Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of anti-tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) monoclonal antibody (infliximab) in the treatment of spondyloarthropathy (SpA) associated with active and inactive Crohn's disease (CD).
Methods: Twenty four patients with SpA associated with active or inactive CD (16 active, 8 quiescent) were treated with anti-TNFα monoclonal antibody (infliximab) with repeated infusions for a period of 12–18 months. The treatment aimed at ameliorating the general musculoskeletal and spinal pain, controlling peripheral arthritis and enthesitis, decreasing the BASDAI score, modifying acute phase reactants, and reducing CD activity.
Results: Infliximab improved both gastrointestinal (p<0.01) and overall articular symptoms (BASDAI, p<0.01; general musculoskeletal and spinal pain, p<0.01; peripheral arthritis, p<0.01) in patients with active CD. Additionally, infliximab effectively controlled not only axial involvement and peripheral arthritis but also enthesitis (p<0.01) and prevented inflammatory bowel disease reactivation in patients with inactive CD and low inflammatory markers. Amelioration of gut and musculoskeletal involvement persisted for up to 12 months.
Conclusion: Infliximab may act on the inflammation of entheses and of periarticular structures, which usually does not cause a change in the haematological markers that are the main indicators of pain and joint ankylosis in SpA. Infliximab induces and maintains remission of CD while at the same time treating active and severe SpA, suggesting that it should be the preferred drug for the treatment of active and severe SpA associated with active or quiescent CD.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (146.3 KB).
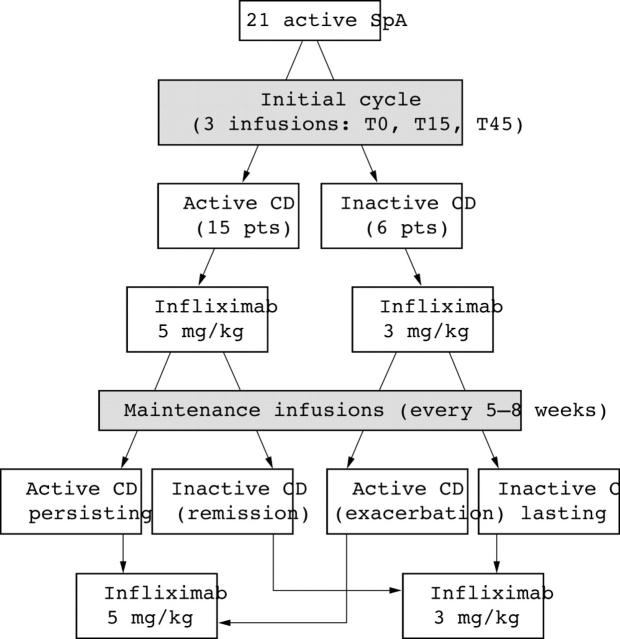
Figure 1.
Therapeutic flow chart for the treatment of active SpA associated with active or inactive CD.
Figure 2.
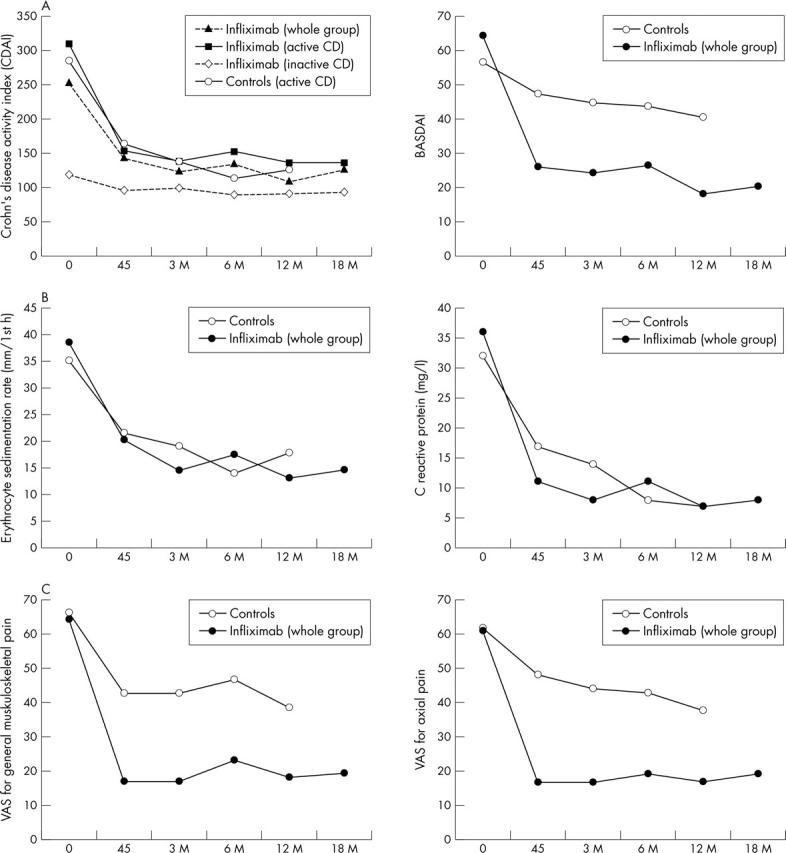
(A, B, C) Clinical and laboratory data (mean) of the patients with SpA and CD at baseline and during treatment with infliximab or various other conventional treatments (baseline, 45 days, 3, 6, 12, 18 months). The values of CDAI are split into two additional groups: patients with active or inactive CD at baseline.
