Abstract
Methods: 20 patients with clinically active synovitis of a small joint unresponsive to systemic drug treatment underwent a sonographic guided intralesional injection with triamcinolone acetonide. Clinical examinations were carried out by a trained rheumatologist. GSS and PDS examinations were performed independently by two examiners unaware of the results of the clinical examination. Joint cavity widening and power Doppler signal were evaluated and graded on a semiquantitative scale ranging from 1 to 4. Clinical and sonographic follow up examinations were carried out 2 weeks after the injection with triamcinolone acetonide.
Results: All intra-articular injections were successfully carried out and documented under sonographic guidance. In 19/20 patients, baseline sonographic examinations clearly detected morphological and perfusional signs of synovitis. At follow up examinations, clinical and sonographic scores had improved significantly.
Conclusion: GSS and PDS appear to be a useful adjunctive tool for assessing short term soft tissue changes induced by intra-articular injection treatment with triamcinolone acetonide in small joints of patients with chronic arthritis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (137.7 KB).
Figure 1 .
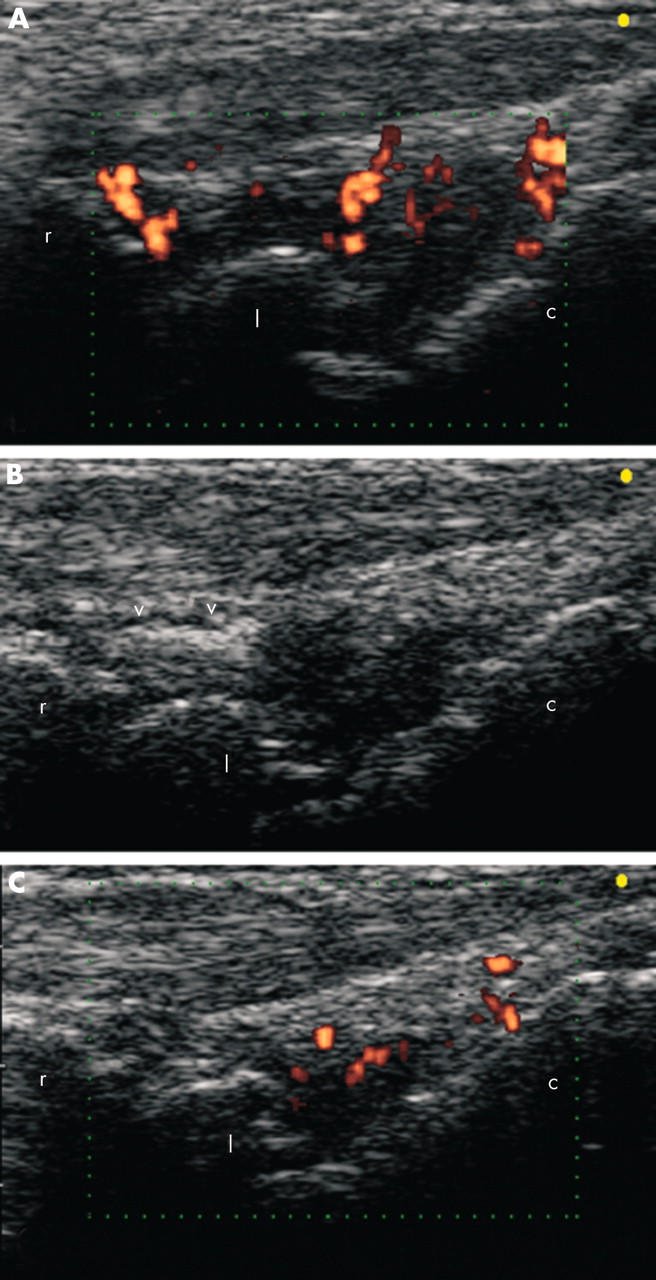
(A, B) Baseline ultrasound examination on longitudinal dorsal scan of the wrist joint of an 82 year old patient with rheumatoid arthritis (patient number 4). An intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide (30 mg) was performed under sonographic guidance. Triamcinolone appeared as an echogenic area within the radiocarpal joint cavity (V). (C) Follow up ultrasound examination detected a clearly evident decrease of both joint cavity widening (GSS score reduced from 3 to 1) and power Doppler signals (PDS score reduced from 4 to 2). c, capitate bone; l, lunate bone; r, radius.
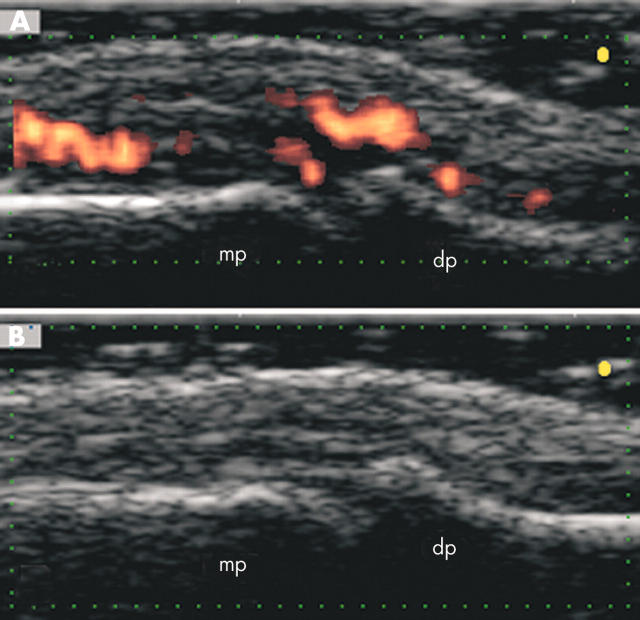
Figure 2 .
A 30 year old patient with psoriatic arthritis (patient number 17) presented at baseline clinical examination with a severe pain of the distal interphalangeal joint of his left second finger (VAS score 8; tenderness score 3). At follow up clinical examination the patient had complete remission of pain (VAS score 0; tenderness score 0). (A) Baseline ultrasound examination on longitudinal dorsal scan detected evident signs of active synovitis: joint cavity widening (GSS score 2) and intra-articular power Doppler signals (PDS score 4). A sonographic guided injection with 10 mg of triamcinolone acetonide was performed. (B) Two weeks after the injection an ultrasound examination performed at the same plane of scanning showed the disappearance of both GSS (score 1) and PDS (score 1) findings. dp, distal phalanx; mp, middle phalanx.