Abstract
Methods: Duodenal biopsy samples from 13 patients with RA and 15 control subjects were studied. The mRNA expression of CCR4, CCR5, IL2, IL10, IFNγ, TNFα, and TGFß in intestinal biopsy samples was demonstrated by real time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction.
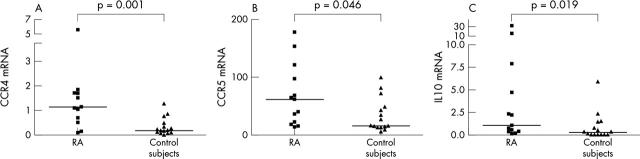
Results: The mRNA expression of CCR4, CCR5, and IL10 in intestinal biopsy samples was increased in patients with RA in comparison with control subjects (p = 0.001, p = 0.046, p = 0.019). No difference in the expression levels of IL2, IFNγ, TNFα, or TGFß was seen between patients with RA and controls.
Conclusions: The increased intestinal mRNA expression of IL10, CCR5, and CCR4 suggests that gut associated immune cells are activated in patients with RA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (73.2 KB).
Figure 1.
Chemokine receptor CCR4 (A) and CCR5 (B) and cytokine IL10 (C) specific mRNA detected by quantitative real time RT-PCR in duodenal biopsy samples from patients with RA and from healthy controls. Individual results are shown as relative amount (2–ΔΔCt) of target gene compared with calibrator, both normalised to an endogenous reference (18S). The median values are indicated by horizontal lines and p values of the Mann-Whitney test are shown.