Abstract
Methods: Anti-PS/PT IgG Ab was examined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 112 patients with SSc. Thirty three healthy volunteers and 30 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) were also investigated as controls.
Results: Anti-PS/PT Ab was detected in 18/112 (16%) patients with SSc and 10/30 (33%) patients with SLE, whereas it was not detected in any normal controls. Anti-PS/PT Ab was more frequently detected in patients with SSc with peripheral ischaemia and lung disease (pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension) than in patients with SSc without the Ab. However, anti-PS/PT Ab was not associated with the severity of skin sclerosis. Importantly, two patients were negative for both lupus anticoagulant and Ab against cardiolipin ß2-glycoprotein I complex among six anti-PS/PT Ab positive patients with SSc and a thromboembolic episode.
Conclusions: Anti-PS/PT Ab is associated with thromboembolism, peripheral ischaemia, and lung involvement in some patients with SSc. Examination of this Ab may be useful to recognise the risk of thromboembolism in patients with SSc.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (73.6 KB).
Figure 1.
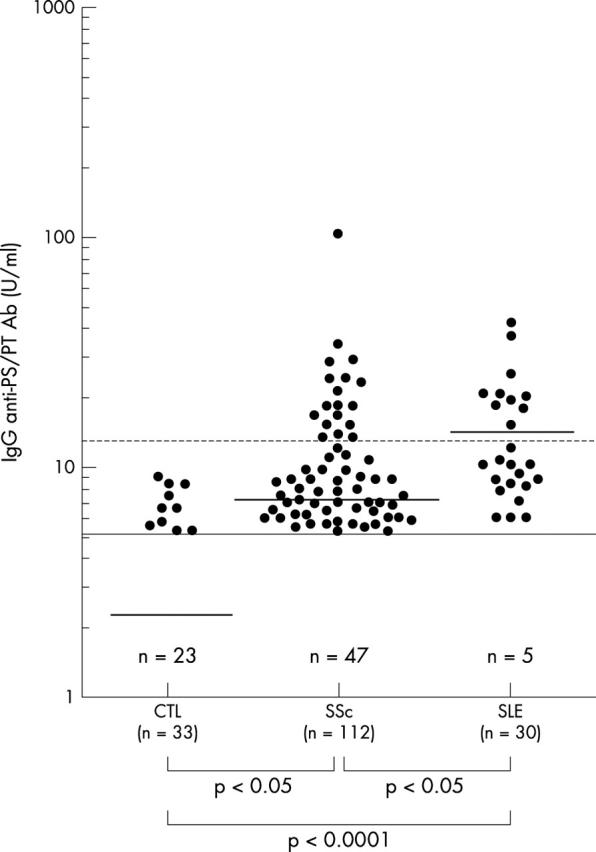
Abs against PS/PT in serum samples from patients with SSc, SLE, and normal controls (CTL). Anti-PS/PT Ab levels were determined by ELISA. The horizontal line shows the detection limit (5 U/ml) and the number below the line indicates the number of patients with undetectable levels. The broken line represents the cut off value (12 U/ml). The short bar indicates the mean value in each group.


