Abstract
Objective: To determine the effect of different treatment strategies (early versus delayed) on the radiological progression of joint damage during 4 years. Additionally, to determine the effect of treatment strategy on the association of HLA class II alleles and joint damage.
Methods: Progression of radiographic damage and association of radiographic damage and genetic predisposition were compared in two cohorts, one treated according to the delayed treatment strategy (initial treatment with analgesics), the other treated according to the early treatment strategy (treatment with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) chloroquine or sulfasalazine). Radiographic damage was measured by the modified Sharp-van der Heijde method. Genetic predisposition was determined by high resolution HLA-DR and DQ typing.
Results: A completers-only analysis of 153 patients (originally 206 patients) in a non-randomised design showed less radiographic progression from 0 to 4 years in the early treatment group (median Sharp progression rate 1.3 points/year, n = 75) than in the delayed treatment group (2.5 points/year, n = 78) (p = 0.03). The progression from 1 to 4 years did not differ significantly between the groups. At 4 years, joint destruction in both groups was positively correlated with the presence of the shared epitope.
Conclusions: The beneficial effect of early DMARD treatment on the radiological progression of joint damage is still present at 4 years. However, the rate of joint destruction from 1 to 4 years did not differ between the delayed and early treatment group. Neither the radiographic nor the immunogenetic data suggest that longlasting disease modification has been induced by early treatment.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (236.8 KB).
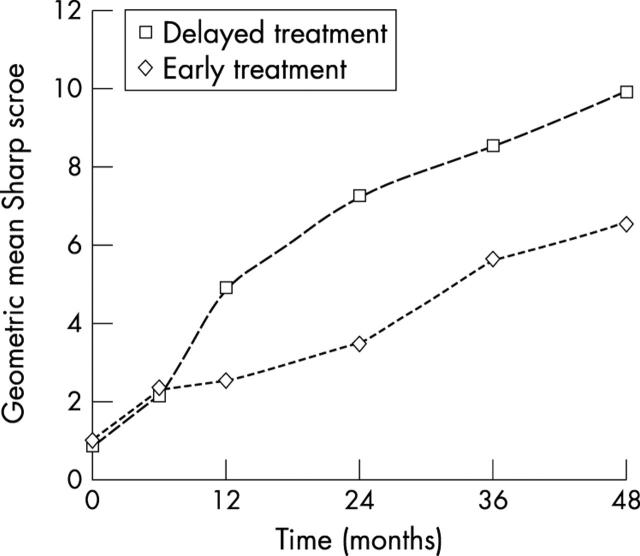
Figure 1 .
Geometric mean Sharp score (see "Patients and methods; Statistical analysis") of early (group 2) versus delayed treatment (group 1) strategy from study entry to 4 years. 95% CI for t = 0 in group 1 (0.49 to 1.49), group 2 (0.58 to 1.70); for t = 6 in group 1 (1.32 to 3.35), in group 2 (1.45 to 3.61); for t = 12 in group 1 (3.32 to 7.24), in group 2 (1.62 to 3.81); for t = 24 in group 1 (4.95 to 10.63), in group 2 (2.28 to 5.22); for t = 36 in group 1 (5.88 to 12.34), in group 2 (3.79 to 8.26); for t = 48 in group 1 (6.77 to 14.43), in group 2 (4.40 to 9.68).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G., Allander E., Lund B., Berg E., Brodin U., Pettersson H., Trang L. Auranofin improves outcome in early rheumatoid arthritis. Results from a 2-year, double blind placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;15(12):1747–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calgüneri M., Pay S., Calişkaner Z., Apraş S., Kiraz S., Ertenli I., Cobankara V. Combination therapy versus monotherapy for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1999 Nov-Dec;17(6):699–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash J. M., Klippel J. H. Second-line drug therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1368–1375. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egsmose C., Lund B., Borg G., Pettersson H., Berg E., Brodin U., Trang L. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis benefit from early 2nd line therapy: 5 year followup of a prospective double blind placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol. 1995 Dec;22(12):2208–2213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Salmon M., Bradley H., Wordsworth P., Tunn E., Bacon P. A., Waring R. Genetically determined factors as predictors of radiological change in patients with early symmetrical arthritis. BMJ. 1992 Dec 5;305(6866):1387–1389. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6866.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furst D. E. Rational use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Drugs. 1990 Jan;39(1):19–37. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199039010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannonen P., Möttönen T., Hakola M., Oka M. Sulfasalazine in early rheumatoid arthritis. A 48-week double-blind, prospective, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Nov;36(11):1501–1509. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsmans H. M., Jacobs J. W., van der Heijde D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., Schenk Y., Bijlsma J. W. The course of radiologic damage during the first six years of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Sep;43(9):1927–1940. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<1927::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landewé Robert B. M., Boers Maarten, Verhoeven Arco C., Westhovens Rene, van de Laar Mart A. F. J., Markusse Harry M., van Denderen J. Christiaan, Westedt Marie Louise, Peeters Andre J., Dijkmans Ben A. C. COBRA combination therapy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: long-term structural benefits of a brief intervention. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):347–356. doi: 10.1002/art.10083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lard L. R., Boers M., Verhoeven A., Vos K., Visser H., Hazes J. M. W., Zwinderman A. H., Schreuder G. M. T., Breedveld F. C., De Vries R. R. P. Early and aggressive treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients affects the association of HLA class II antigens with progression of joint damage. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Apr;46(4):899–905. doi: 10.1002/art.10151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lard L. R., Visser H., Speyer I., vander Horst-Bruinsma I. E., Zwinderman A. H., Breedveld F. C., Hazes J. M. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of two cohorts who received different treatment strategies. Am J Med. 2001 Oct 15;111(6):446–451. