Abstract
Methods: CD19+, CD4+, and CD8+ lymphocytes were isolated from the peripheral blood of nine patients with SLE and nine healthy controls by means of magnetic bead-coupled antibodies and tested for telomerase activity with the TRAP assay.
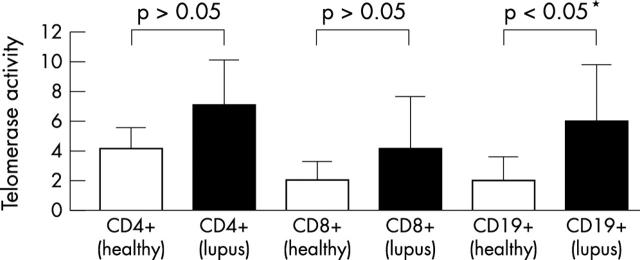
Results: Telomerase activity was significantly increased in CD19+ B cells from patients with SLE. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from lupus patients displayed increased mean telomerase activity, although the difference from normal controls did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusions: Increased telomerase activity in the B and the T cell lineage might indicate activation and proliferation of these lymphocytes.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (72.4 KB).
Figure 1.
Telomerase activity measured by the TRAP assay. For semiquantitative analysis a dilution series of HeLa extract was assayed in parallel. The experimental samples were expressed as corresponding nanograms of HeLa protein. Mean and standard deviation are indicated.
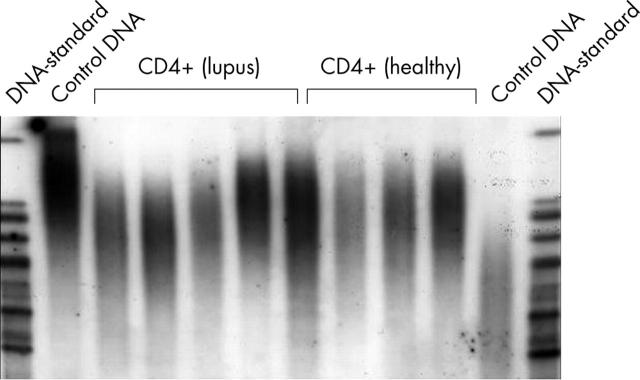
Figure 2.
Telomere length was determined by measuring the terminal restriction fragment length using the Southern blot method (TeloTTAGGG telomere length assay, Roche). A representative blot for CD4+ cells is shown. A DNA ladder and control DNA with long telomeres (left side) and short telomeres (right side) are included on the blot. Owing to their heterogeneity, telomere restriction fragments appear as smears on the blot.