Abstract
Methods: An exhaustive systematic search was performed. Inclusion criteria were: RCT or controlled study, duration of 5 days at least, inactive control, assessment of minor or major NSAID adverse effects, publication range January 1985 to January 2003. The publications retrieved were assessed during a specifically dedicated WHO meeting including leading experts in all related fields. Statistics were performed conservatively. Meta-regression was performed by regressing NSAID adjusted estimates against study duration categories.
Results: Among RCT data, indolic derivates provided a significantly higher risk of GI complications related to NSAID use than for non-users: RR = 2.25 (1.00; 5.08) than did other compounds: naproxen: RR = 1.83 (1.25; 2.68); diclofenac: RR = 1.73 (1.21; 2.46); piroxicam: RR = 1.66 (1.14; 2.44); tenoxicam: RR = 1.43 (0.40; 5.14); meloxicam: RR = 1.24 (0.98; 1.56), and ibuprofen: RR = 1.19 (0.93; 1.54). Indometacin users had a maximum relative risk for complication at 14 days. The other compounds presented a better profile, with a maximum risk at 50 days. Significant additional risk factors included age, dose, and underlying disease. The controlled cohort studies provided higher estimates: RR = 2.22 (1.7; 2.9). Publication bias testing was significant, towards a selective publication of deleterious effects of NSAIDs from small sized studies.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis characterised the "compound" and "time" aspects of the GI toxicity of non-selective NSAIDs. The risk/benefit ratio of such compounds should thus be carefully and individually evaluated at the start of long term treatment.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (415.4 KB).
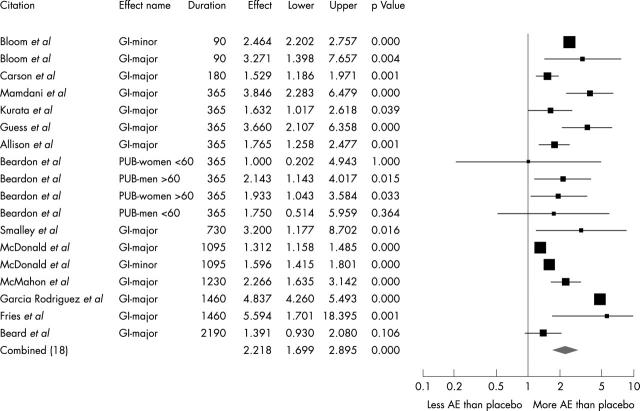
Figure 1.
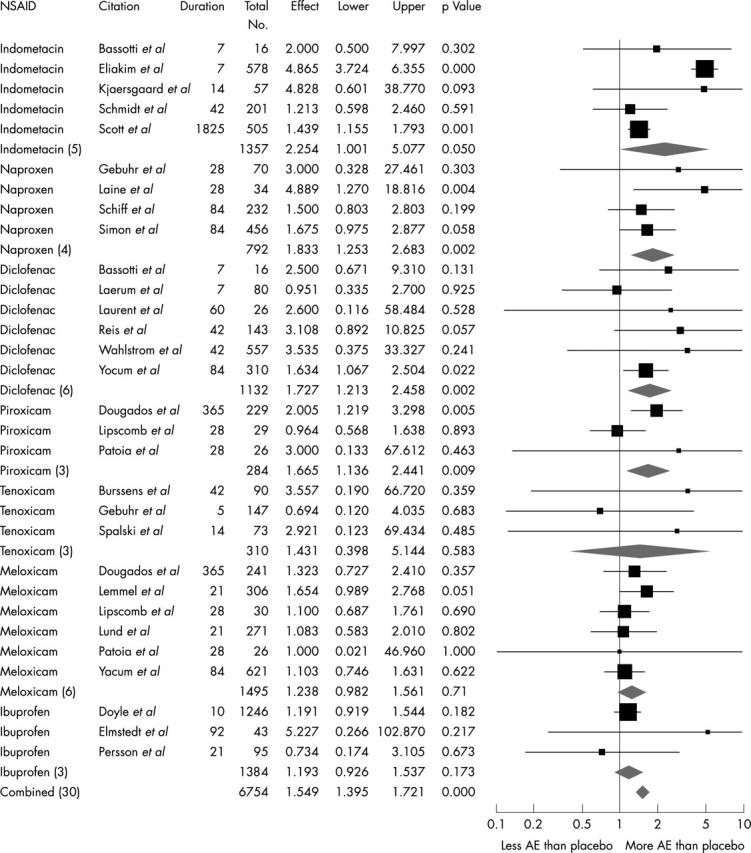
Relative risk of GI complications depending on NSAID (RCT).
