Abstract
Objective: To determine whether arthrographic distension with a mixture of saline and steroid, in patients with painful stiff shoulder for at least 3 months, is better than placebo in improving function, pain, and range of motion at 3, 6, and 12 weeks.
Methods: A randomised, placebo controlled trial with participant and outcome assessor blinding in which shoulder joint distension with normal saline and corticosteroid was compared with placebo (arthrogram). Outcome measures, assessed at 3, 6, and 12 weeks, included a shoulder-specific disability measure (SPADI), a patient preference measure (Problem Elicitation Technique (PET)), pain, and range of active motion.
Results: From 96 potential participants, 48 were recruited. Four withdrew from the placebo group after the 3 week assessment and three subsequently received arthrographic distension with saline and steroid. At 3 weeks, significantly greater improvement in SPADI (p = 0.005), PET, overall pain, active total shoulder abduction, and hand behind back was found in participants in the joint distension and steroid group than in the placebo group. At 6 weeks the results of the intention to treat analysis favoured joint distension, although the between-group differences were only significant for improvement in PET (difference in mean change in PET between groups = 45.9 (95% CI 3.2 to 88.7). Excluding the four withdrawals, the between-group differences for the disability and pain measures significantly favoured distension over placebo. At 12 weeks, both the intention to treat analysis and an analysis excluding the four withdrawals demonstrated a significantly greater improvement in PET score for the distension group.
Conclusions: Short term efficacy of arthrographic distension with normal saline and corticosteroid over placebo was demonstrated in patients with painful stiff shoulder.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (278.7 KB).
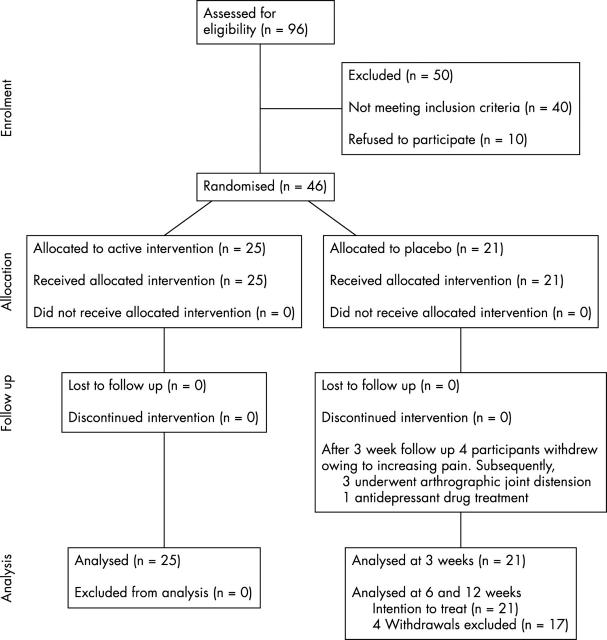
Figure 1 .
Movement of participants through the trial.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREN L., LUNDBERG B. J. TREATMENT OF RIGID SHOULDERS BY JOINT DISTENSION DURING ARTHROGRAPHY. Acta Orthop Scand. 1965;36:45–53. doi: 10.3109/17453676508989370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adebajo A. O., Nash P., Hazleman B. L. A prospective double blind dummy placebo controlled study comparing triamcinolone hexacetonide injection with oral diclofenac 50 mg TDS in patients with rotator cuff tendinitis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Sep;17(9):1207–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman D. G., Doré C. J. Randomisation and baseline comparisons in clinical trials. Lancet. 1990 Jan 20;335(8682):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90014-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry H., Fernandes L., Bloom B., Clark R. J., Hamilton E. B. Clinical study comparing acupuncture, physiotherapy, injection and oral anti-inflammatory therapy in shoulder-cuff lesions. Curr Med Res Opin. 1980;7(2):121–126. doi: 10.1185/03007998009112038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair B., Rokito A. S., Cuomo F., Jarolem K., Zuckerman J. D. Efficacy of injections of corticosteroids for subacromial impingement syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996 Nov;78(11):1685–1689. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199611000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchbinder R., Bombardier C., Yeung M., Tugwell P. Which outcome measures should be used in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials? Clinical and quality-of-life measures' responsiveness to treatment in a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Nov;38(11):1568–1580. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulgen D. Y., Binder A. I., Hazleman B. L., Dutton J., Roberts S. Frozen shoulder: prospective clinical study with an evaluation of three treatment regimens. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Jun;43(3):353–360. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carette Simon, Moffet Hélène, Tardif Johanne, Bessette Louis, Morin Frédéric, Frémont Pierre, Bykerk Vivian, Thorne Carter, Bell Mary, Bensen William. Intraarticular corticosteroids, supervised physiotherapy, or a combination of the two in the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Mar;48(3):829–838. doi: 10.1002/art.10954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil V., Dussault R. G., Leduc B. E., Fleury J. Capsulite rétractile de l'épaule: étude comparative de l'arthrographie avec corticothérapie intra-articulaire avec ou sans distension capsulaire. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1992 Apr;43(2):127–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft P., Rigby A. S., Boswell R., Schollum J., Silman A. The prevalence of chronic widespread pain in the general population. J Rheumatol. 1993 Apr;20(4):710–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund A. L., Rydell N. Combination treatment for adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992 Sep;(282):105–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed D. O., Gallivan W. R., Jr Office management of frozen shoulder syndrome. Treatment with hydraulic distension under local anesthesia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989 May;(242):177–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gam A. N., Schydlowsky P., Rossel I., Remvig L., Jensen E. M. Treatment of "frozen shoulder" with distension and glucorticoid compared with glucorticoid alone. A randomised controlled trial. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(6):425–430. doi: 10.1080/030097498442244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavant M. L., Rizk T. E., Gold R. E., Flick P. A. Distention arthrography in the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1994 Mar-Apr;5(2):305–308. doi: 10.1016/s1051-0443(94)71488-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller N. L., Pocock S. J. Interim analyses in randomized clinical trials: ramifications and guidelines for practitioners. Biometrics. 