Figure 3.
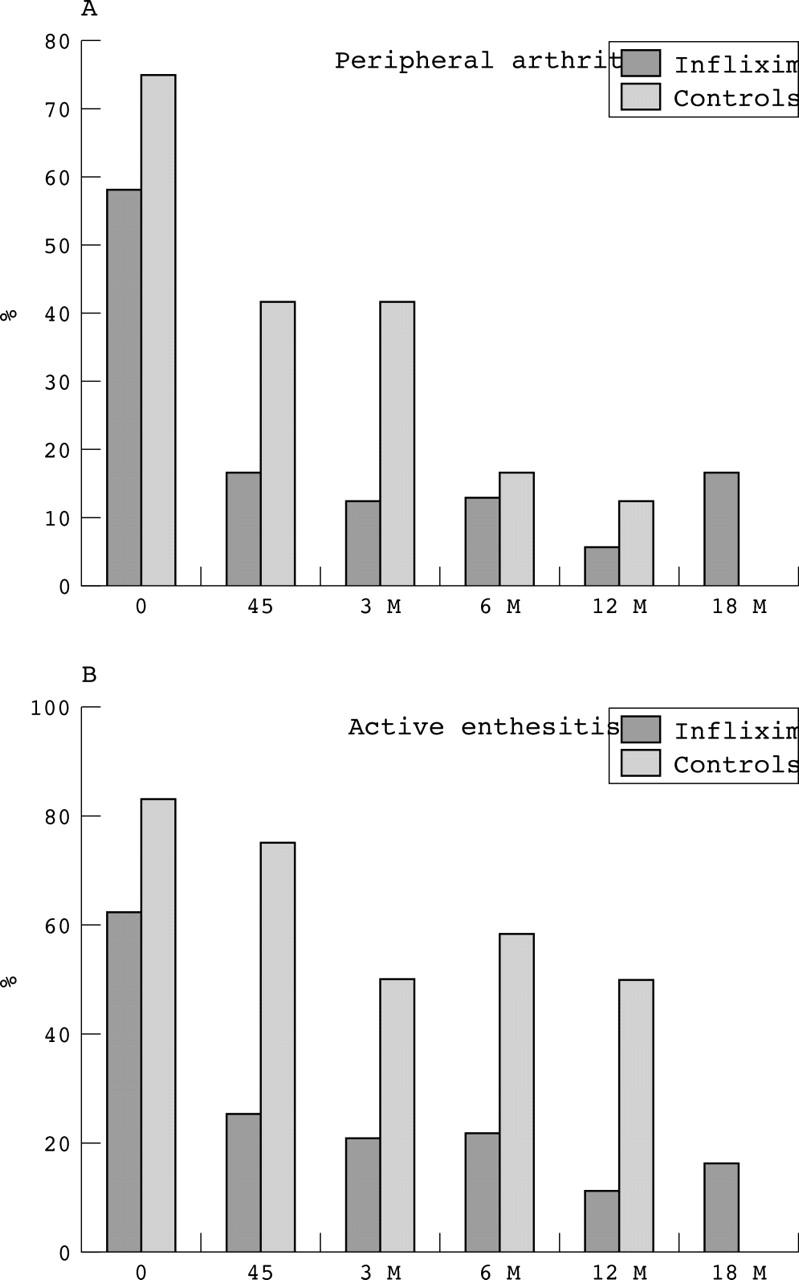
Percentage of patients presenting peripheral arthritis (A) or active enthesitis (B) at baseline and during the treatment (45 days, 3, 6, 12, 18 months) with infliximab or various other drugs (azathioprine, mesalazine, steroids, metronidazole, antibiotics). *The data reported at 12 months are relative to patients (10/21) who prolonged the treatment with infliximab for up to 12 months; no controls are available for this group.
