited by TGFß1 treatment. Results are representative data from six determinations. anti-Fas IgM (-); addition of control mouse IgM.