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möttönen T., Hannonen P., Leirisalo-Repo M., Nissilä M., Kautiainen H., Korpela M., Laasonen L., Julkunen H., Luukkainen R., Vuori K. Comparison of combination therapy with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised trial. FIN-RACo trial group. Lancet. 1999 May 8;353(9164):1568–1573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möttönen T., Paimela L., Ahonen J., Helve T., Hannonen P., Leirisalo-Repo M. Outcome in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated according to the "sawtooth" strategy. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jun;39(6):996–1005. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell J. R., Nepom B. S., Haire C., Gersuk V. H., Gaur L., Moore G. F., Drymalski W., Palmer W., Eckhoff P. J., Klassen L. W. HLA-DRB1 typing in rheumatoid arthritis: predicting response to specific treatments. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Apr;57(4):209–213. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.4.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltomaa R., Paimela L., Helve T., Leirisalo-Repo M. Effect of treatment on the outcome of very early rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2001;30(3):143–148. doi: 10.1080/030097401300162905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Callahan L. F. What is the natural history of rheumatoid arthritis? Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1993 Feb;19(1):123–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T. Rheumatoid arthritis: disappointing long-term outcomes despite successful short-term clinical trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41(11):1037–1041. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(88)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Symmons D. P., Coulton B. L., Popert A. J. Long-term outcome of treating rheumatoid arthritis: results after 20 years. Lancet. 1987 May 16;1(8542):1108–1111. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91672-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand Vibeke, Sharp John T. Radiographic data from recent randomized controlled trials in rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jan;48(1):21–34. doi: 10.1002/art.10683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser H., Gelinck L. B., Kampfraath A. H., Breedveld F. C., Hazes J. M. Diagnostic and prognostic characteristics of the enzyme linked immunosorbent rheumatoid factor assays in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996 Mar;55(3):157–161. doi: 10.1136/ard.55.3.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hicok K. C., Conn D. L., Goronzy J. J. The influence of HLA-DRB1 genes on disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 15;117(10):801–806. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-10-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R., Dwyer E., Rose S. The genetic basis of rheumatoid arthritis. The shared epitope hypothesis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Nov;18(4):761–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe F., Sharp J. T. Radiographic outcome of recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: a 19-year study of radiographic progression. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1571–1582. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1571::AID-ART7>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanelli E., Breedveld F. C., de Vries R. R. HLA class II association with rheumatoid arthritis: facts and interpretations. Hum Immunol. 2000 Dec;61(12):1254–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(00)00185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., Schreuder G. M., D'Amaro J., Breedveld F. C. Association of HLA-DR4 with a more progressive disease course in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results of a followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jul;34(7):822–830. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Vandenbroucke J. P., Breedveld F. C. The severity of rheumatoid arthritis: a 6-year followup study of younger women with symptoms of recent onset. J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;21(9):1620–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide A., Jacobs J. W., Bijlsma J. W., Heurkens A. H., van Booma-Frankfort C., van der Veen M. J., Haanen H. C., Hofman D. M., van Albada-Kuipers G. A., ter Borg E. J. The effectiveness of early treatment with "second-line" antirheumatic drugs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Apr 15;124(8):699–707. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-8-199604150-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M. Plain X-rays in rheumatoid arthritis: overview of scoring methods, their reliability and applicability. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1996 Aug;10(3):435–453. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(96)80043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Riel P. L., van Leeuwen M. A., van 't Hof M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Prognostic factors for radiographic damage and physical disability in early rheumatoid arthritis. A prospective follow-up study of 147 patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;31(8):519–525. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.8.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Horst-Bruinsma I. E., Visser H., Hazes J. M., Breedveld F. C., Verduyn W., Schreuder G. M., de Vries R. R., Zanelli E. HLA-DQ-associated predisposition to and dominant HLA-DR-associated protection against rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 1999 Feb;60(2):152–158. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(98)00101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]