Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the genetic influence of PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms of oestrogen receptor α (ORα) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in Korea.
Methods: Genomic DNA from 268 female controls and 137 female SLE patients (41 childhood onset and 96 adult onset) were analysed using PvuII and XbaI restriction fragment length polymorphism. Comparison of the frequencies of alleles and genotypes was made in control and patient groups and in childhood onset and adult onset SLE subgroups.
Results: Although the Pp genotype occurred more often in SLE patients than in controls (pc = 0.017), ORα genotype distributions of adult onset SLE did not differ significantly from controls. The PP, Pp, and xx genotypes occurred less often in childhood onset SLE (pc = 0.0045, 0.0498, and 0.0255, respectively) than in controls. Additionally, the PP genotype was less common in childhood onset than in adult onset SLE (pc = 0.016). SLE patients with the PP genotypes were older at disease onset than those with the other genotypes (p = 0.001). Patients with the Xx genotype had an earlier onset of SLE than those with the xx genotype (p = 0.025). The frequency of the combined ppXx genotype was greater in childhood onset SLE than in controls (pc = 0.0009) or adult onset SLE (pc = 0.027). The same trend was supported by subgroup analyses according to age at menarche and logistic multivariate analyses.
Conclusions: ORα polymorphisms are significantly associated with the age at disease onset in Koreans with SLE.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (109.9 KB).
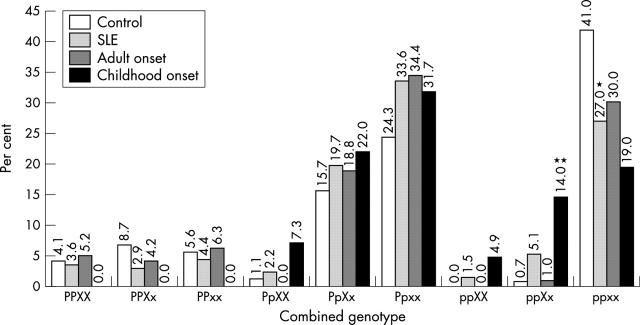
Figure 1.
Combined genotype of oestrogen receptor α polymorphism in controls and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). For the combination of the PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms, all combinations of genotypes were observed in SLE patients and the three major combined genotypes: ppxx, Ppxx, and PpXx. SLE patients were less likely to have the ppxx genotype than controls (*pc = 0.032, OR = 0.52 (95% CI, 0.32 to 0.83)). The frequency of the ppXx genotype was significantly higher in the childhood onset SLE subgroup than in the control group or the adult onset subgroup (**pc = 0.0009, OR = 22.80 (3.94 to 170.36) v controls; pc = 0.027, OR = 16.29 (1.83 to 371.63) v adult onset SLE). CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An Ping, Nelson George W., Wang Lihua, Donfield Sharyne, Goedert James J., Phair John, Vlahov David, Buchbinder Susan, Farrar William L., Modi William. Modulating influence on HIV/AIDS by interacting RANTES gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jul 11;99(15):10002–10007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.142313799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen T. I., Heimdal K. R., Skrede M., Tveit K., Berg K., Børresen A. L. Oestrogen receptor (ESR) polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility. Hum Genet. 1994 Dec;94(6):665–670. doi: 10.1007/BF00206961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsten H., Tarkowski A. Histocompatibility complex gene products and exposure to oestrogen: two independent disease accelerating factors in murine lupus. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Oct;38(4):341–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M., Lubahn D. B., Hoffman R. W. DNA microsatellite markers for estrogen receptor-beta are not associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001 Apr;28(4):924–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Annabelle, Fontana Pierre, Bachelot-Loza Christilla, Reny Jean-Luc, Biéche Ivan, Desvard Florence, Aiach Martine, Gaussem Pascale. An intronic polymorphism in the PAR-1 gene is associated with platelet receptor density and the response to SFLLRN. Blood. 2002 Oct 24;101(5):1833–1840. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-07-2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., MacLaughlin S., Marvin R. D., Abdou N. I. Estrogen decreases in vitro apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from women with normal menstrual cycles and decreases TNF-alpha production in SLE but not in normal cultures. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997 Mar;82(3):258–262. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.4300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Font J., Cervera R., Espinosa G., Pallarés L., Ramos-Casals M., Jiménez S., García-Carrasco M., Seisdedos L., Ingelmo M. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in childhood: analysis of clinical and immunological findings in 34 patients and comparison with SLE characteristics in adults. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Aug;57(8):456–459. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.8.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa F., Lyons M. B., Lee L. A., Coulter S. N., Norris D. A. Estradiol enhances binding to cultured human keratinocytes of antibodies specific for SS-A/Ro and SS-B/La. Another possible mechanism for estradiol influence of lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1480–1488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington David M., Howard Timothy D., Hawkins Gregory A., Reboussin David M., Xu Jianfeng, Zheng Siqun L., Brosnihan K. Bridget, Meyers Deborah A., Bleecker Eugene R. Estrogen-receptor polymorphisms and effects of estrogen replacement on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in women with coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2002 Mar 28;346(13):967–974. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg M. C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1725–1725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda N., Tsuchida T., Tamaki K. Estrogen enhancement of anti-double-stranded DNA antibody and immunoglobulin G production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Feb;42(2):328–337. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<328::AID-ANR16>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurabayashi T., Tomita M., Matsushita H., Yahata T., Honda A., Takakuwa K., Tanaka K. Association of vitamin D and estrogen receptor gene polymorphism with the effect of hormone replacement therapy on bone mineral density in Japanese women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 May;180(5):1115–1120. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70603-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie C. C., Stam L. F. The effect of an intronic polymorphism on alcohol dehydrogenase expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1994 Oct;138(2):379–385. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., McCurdy D. K., Bernstein B. H., King K. K., Hanson V. Systemic lupus erythematosus in the first decade of life. Pediatrics. 1989 Feb;83(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Zhi-Hong, Cheng Zhao-Hong, Gong Ru-Jun, Liu Hao, Liu Dong, Li Lei-Shi. Sex differences in estrogen receptor gene polymorphism and its association with lupus nephritis in Chinese. Nephron. 2002 Feb;90(2):174–180. doi: 10.1159/000049039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger K., Repp R., Jansen M., Geisselbrecht M., Wassmuth R., Westerdaal N. A. C., Pfahlberg A., Manger B., Kalden J. R., van de Winkel J. G. J. Fcgamma receptor IIa, IIIa, and IIIb polymorphisms in German patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: association with clinical symptoms. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Sep;61(9):786–792. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.9.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reveille J. D., Schrohenloher R. E., Acton R. T., Barger B. O. DNA analysis of HLA-DR and DQ genes in American blacks with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Oct;32(10):1243–1251. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider V., Jones S., Evans M., Bassiri H., Afsar Z., Abdou N. I. Estrogen increases CD40 ligand expression in T cells from women with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2001 Dec;28(12):2644–2649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmén T., Heikkinen A. M., Mahonen A., Kröger H., Komulainen M., Saarikoski S., Honkanen R., Mäenpä P. H. Early postmenopausal bone loss is associated with PvuII estrogen receptor gene polymorphism in Finnish women: effect of hormone replacement therapy. J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Feb;15(2):315–321. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Guerrero J., Karlson E. W., Liang M. H., Hunter D. J., Speizer F. E., Colditz G. A. Past use of oral contraceptives and the risk of developing systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 May;40(5):804–808. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandborg C. I. Childhood systemic lupus erythematosus and neonatal lupus syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1998 Sep;10(5):481–487. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199809000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrou I., Zois C., Ioannidis J. P. A., Tsatsoulis A. Association of polymorphisms of the oestrogen receptor alpha gene with the age of menarche. Hum Reprod. 2002 Apr;17(4):1101–1105. doi: 10.1093/humrep/17.4.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Guerrero J., Liang M. H., Karlson E. W., Hunter D. J., Colditz G. A. Postmenopausal estrogen therapy and the risk for developing systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Mar 15;122(6):430–433. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-6-199503150-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond T. S., Murante F. G., Staples J. E., Silverstone A. E., Korach K. S., Gasiewicz T. A. Role of estrogen receptor alpha in hematopoietic stem cell development and B lymphocyte maturation in the male mouse. Endocrinology. 2000 Jul;141(7):2309–2318. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.7.7560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker L. B., Menon S., Schaller J. G., Isenberg D. A. Adult- and childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of onset, clinical features, serology, and outcome. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;34(9):866–872. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.9.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiyama T., Ueyama H., Inoue K., Nishioka J., Ohkubo I., Hukuda S. Estrogen receptor gene polymorphism and generalized osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1998 Jan;25(1):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiderpass E., Persson I., Melhus H., Wedrén S., Kindmark A., Baron J. A. Estrogen receptor alpha gene polymorphisms and endometrial cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 2000 Apr;21(4):623–627. doi: 10.1093/carcin/21.4.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Elenkov I. J. Hormonal regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-12 and interleukin-10 production by activated macrophages. A disease-modifying mechanism in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Jun 22;876:14–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]