Abstract
Background: Ultrasonography allows assessment of soft tissue structures and has become a valued tool for diagnosing synovitis.
Objective: To assess the learning curve for ultrasonography in evaluating synovitis of the small joints in rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: Metacarpophalangeal (MCP), metatarsophalangeal (MTP), and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints were evaluated using ultrasonography (Esaote AU 5 Epi, linear probe 10–13 MHz) by four rheumatologists, the first being experienced (senior), the others having no (fellows 1 and 2) or little (fellow 3) experience in ultrasonography. For each fellow, the learning curve was divided into blocks. In each block the fellow examined five consecutive patients with the senior; then, blinded to the senior's results, two further patients alone (seven patients examined per block). For each evaluation, the MCP, PIP, and MTP joints were individually tagged as having synovitis or not. The ultrasonography results were compared between fellow and senior for the two last patients of each block, using proportions of agreement and κ statistics.
Results: 70 patients were evaluated (seven practice patients, followed by nine blocks). For fellows 1 and 2, the proportions of agreement were respectively 42% and 47% (κ = 0 and 0) at the first evaluation, and rose progressively to 82% and 82% (κ = 0.63 and 0.62) at the ninth evaluation. For fellow 3, initially good results were followed by decreased accuracy.
Conclusions: Detecting synovitis of the MCP, PIP, and MTP joints using ultrasonography can be done accurately by rheumatologists initially not experienced in this technique. At least 70 examinations were necessary to develop competence.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (100.0 KB).
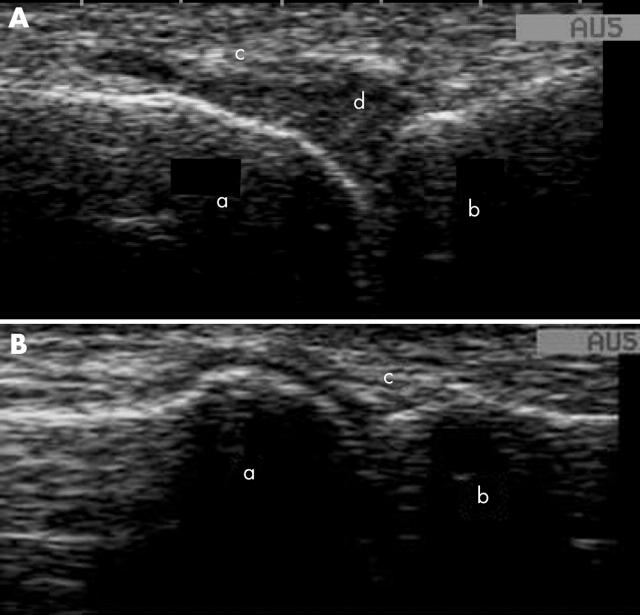
Figure 1.
Ultrasonographic picture of second metatarsophalangeal joint with synovitis (panel A) and without synovitis (panel B). a, metatarsal head; b, base of phalanges; c, joint capsule (side view); d, synovitis; e, joint effusion.
Figure 2.
