Abstract
Objective: To determine immunohistological markers in synovial tissue of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) which are associated with unfavourable disease outcome.
Methods: Synovial tissue was obtained from 36 patients with RA within 1 year after the initial symptoms and before starting disease modifying antirheumatic drug treatment. Clinical, laboratory, and radiological assessments (Larsen score) were performed at the time of the biopsy and at the end of follow up (mean 58 months, range 38–72). Immunohistological analysis was performed to detect T cells, B cells, plasma cells, fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), macrophages, and granzyme B+ cytotoxic cells. The sections were evaluated by digital image analysis.
Results: Patients were divided into two groups based upon the radiological progression per year of follow up: group I with mild progression (n = 20; Larsen <2 points/year); group II with more severe progression (n = 16; Larsen ⩾2 points/year). Regression analysis with a univariate model showed that the numbers of granzyme B+ cytotoxic cells (relative risk (RR) = 12, p = 0.003), T cells (RR = 11, p = 0.013), and FLS (RR = 10, p = 0.020) discriminated between groups I and II. A multivariate model demonstrated that the numbers of T cells (RR = 1.2, p = 0.015) and FLS (RR = 1.4, p = 0.013) were independent discriminators between groups I and II.
Conclusion: The numbers of granzyme B+ cytotoxic cells, T cells, and FLS in synovial tissue of patients with RA are related to the severity of joint damage. The data suggest a pathogenetic role for these cells in the process of joint damage.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (498.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
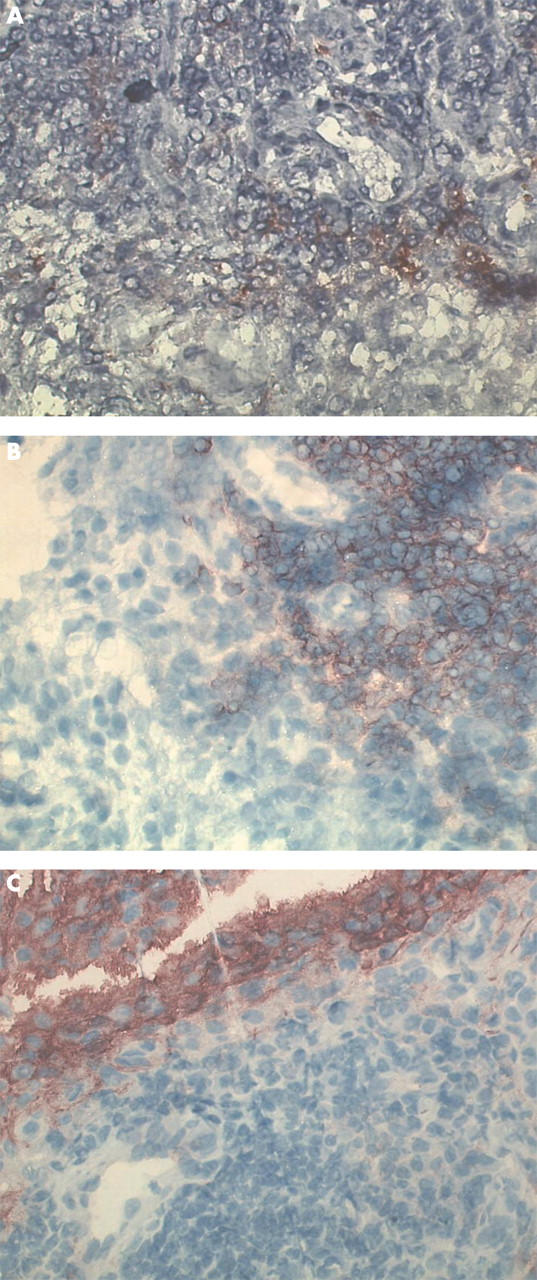
Example of strong positive staining for granzyme B+ cells (A), T cells (B), and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (C) in a patient with unfavourable radiological outcome (x400).
Figure 2 .
