Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of monotherapy with adalimumab in patients with RA for whom previous DMARD treatment has failed.
Methods: In a 26 week, double blind, placebo controlled, phase III trial, 544 patients with RA were randomised to monotherapy with adalimumab 20 mg every other week, 20 mg weekly, 40 mg every other week, 40 mg weekly, or placebo. The primary efficacy end point was ≥20% improvement in the ACR core criteria (ACR20 response). Secondary efficacy end points included ACR50, ACR70, EULAR responses, and the Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ DI).
Results: After 26 weeks, patients treated with adalimumab 20 mg every other week, 20 mg weekly, 40 mg every other week, and 40 mg weekly had significantly better response rates than those treated with placebo: ACR20 (35.8%, 39.3%, 46.0%, 53.4%, respectively v 19.1%; p⩽0.01); ACR50 (18.9%, 20.5%, 22.1%, 35.0% v 8.2%; p⩽0.05); ACR70 (8.5%, 9.8%, 12.4%, 18.4% v 1.8%; p⩽0.05). Moderate EULAR response rates were significantly greater with adalimumab than with placebo (41.5%, 48.2%, 55.8%, 63.1% v 26.4%; p⩽0.05). Patients treated with adalimumab achieved better improvements in mean HAQ DI than those receiving placebo (–0.29, –0.39, –0.38, –0.49 v –0.07; p⩽0.01). No significant differences were found between adalimumab and placebo treated patients for serious adverse events, serious infections, or malignancies. Injection site reaction occurred in 10.6% and 0.9% of adalimumab and placebo treated patients, respectively (p⩽0.05).
Conclusion: Among patients with RA for whom previous DMARD treatment had failed, adalimumab monotherapy achieved significant, rapid, and sustained improvements in disease activity and improved physical function and was safe and well tolerated.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (478.0 KB).
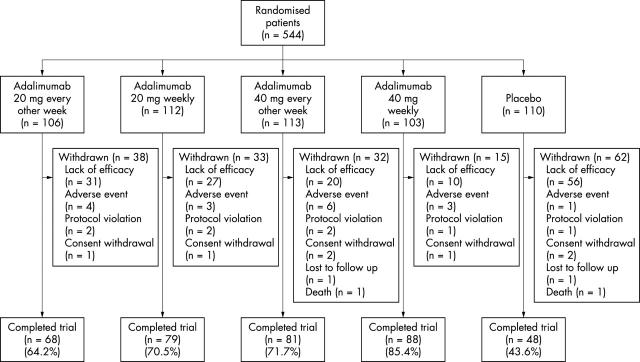
Figure 1 .
Patient disposition.
Figure 2 .
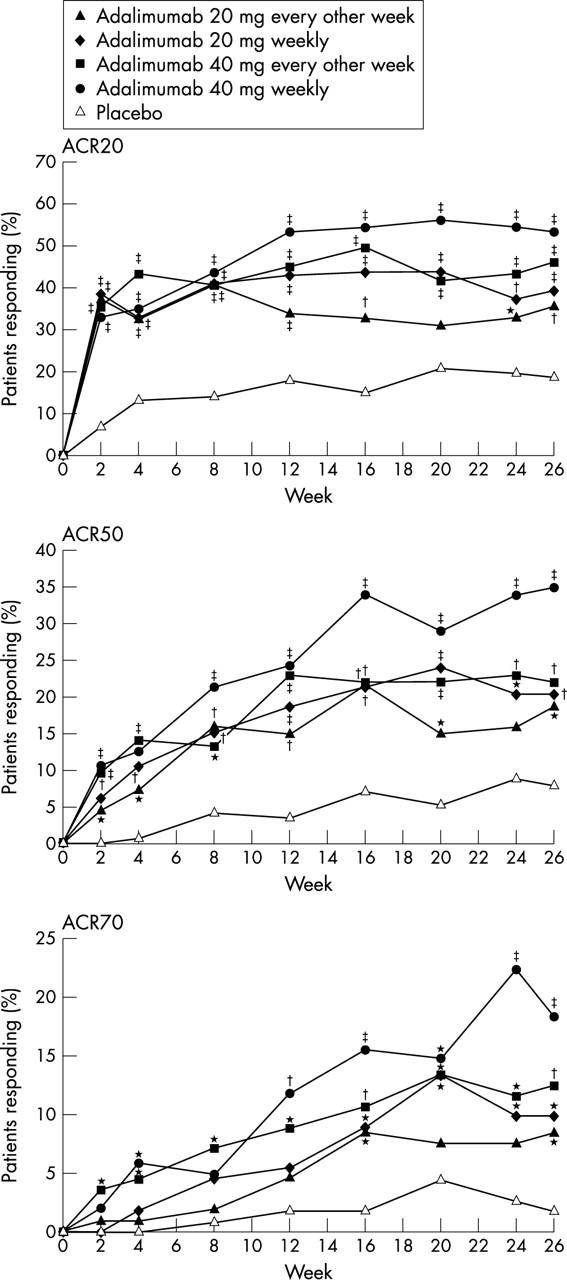
Percentages of patients treated with adalimumab or placebo who had at least 20%, 50%, and 70% improvements in ACR response criteria (ACR20, ACR50, ACR70; observed values). Comparison versus placebo (Pearson's χ2 test): *p⩽0.05; †p⩽0.01; ‡p⩽0.001.