1987 Mar;43(1):213–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Buchbinder R., Forbes A., Bellamy N. A standardized protocol for measurement of range of movement of the shoulder using the Plurimeter-V inclinometer and assessment of its intrarater and interrater reliability. Arthritis Care Res. 1998 Feb;11(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/art.1790110108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Buchbinder R., Glazier R., Forbes A. Systematic review of randomised controlled trials of interventions for painful shoulder: selection criteria, outcome assessment, and efficacy. BMJ. 1998 Jan 31;316(7128):354–360. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7128.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazleman B. L. The painful stiff shoulder. Rheumatol Phys Med. 1972 Nov;11(8):413–421. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/11.8.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald S. L., Riddle D. L., Lamb R. L. The shoulder pain and disability index: the construct validity and responsiveness of a region-specific disability measure. Phys Ther. 1997 Oct;77(10):1079–1089. doi: 10.1093/ptj/77.10.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. Y., Chan K. M. Arthroscopic distension in the management of frozen shoulder. Int Orthop. 1991;15(2):79–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00179702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L. G., Barton M. A., Wallace W. A., Ferrousis J., Dunn N. A., Bossingham D. H. Intra-articular distension and steroids in the management of capsulitis of the shoulder. BMJ. 1991 Jun 22;302(6791):1498–1501. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6791.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M., Haq A. M., Wright V., Longton E. B. Periarthritis of the shoulder: a controlled trial of physiotherapy. Physiotherapy. 1973 Oct 10;59(10):312–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyd J. A., Loyd H. M. Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: arthrographic diagnosis and treatment. South Med J. 1983 Jul;76(7):879–883. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198307000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg B. J. The frozen shoulder. Clinical and radiographical observations. The effect of manipulation under general anesthesia. Structure and glycosaminoglycan content of the joint capsule. Local bone metabolism. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1969;119:1–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy K. A., Baxter A. D., Oni O. O., Finlay D. The value of shoulder distension arthrography with intraarticular injection of steroid and local anaesthetic: a follow-up study. Br J Radiol. 1994 Mar;67(795):263–266. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-67-795-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neviaser R. J., Neviaser T. J. The frozen shoulder. Diagnosis and management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987 Oct;(223):59–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neviaser T. J. Adhesive capsulitis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987 Jul;18(3):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri M., Dobrow R., Neiman R., Whiting-O'Keefe Q., Seaman W. E. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the treatment of the painful shoulder. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Sep;30(9):1040–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plafki C., Steffen R., Willburger R. E., Wittenberg R. H. Local anaesthetic injection with and without corticosteroids for subacromial impingement syndrome. Int Orthop. 2000;24(1):40–42. doi: 10.1007/s002640050010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves B. The natural history of the frozen shoulder syndrome. Scand J Rheumatol. 1975;4(4):193–196. doi: 10.3109/03009747509165255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizk T. E., Pinals R. S., Talaiver A. S. Corticosteroid injections in adhesive capsulitis: investigation of their value and site. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1991 Jan;72(1):20–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach K. E., Budiman-Mak E., Songsiridej N., Lertratanakul Y. Development of a shoulder pain and disability index. Arthritis Care Res. 1991 Dec;4(4):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ströbel G. Therapeutische Langzeitwirkung unterschiedlicher intraartikulärer Injektionsbehandlung der schmerzhaften Schulter--Auswirkung auf Schmerz, Beweglichkeit und Arbeitsfähigkeit. Rehabilitation (Stuttg) 1996 Aug;35(3):176–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugwell P., Bombardier C., Buchanan W. W., Goldsmith C. H., Grace E., Hanna B. The MACTAR Patient Preference Disability Questionnaire--an individualized functional priority approach for assessing improvement in physical disability in clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;14(3):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio P. C., Hazleman B. L., King R. H. A double-blind trial comparing subacromial methylprednisolone and lignocaine in acute rotator cuff tendinitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;32(8):743–745. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.8.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Jr, Holleman D. R., Jr, Simel D. L. Measuring shoulder function with the Shoulder Pain and Disability Index. J Rheumatol. 1995 Apr;22(4):727–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withrington R. H., Girgis F. L., Seifert M. H. A placebo-controlled trial of steroid injections in the treatment of supraspinatus tendonitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1985;14(1):76–78. doi: 10.3109/03009748509102022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong B. A., Dahmen R., Hogeweg J. A., Marti R. K. Intra-articular triamcinolone acetonide injection in patients with capsulitis of the shoulder: a comparative study of two dose regimens. Clin Rehabil. 1998 Jun;12(3):211–215. doi: 10.1191/026921598673772420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Royen B. J., Pavlov P. W. Treatment of frozen shoulder by distension and manipulation under local anaesthesia. Int Orthop. 1996;20(4):207–210. doi: 10.1007/s002640050064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]