Abstract
Background: Autoantibodies such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anticitrullinated protein antibodies can be detected in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) sera.
Objective: To determine the diagnostic values of RF, anticitrullinated protein antibodies, and the shared epitope (SE), and their associations with radiological progression rates and extra-articular manifestations.
Methods: Population 1 consisted of sera from 315 patients, consecutively sent for detection of anticitrullinated protein antibodies, of which 264 were used to determine the sensitivity and specificity of RF and of antibodies against three synthetic citrullinated peptides: peptide A (pepA), peptide B (pepB), and CCP2. Population 2 consisted of sera from 180 longstanding RA patients and was used to determine associations of RA associated antibodies and the SE with radiological progression rates and extra-articular manifestations. Antibodies to pepA and pepB were detected by line immunoassay, and antibodies to CCP2 by ELISA. HLA Class II typing was performed by LiPA.
Results: In population 1, we defined adapted cut offs corresponding to a specificity of ⩾98.5%. This yielded the following sensitivities: RF 12.8%; anti-pepA antibodies 63.6%; anti-pepB antibodies 54.2%; and anti-CCP2 antibodies 73.7%. In population 2, significant differences in radiological progression rates were found between positive and negative patients for different RA antibodies and the SE. RF, but not anticitrullinated protein antibodies or the SE, were more frequent in patients with extra-articular manifestations.
Conclusion: A valid comparison of RA associated antibodies shows superior sensitivity of the anticitrullinated protein antibodies compared with RF. The presence of RA associated antibodies and the SE are indicative for poorer radiological outcome, and presence of extra-articular manifestations is associated with RF but not with anticitrullinated protein antibodies.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (132.6 KB).
Figure 1.
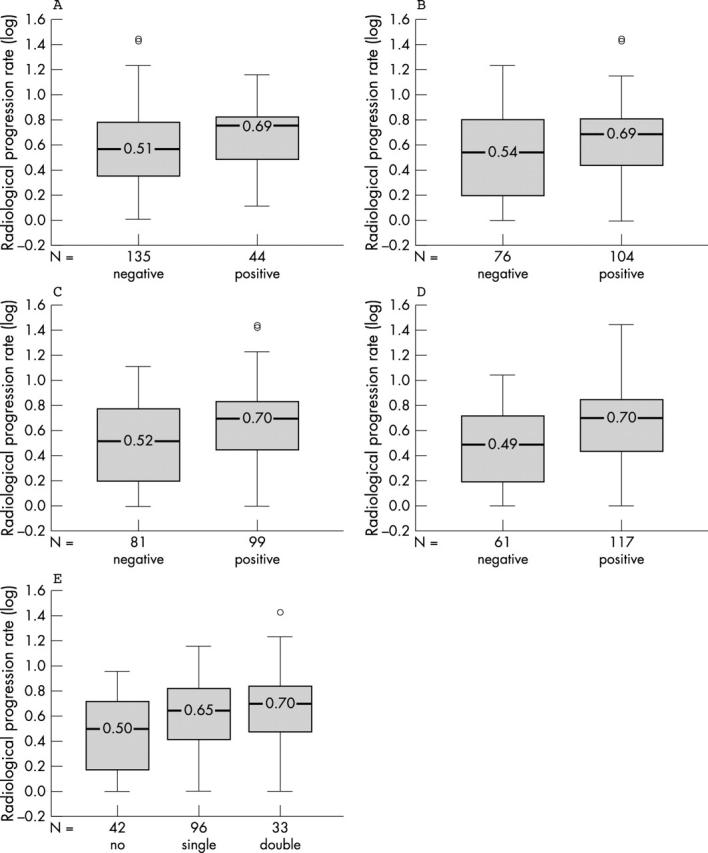
Radiological progression rates according to the autoantibody status (positive or negative) and the shared epitope status (SE) (no, single or double SE). Median radiological progression rates (logarithmic transformation) are indicated. (A) RF (p = 0.043); (B) anti-peptide A antibodies (p = 0.024); (C) anti-peptide B antibodies (p = 0.008); (D) anti-CCP2 antibodies (p = 0.001); (E) SE. SE, single versus negative: p = 0.040; SE, double versus negative: p = 0.036; SE, single versus double: p = NS; SE, single or double versus negative: p = 0.009 (not shown in figure).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Palosuo T., Lukka M., Kurki P., Isomäki H., Kautiainen H., von Essen R. Antifilaggrin antibodies in recent-onset arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1999;28(2):113–116. doi: 10.1080/030097499442586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bas S., Perneger T. V., Mikhnevitch E., Seitz M., Tiercy J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Guerne P. A. Association of rheumatoid factors and anti-filaggrin antibodies with severity of erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Oct;39(10):1082–1088. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.10.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzaro N., Mazzanti G., Tonutti E., Villalta D., Tozzoli R. Diagnostic accuracy of the anti-citrulline antibody assay for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem. 2001 Jun;47(6):1089–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Cannon G. W., Schiff M., Weaver A., Fox R., Olsen N., Furst D., Sharp J., Moreland L., Caldwell J. Two-year, blinded, randomized, controlled trial of treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with methotrexate. Utilization of Leflunomide in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial Investigator Group. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):1984–1992. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<1984::AID-ART346>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girbal-Neuhauser E., Durieux J. J., Arnaud M., Dalbon P., Sebbag M., Vincent C., Simon M., Senshu T., Masson-Bessière C., Jolivet-Reynaud C. The epitopes targeted by the rheumatoid arthritis-associated antifilaggrin autoantibodies are posttranslationally generated on various sites of (pro)filaggrin by deimination of arginine residues. J Immunol. 