Figure 4.
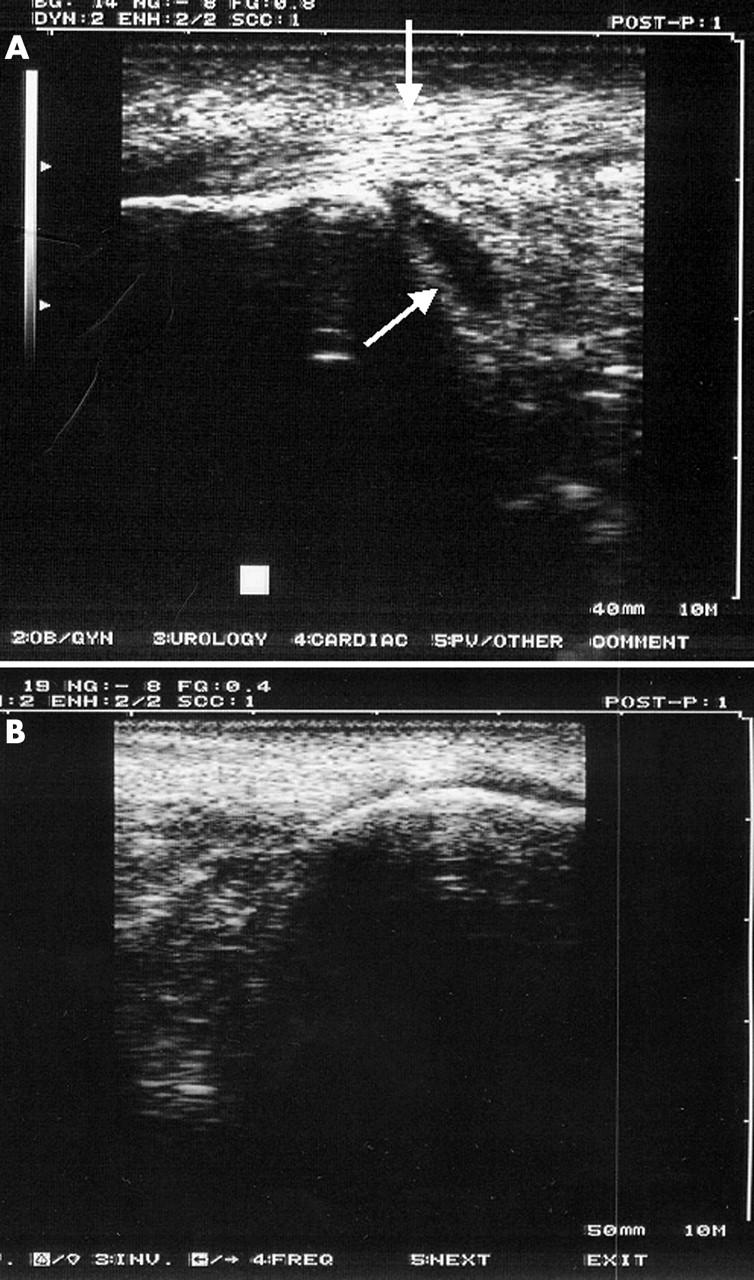
(A) Thickening and homogeneous hypoechogenicity of the Achilles tendon enthesis with distension of the retrocalcaneal bursa (arrows) which disappeared after 45 days of treatment with infliximab (B).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott I. D., McDonald D., Williams A., Ghosh S. Clinical use of Infliximab in Crohn's disease: the Edinburgh experience. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Oct;15(10):1639–1646. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.01092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Haibel H., Sieper J., Reddig J., Braun J. Infliximab treatment of severe ankylosing spondylitis: one-year followup. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Dec;44(12):2936–2937. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200112)44:12<2936::aid-art483>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Khan M. A., Sieper J. Enthesitis and ankylosis in spondyloarthropathy: what is the target of the immune response? Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Dec;59(12):985–994. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.12.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun Juergen, Sieper Joachim. Therapy of ankylosing spondylitis and other spondyloarthritides: established medical treatment, anti-TNF-alpha therapy and other novel approaches. Arthritis Res. 2002 Aug 6;4(5):307–321. doi: 10.1186/ar592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope A. P., Londei M., Chu N. R., Cohen S. B., Elliott M. J., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Chronic exposure to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in vitro impairs the activation of T cells through the T cell receptor/CD3 complex; reversal in vivo by anti-TNF antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):749–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI117394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'haens G., Van Deventer S., Van Hogezand R., Chalmers D., Kothe C., Baert F., Braakman T., Schaible T., Geboes K., Rutgeerts P. Endoscopic and histological healing with infliximab anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies in Crohn's disease: A European multicenter trial. Gastroenterology. 1999 May;116(5):1029–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Kalden J. R., Antoni C., Smolen J. S., Leeb B., Breedveld F. C., Macfarlane J. D., Bijl H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1105–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer Stephen B., Feagan Brian G., Lichtenstein Gary R., Mayer Lloyd F., Schreiber S., Colombel Jean Frederic, Rachmilewitz Daniel, Wolf Douglas C., Olson Allan, Bao Weihang. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002 May 4;359(9317):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08512-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herfarth Hans, Obermeier Florian, Andus Tilo, Rogler Gerhard, Nikolaus Susanna, Kuehbacher Tanja, Schreiber Stefan. Improvement of arthritis and arthralgia after treatment with infliximab (Remicade) in a German prospective, open-label, multicenter trial in refractory Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Oct;97(10):2688–2690. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.06064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. M., Trinh H., Le J., Siegel S., Shealy D., McDonough M., Scallon B., Moore M. A., Vilcek J., Daddona P. Construction and initial characterization of a mouse-human chimeric anti-TNF antibody. Mol Immunol. 1993 Nov;30(16):1443–1453. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90106-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E., Van den Bosch F., Baeten D., Herssens A., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Repeated infusions of infliximab, a chimeric anti-TNFalpha monoclonal antibody, in patients with active spondyloarthropathy: one year follow up. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Mar;61(3):207–212. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., van der Heijde D. M., St Clair E. W., Furst D. E., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Weisman M., Emery P., Feldmann M. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1594–1602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R., St Clair E. W., Breedveld F., Furst D., Kalden J., Weisman M., Smolen J., Emery P., Harriman G., Feldmann M. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)05246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maksymowych Walter P., Jhangri Gian S., Lambert Robert G., Mallon Cathy, Buenviaje Heidi, Pedrycz Ewa, Luongo Rolfe, Russell Anthony S. Infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective observational inception cohort analysis of efficacy and safety. J Rheumatol. 2002 May;29(5):959–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-González O., Cantero-Hinojosa J., Paule-Sastre P., Gómez-Magán J. C., Salvatierra-Ríos D. Intestinal permeability in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and their healthy relatives. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Jul;33(7):644–647. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.7.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzo-Ortega H., McGonagle D., O'Connor P., Emery P. Efficacy of etanercept for treatment of Crohn's related spondyloarthritis but not colitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Jan;62(1):74–76. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard T. R., Wordsworth B. P., Jewell D. P. Peripheral arthropathies in inflammatory bowel disease: their articular distribution and natural history. Gut. 1998 Mar;42(3):387–391. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Present D. H., Rutgeerts P., Targan S., Hanauer S. B., Mayer L., van Hogezand R. A., Podolsky D. K., Sands B. E., Braakman T., DeWoody K. L. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999 May 6;340(18):1398–1405. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199905063401804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvarani C, Fornaciari G, Beltrami M, Macchioni PL. Musculoskeletal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Intern Med. 2000 Aug;11(4):210–214. doi: 10.1016/s0953-6205(00)00093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Hanauer S. B., van Deventer S. J., Mayer L., Present D. H., Braakman T., DeWoody K. L., Schaible T. F., Rutgeerts P. J. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor alpha for Crohn's disease. Crohn's Disease cA2 Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1997 Oct 9;337(15):1029–1035. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199710093371502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bosch Filip, Kruithof Elli, Baeten Dominique, Herssens Annemie, de Keyser Filip, Mielants Herman, Veys Eric M. Randomized double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) versus placebo in active spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):755–765. doi: 10.1002/art.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Baeten D., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., De Vos M., De Keyser F., Mielants H. Crohn's disease associated with spondyloarthropathy: effect of TNF-alpha blockade with infliximab on articular symptoms. Lancet. 2000 Nov 25;356(9244):1821–1822. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)03239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]