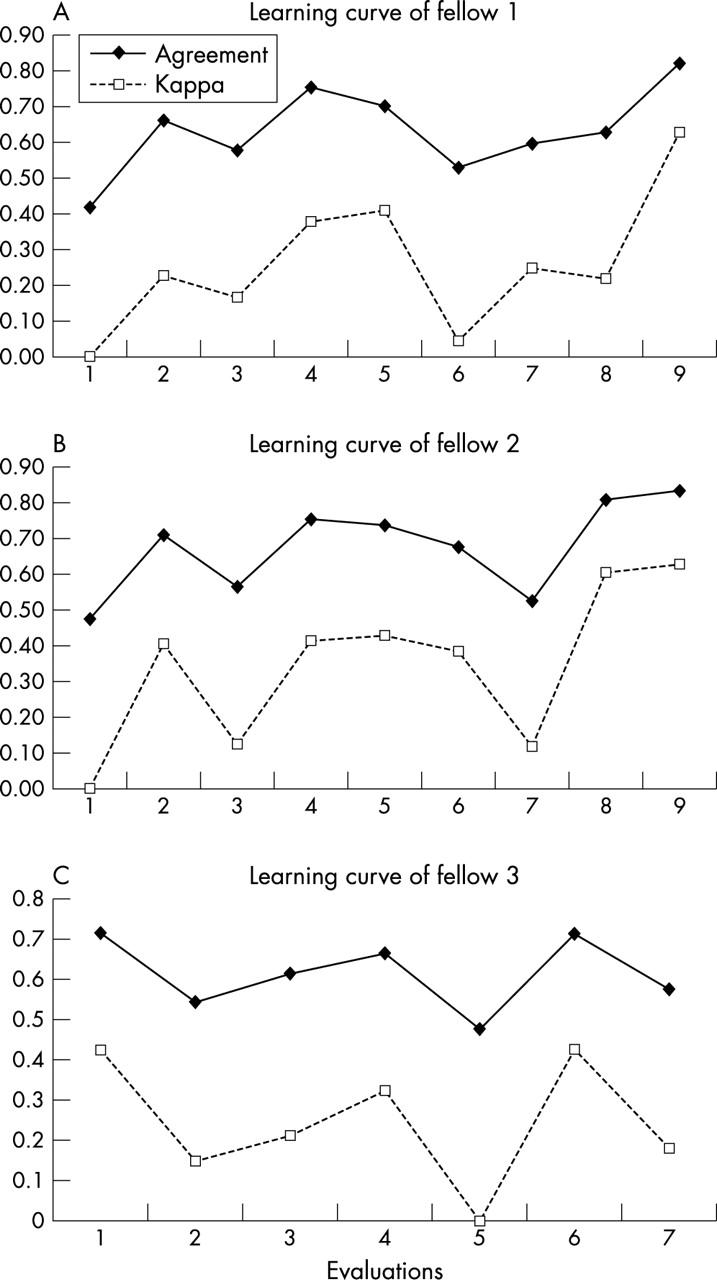
Non-experienced rheumatologists' learning curve for detecting synovitis of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP), metatarsophalangeal (MTP), and proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints using ultrasonography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proportions of agreement and κ coefficients from the first to the ninth evaluation for fellows 1 (A) and 2 (B), and from the first to the seventh evaluation for fellow 3 (C).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus M., Kamradt T., Sandrock D., Loreck D., Fritz J., Wolf K. J., Raber H., Hamm B., Burmester G. R., Bollow M. Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1232–1245. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1232::AID-ANR21>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaghan P. G., McGonagle D., Wakefield R., Emery P. New approaches to imaging of early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999 Nov-Dec;17(6 Suppl 18):S37–S42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Breedveld F. C., Dougados M., Kalden J. R., Schiff M. H., Smolen J. S. Early referral recommendation for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis: evidence based development of a clinical guide. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Apr;61(4):290–297. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.4.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goupille P., Roulot B., Akoka S., Avimadje A. M., Garaud P., Naccache L., Le Pape A., Valat J. P. Magnetic resonance imaging: a valuable method for the detection of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001 Jan;28(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi W., Lamanna G., Farina A., Cervini C. Synovitis of small joints: sonographic guided diagnostic and therapeutic approach. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Oct;58(10):595–597. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.10.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozycki G. S., Ballard R. B., Feliciano D. V., Schmidt J. A., Pennington S. D. Surgeon-performed ultrasound for the assessment of truncal injuries: lessons learned from 1540 patients. Ann Surg. 1998 Oct;228(4):557–567. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199810000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röthlin M. A., Näf R., Amgwerd M., Candinas D., Frick T., Trentz O. Ultrasound in blunt abdominal and thoracic trauma. J Trauma. 1993 Apr;34(4):488–495. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199304000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraux A., Berthelot J. M., Chalès G., Le Henaff C., Thorel J. B., Hoang S., Valls I., Devauchelle V., Martin A., Baron D. Ability of the American College of Rheumatology 1987 criteria to predict rheumatoid arthritis in patients with early arthritis and classification of these patients two years later. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Nov;44(11):2485–2491. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2485::aid-art428>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speed C. A., Bearcroft P. W. P. Training in musculoskeletal sonography: report from the first BSR course. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002 Mar;41(3):346–346. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.3.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M., Bergin D., Whelan B., Maher M., Murray J., McCarthy C. Power Doppler ultrasound assessment of rheumatoid hand synovitis. J Rheumatol. 2001 Sep;28(9):1979–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]