1999 Jan 1;162(1):585–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbach-Mansky R., Lee J., McCoy A., Hoxworth J., Yarboro C., Smolen J. S., Steiner G., Rosen A., Zhang C., Ménard H. A. Rheumatoid arthritis associated autoantibodies in patients with synovitis of recent onset. Arthritis Res. 2000 Mar 31;2(3):236–243. doi: 10.1186/ar93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman Jennifer D., Criswell Lindsey A. The shared epitope and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2002 Feb;28(1):59–78. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(03)00069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison B., Thomson W., Symmons D., Ollier B., Wiles N., Payton T., Barrett E., Silman A. The influence of HLA-DRB1 alleles and rheumatoid factor on disease outcome in an inception cohort of patients with early inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Oct;42(10):2174–2183. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2174::AID-ANR19>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill Jonathan A., Southwood Scott, Sette Alessandro, Jevnikar Anthony M., Bell David A., Cairns Ewa. Cutting edge: the conversion of arginine to citrulline allows for a high-affinity peptide interaction with the rheumatoid arthritis-associated HLA-DRB1*0401 MHC class II molecule. J Immunol. 2003 Jul 15;171(2):538–541. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.2.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsmans H. M., Jacobs J. W., van der Heijde D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., Schenk Y., Bijlsma J. W. The course of radiologic damage during the first six years of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Sep;43(9):1927–1940. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<1927::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen Annemarie L. M. A., van der Horst-Bruinsma Irene, van Schaardenburg Dirkjan, van de Stadt Rob J., de Koning Margret H. M. T., Dijkmans Ben A. C. Rheumatoid factor and antibodies to cyclic citrullinated Peptide differentiate rheumatoid arthritis from undifferentiated polyarthritis in patients with early arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002 Oct;29(10):2074–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenhäuser S., Wagner U., Schuster E., Wassmuth R., Arnold S., Seidel W., Tröltzsch M., Loeffler M., Häntzschel H. Immunogenetic markers and seropositivity predict radiological progression in early rheumatoid arthritis independent of disease activity. J Rheumatol. 2001 Apr;28(4):735–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroot E. J., de Jong B. A., van Leeuwen M. A., Swinkels H., van den Hoogen F. H., van't Hof M., van de Putte L. B., van Rijswijk M. H., van Venrooij W. J., van Riel P. L. The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1831–1835. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200008)43:8<1831::AID-ANR19>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., van der Heijde D. M., St Clair E. W., Furst D. E., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Weisman M., Emery P., Feldmann M. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1594–1602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattey D. L., Hassell A. B., Dawes P. T., Cheung N. T., Poulton K. V., Thomson W., Hajeer A. H., Ollier W. E. Independent association of rheumatoid factor and the HLA-DRB1 shared epitope with radiographic outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Jul;44(7):1529–1533. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200107)44:7<1529::AID-ART275>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer O., Labarre C., Dougados M., Goupille Ph, Cantagrel A., Dubois A., Nicaise-Roland P., Sibilia J., Combe B. Anticitrullinated protein/peptide antibody assays in early rheumatoid arthritis for predicting five year radiographic damage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Feb;62(2):120–126. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.2.