Figure 3 .
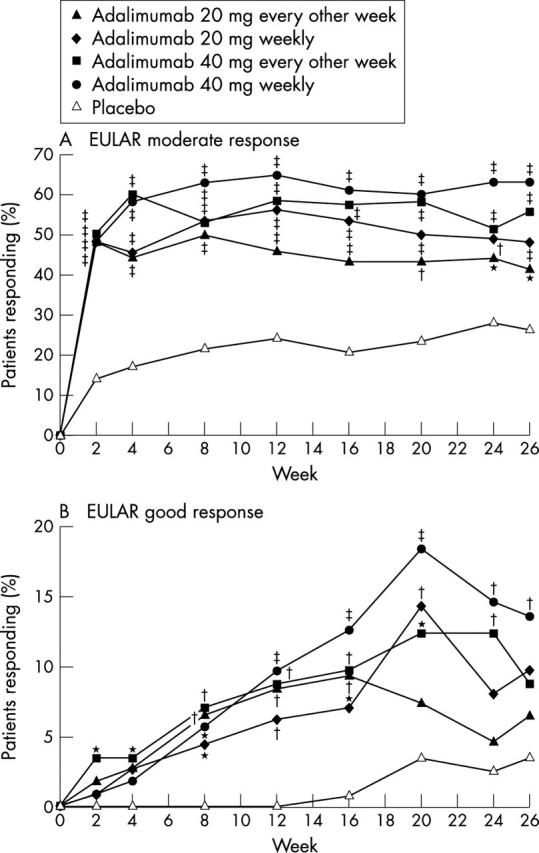
Percentages of patients treated with adalimumab or placebo who had improvements in the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) response criteria (observed values). Comparison versus placebo (Pearson's χ2 test): *p⩽0.05; †p⩽0.01; ‡p⩽0.001.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Rheumatoid Arthritis Guidelines Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: 2002 Update. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):328–346. doi: 10.1002/art.10148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera P., Joosten L. A., den Broeder A. A., van de Putte L. B., van Riel P. L., van den Berg W. B. Effects of treatment with a fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody on the local and systemic homeostasis of interleukin 1 and TNFalpha in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Jul;60(7):660–669. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.7.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera P., van der Maas A., van Ede A. E., Kiemeney B. A. L. M., Laan R. F. J. M., van de Putte L. B. A., van Riel P. L. C. M. Drug survival, efficacy and toxicity of monotherapy with a fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha antibody compared with methotrexate in long-standing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002 Apr;41(4):430–439. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.4.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Kalden J. R., Antoni C., Smolen J. S., Leeb B., Breedveld F. C., Macfarlane J. D., Bijl H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1105–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Chernoff M., Fried B., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Kieszak S., Lightfoot R. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jun;36(6):729–740. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Spitz P. W., Young D. Y. The dimensions of health outcomes: the health assessment questionnaire, disability and pain scales. J Rheumatol. 1982 Sep-Oct;9(5):789–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furst D. E., Keystone E. C., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Antoni C. E., Burmester G. R., Crofford L. J., Kavanaugh A. Updated consensus statement on tumour necrosis factor blocking agents for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases (April 2001). Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Nov;60 (Suppl 3):iii2–iii5. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.90003.iii2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith C. H., Boers M., Bombardier C., Tugwell P. Criteria for clinically important changes in outcomes: development, scoring and evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis patient and trial profiles. OMERACT Committee. J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20(3):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane J., Gershon S., Wise R. P., Mirabile-Levens E., Kasznica J., Schwieterman W. D., Siegel J. N., Braun M. M. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001 Oct 11;345(15):1098–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroesen S., Widmer A. F., Tyndall A., Hasler P. Serious bacterial infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis under anti-TNF-alpha therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003 May;42(5):617–621. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. M., Weinblatt M. E. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001 Sep 15;358(9285):903–911. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R., St Clair E. W., Breedveld F., Furst D., Kalden J., Weisman M., Smolen J., Emery P., Harriman G., Feldmann M. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)05246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W., Baumgartner S. W., Schiff M. H., Tindall E. A., Fleischmann R. M., Weaver A. L., Ettlinger R. E., Cohen S., Koopman W. J., Mohler K. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med. 1997 Jul 17;337(3):141–147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199707173370301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W., Schiff M. H., Baumgartner S. W., Tindall E. A., Fleischmann R. M., Bulpitt K. J., Weaver A. L., Keystone E. C., Furst D. E., Mease P. J. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Mar 16;130(6):478–486. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-6-199903160-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant M. J., Williams A. L., O'Sullivan M. M., Lewis P. A., Coles E. C., Jessop J. D. Relationship between time-integrated C-reactive protein levels and radiologic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jul;43(7):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200007)43:7<1473::AID-ANR9>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokka Tuulikki, Pincus Theodore. Eligibility of patients in routine care for major clinical trials of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Feb;48(2):313–318. doi: 10.1002/art.10817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt Michael E., Keystone Edward C., Furst Daniel E., Moreland Larry W., Weisman Michael H., Birbara Charles A., Teoh Leah A., Fischkoff Steven A., Chartash Elliot K. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jan;48(1):35–45. doi: 10.1002/art.10697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman Michael H., Moreland Larry W., Furst Daniel E., Weinblatt Michael E., Keystone Edward C., Paulus Harold E., Teoh Leah S., Velagapudi Raja B., Noertersheuser Peter A., Granneman G. Richard. Efficacy, pharmacokinetic, and safety assessment of adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody, in adults with rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate: a pilot study. Clin Ther. 2003 Jun;25(6):1700–1721. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(03)80164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsing P. M., van Gestel A. M., Swinkels H. L., Kiemeney L. A., van Riel P. L. The relationship between disease activity, joint destruction, and functional capacity over the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):2009–2017. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2009::AID-ART349>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Broeder A. A., Joosten L. A. B., Saxne T., Heinegård D., Fenner H., Miltenburg A. M. M., Frasa W. L. H., van Tits L. J., Buurman W. A., van Riel P. L. C. M. Long term anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: effect on radiological course and prognostic value of markers of cartilage turnover and endothelial activation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Apr;61(4):311–318. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.4.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Riel P. L., van Gestel A. M., van de Putte L. B. Development and validation of response criteria in rheumatoid arthritis: steps towards an international consensus on prognostic markers. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Sep;35 (Suppl 2):4–7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_2.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte L. B. A., Rau R., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Malaise M. G., van Riel P. L. C. M., Schattenkirchner M., Emery P., Burmester G. R., Zeidler H. Efficacy and safety of the fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody adalimumab (D2E7) in DMARD refractory patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 12 week, phase II study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Dec;62(12):1168–1177. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.009563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., Jacobs J. W. The original "DAS" and the "DAS28" are not interchangeable: comment on the articles by Prevoo et al. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 May;41(5):942–945. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199805)41:5<942::AID-ART26>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., Theunisse L. A., Lubberts E. W., van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Nov;49(11):916–920. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.11.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]