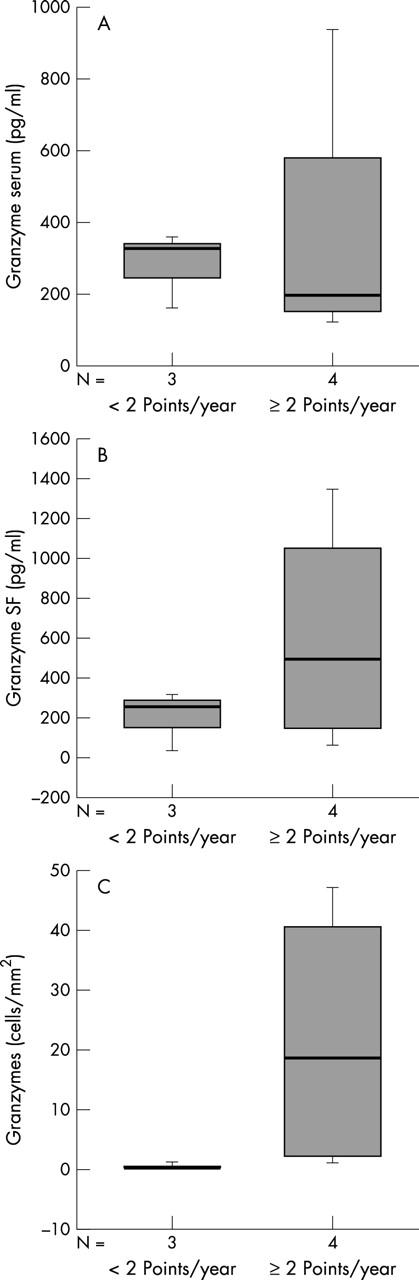
Box plots of the measurements in paired serum, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue of patients with early RA with more favourable (n = 3) and unfavourable (n = 4) radiological outcome. Depicted are (A) granzyme B in serum samples, (B) granzyme B in synovial fluid, and (C) granzyme B+ cells in synovial tissue.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams V. M., Cambridge G., Lydyard P. M., Edwards J. C. Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha production by adhered human monocytes: a key role for Fcgamma receptor type IIIa in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):608–616. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200003)43:3<608::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolon Brad, Shalhoub Victoria, Kostenuik Paul J., Campagnuolo Giuseppe, Morony Sean, Boyle William J., Zack Debra, Feige Ulrich. Osteoprotegerin, an endogenous antiosteoclast factor for protecting bone in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Dec;46(12):3121–3135. doi: 10.1002/art.10680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Stuhlmüller B., Keyszer G., Kinne R. W. Mononuclear phagocytes and rheumatoid synovitis. Mastermind or workhorse in arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Jan;40(1):5–18. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy E. H., Panayi G. S. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 22;344(12):907–916. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103223441207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crotti T. N., Smith M. D., Weedon H., Ahern M. J., Findlay D. M., Kraan M., Tak P. P., Haynes D. R. Receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) expression in synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, osteoarthritis, and from normal patients: semiquantitative and quantitative analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Dec;61(12):1047–1054. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.12.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolhain R. J., Ter Haar N. T., De Kuiper R., Nieuwenhuis I. G., Zwinderman A. H., Breedveld F. C., Miltenburg A. M. Distribution of T cells and signs of T-cell activation in the rheumatoid joint: implications for semiquantitative comparative histology. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Mar;37(3):324–330. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Nov;39(11):1781–1790. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froelich C. J., Zhang X., Turbov J., Hudig D., Winkler U., Hanna W. L. Human granzyme B degrades aggrecan proteoglycan in matrix synthesized by chondrocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):7161–7171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring Steven R., Gravallese Ellen M. Pathogenesis of bone lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002 Jun;4(3):226–231. doi: 10.1007/s11926-002-0069-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravallese E. M., Manning C., Tsay A., Naito A., Pan C., Amento E., Goldring S. R. Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):250–258. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<250::AID-ANR3>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann J., Wishaupt J. O., van Lier R. A., Smeets T. J., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Expression of the activation antigen CD97 and its ligand CD55 in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Apr;42(4):650–658. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199904)42:4<650::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Barg E., Crotti T. N., Holding C., Weedon H., Atkins G. J., Zannetino A., Ahern M. J., Coleman M., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Osteoprotegerin expression in synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathies and osteoarthritis and normal controls. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003 Jan;42(1):123–134. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotake S., Udagawa N., Hakoda M., Mogi M., Yano K., Tsuda E., Takahashi K., Furuya T., Ishiyama S., Kim K. J. Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 May;44(5):1003–1012. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200105)44:5<1003::AID-ANR179>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Haringman J. J., Ahern M. J., Breedveld F. C., Smith M. D., Tak P. P. Quantification of the cell infiltrate in synovial tissue by digital image analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Jan;39(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Versendaal H., Jonker M., Bresnihan B., Post W. J., t Hart B. A., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Asymptomatic synovitis precedes clinically manifest arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Aug;41(8):1481–1488. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199808)41:8<1481::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCachren S. S. Expression of metalloproteinases and metalloproteinase inhibitor in human arthritic synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1085–1093. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye O. J., Vartdal F., Pahle J., Mollnes T. E. IgG and IgA subclass distribution of total immunoglobulin and rheumatoid factors in rheumatoid tissue plasma cells. Scand J Rheumatol. 1990;19(5):333–340. doi: 10.3109/03009749009096788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland Larry W., Alten Rieke, Van den Bosch Filip, Appelboom Thierry, Leon Marc, Emery Paul, Cohen Stanley, Luggen Michael, Shergy William, Nuamah Isaac. Costimulatory blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot, dose-finding, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating CTLA-4Ig and LEA29Y eighty-five days after the first infusion. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jun;46(6):1470–1479. doi: 10.1002/art.10294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherin D., Fitzgerald O., Bresnihan B. Clinical improvement and radiological deterioration in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence that the pathogenesis of synovial inflammation and articular erosion may differ. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Dec;35(12):1263–1268. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.12.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherin D., Fitzgerald O., Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jan;39(1):115–124. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Ladner U., Kriegsmann J., Franklin B. N., Matsumoto S., Geiler T., Gay R. E., Gay S. Synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attach to and invade normal human cartilage when engrafted into SCID mice. Am J Pathol. 1996 Nov;149(5):1607–1615. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pap T., Müller-Ladner U., Gay R. E., Gay S. Fibroblast biology. Role of synovial fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2000 Jun 8;2(5):361–367. doi: 10.1186/ar113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Larsen A., Brooks R. H., Kaye J., Nance E. P., Callahan L. F. Comparison of 3 quantitative measures of hand radiographs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Steinbrocker stage, Kaye modified Sharp score, and Larsen score. J Rheumatol. 1997 Nov;24(11):2106–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronday H. K., van der Laan W. H., Tak P. P., de Roos J. A., Bank R. A., TeKoppele J. M., Froelich C. J., Hack C. E., Hogendoorn P. C., Breedveld F. C. Human granzyme B mediates cartilage proteoglycan degradation and is expressed at the invasive front of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Jan;40(1):55–61. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soden M., Rooney M., Whelan A., Feighery C., Bresnihan B. Immunohistological analysis of the synovial membrane: search for predictors of the clinical course in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Oct;50(10):673–676. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.10.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaeny-Dekking E. H., Hanna W. L., Wolbink A. M., Wever P. C., Kummer J. A., Kummer A. J., Swaak A. J., Middeldorp J. M., Huisman H. G., Froelich C. J. Extracellular granzymes A and B in humans: detection of native species during CTL responses in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1998 Apr 1;160(7):3610–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Bresnihan B. The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Dec;43(12):2619–2633. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200012)43:12<2619::AID-ANR1>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Kummer J. A., Hack C. E., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Erkelens G. W., Meinders A. E., Kluin P. M., Breedveld F. C. Granzyme-positive cytotoxic cells are specifically increased in early rheumatoid synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Dec;37(12):1735–1743. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Smeets T. J., Daha M. R., Kluin P. M., Meijers K. A., Brand R., Meinders A. E., Breedveld F. C. Analysis of the synovial cell infiltrate in early rheumatoid synovial tissue in relation to local disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Feb;40(2):217–225. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Spaeny-Dekking L., Kraan M. C., Breedveld F. C., Froelich C. J., Hack C. E. The levels of soluble granzyme A and B are elevated in plasma and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 May;116(2):366–370. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi H., Iizuka H., Juji T., Nakagawa T., Yamamoto A., Miyazaki T., Koshihara Y., Oda H., Nakamura K., Tanaka S. Involvement of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand/osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis from synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):259–269. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<259::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser Henk, le Cessie Saskia, Vos Koen, Breedveld Ferdinand C., Hazes Johanna M. W. How to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis early: a prediction model for persistent (erosive) arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):357–365. doi: 10.1002/art.10117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanni G., Whelan A., Feighery C., Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophages and joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jan;53(1):39–44. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssef P. P., Kraan M., Breedveld F., Bresnihan B., Cassidy N., Cunnane G., Emery P., Fitzgerald O., Kane D., Lindblad S. Quantitative microscopic analysis of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane samples selected at arthroscopy compared with samples obtained blindly by needle biopsy. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Apr;41(4):663–669. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199804)41:4<663::AID-ART13>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van der Heijde D. M., Te Meerman G. J., van Riel P. L., Houtman P. M., van De Putte L. B., Limburg P. C. The acute-phase response in relation to radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study during the first three years of the disease. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Jun;32 (Suppl 3):9–13. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.suppl_3.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Breedveld F. C. Prognostic factors in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1996 Mar;44:31–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., Schreuder G. M., D'Amaro J., Breedveld F. C. Association of HLA-DR4 with a more progressive disease course in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results of a followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jul;34(7):822–830. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., Schreuder G. M., D'Amaro J., Breedveld F. C. Association of HLA-DR4 with a more progressive disease course in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results of a followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jul;34(7):822–830. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., van der Voort E. A., Breedveld F. C. Clinical significance of rheumatoid factors in early rheumatoid arthritis: results of a follow up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Sep;51(9):1029–1035. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.9.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Vandenbroucke J. P., Breedveld F. C. Factors predicting outcome of rheumatoid arthritis: results of a followup study. J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;20(8):1288–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M. Joint erosions and patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Nov;34 (Suppl 2):74–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., Van de Putte L. Disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jan;51(1):140–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