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno I., Valenzuela A., García A., Yélamos J., Sánchez B., Hernánz W. Association of the shared epitope with radiological severity of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996 Jan;23(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira L., Sebbag M., Vincent C., Arnaud M., Fournié B., Cantagrel A., Jolivet M., Serre G. Performance of two ELISAs for antifilaggrin autoantibodies, using either affinity purified or deiminated recombinant human filaggrin, in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Sep;60(9):882–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paimela L., Leirisalo-Repo M., Helve T., Koskimies S. The prognostic value of HLA DR4 and B27 antigens in early rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1993;22(5):220–224. doi: 10.3109/03009749309095126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant M. J., Jones P. W., Saklatvala J., Ollier W. E., Dawes P. T. Patterns of radiological progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: results of an 8 year prospective study. J Rheumatol. 1998 Mar;25(3):417–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens G. A., Visser H., de Jong B. A., van den Hoogen F. H., Hazes J. M., Breedveld F. C., van Venrooij W. J. The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):155–163. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<155::AID-ANR20>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellekens G. A., de Jong B. A., van den Hoogen F. H., van de Putte L. B., van Venrooij W. J. Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1998 Jan 1;101(1):273–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Wolfe F., Mitchell D. M., Bloch D. A. The progression of erosion and joint space narrowing scores in rheumatoid arthritis during the first twenty-five years of disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jun;34(6):660–668. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Sawada T., Murakami A., Matsui T., Tohma S., Nakazono K., Takemura M., Takasaki Y., Mimori T., Yamamoto K. High diagnostic performance of ELISA detection of antibodies to citrullinated antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32(4):197–204. doi: 10.1080/03009740310003677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Union Ann, Meheus Lydie, Humbel René Louis, Conrad Karsten, Steiner Guenter, Moereels Henri, Pottel Hans, Serre Guy, De Keyser Filip. Identification of citrullinated rheumatoid arthritis-specific epitopes in natural filaggrin relevant for antifilaggrin autoantibody detection by line immunoassay. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 May;46(5):1185–1195. doi: 10.1002/art.10229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vencovský J., Machácek S., Sedová L., Kafková J., Gatterová J., Pesáková V., Růzicková S. Autoantibodies can be prognostic markers of an erosive disease in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 May;62(5):427–430. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.5.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent C., Simon M., Sebbag M., Girbal-Neuhauser E., Durieux J. J., Cantagrel A., Fournié B., Mazières B., Serre G. Immunoblotting detection of autoantibodies to human epidermis filaggrin: a new diagnostic test for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1998 May;25(5):838–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent C., de Keyser F., Masson-Bessière C., Sebbag M., Veys E. M., Serre G. Anti-perinuclear factor compared with the so called "antikeratin" antibodies and antibodies to human epidermis filaggrin, in the diagnosis of arthritides. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Jan;58(1):42–48. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent Christian, Nogueira Leonor, Sebbag Mireille, Chapuy-Regaud Sabine, Arnaud Michel, Letourneur Odile, Rolland Dominique, Fournié Bernard, Cantagrel Alain, Jolivet Michel. Detection of antibodies to deiminated recombinant rat filaggrin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a highly effective test for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Aug;46(8):2051–2058. doi: 10.1002/art.10436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe F., Sharp J. T. Radiographic outcome of recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: a 19-year study of radiographic progression. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1571–1582. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1571::AID-ART7>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Jaarsveld C. H., ter Borg E. J., Jacobs J. W., Schellekens G. A., Gmelig-Meyling F. H., van Booma-Frankfort C., de Jong B. A., van Venrooij W. J., Bijlsma J. W. The prognostic value of the antiperinuclear factor, anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999 Nov-Dec;17(6):689–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