Figure 4.
Relative risk of GI complications provided by longitudinal controlled cohort studies. PUB, perforation, ulcers, or bleeding.
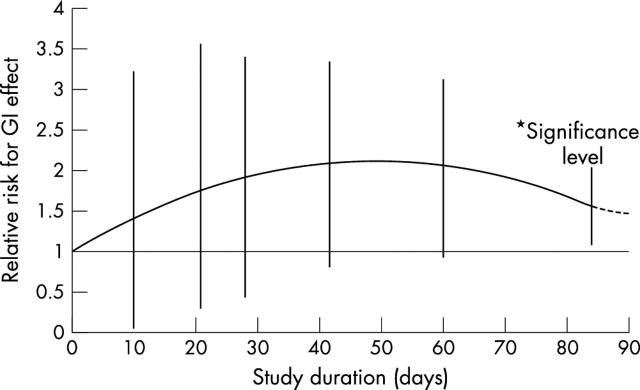
Figure 2.
Meta-regression of relative risk against study duration (non-indometacin compounds).
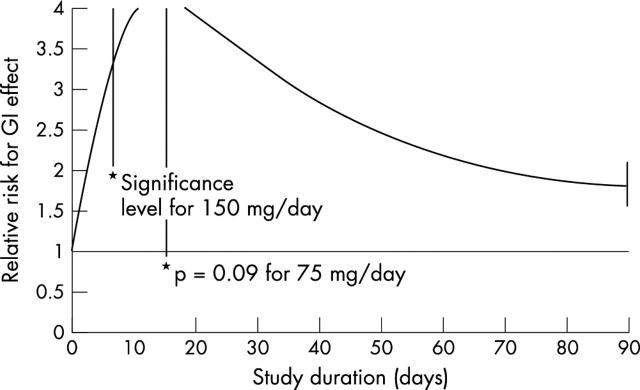
Figure 3.
Meta-regression of relative risk against study duration (indometacin).
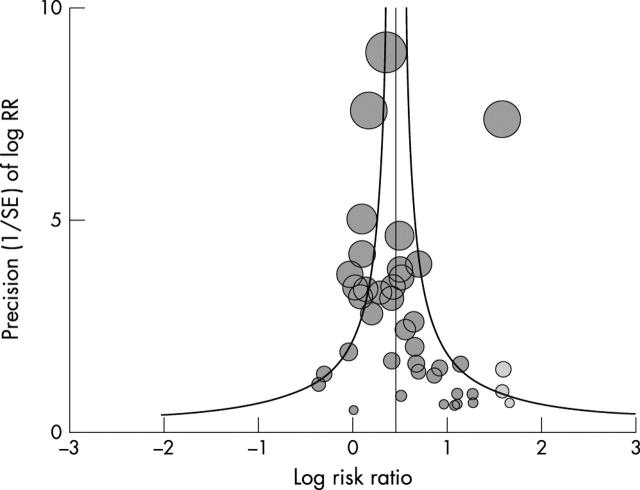
Figure 5.
Funnel plot.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. C., Howatson A. G., Torrance C. J., Lee F. D., Russell R. I. Gastrointestinal damage associated with the use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 10;327(11):749–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209103271101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassotti G., Bucaneve G., Furno P., Morelli A., Del Favero A. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study on effects of diclofenac sodium and indomethacin on postprandial gastric motility in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1998 Jun;43(6):1172–1176. doi: 10.1023/a:1018883102636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard K., Walker A. M., Perera D. R., Jick H. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hospitalization for gastroesophageal bleeding in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Sep;147(9):1621–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardon P. H., Brown S. V., McDevitt D. G. Gastrointestinal events in patients prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a controlled study using record linkage in Tayside. Q J Med. 1989 Jun;71(266):497–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry H., Bird H. A., Black C., Blake D. R., Freeman A. M., Golding D. N., Hamilton E. B., Jayson M. I., Kidd B., Kohn H. A double blind, multicentre, placebo controlled trial of lornoxicam in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Feb;51(2):238–242. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.2.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. S. Risk and cost of gastrointestinal side effects associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Arch Intern Med. 1989 May;149(5):1019–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollini P., García Rodríguez L. A., Pérez Gutthann S., Walker A. M. The impact of research quality and study design on epidemiologic estimates of the effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on upper gastrointestinal tract disease. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Jun;152(6):1289–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Laine L., Reicin A., Shapiro D., Burgos-Vargas R., Davis B., Day R., Ferraz M. B., Hawkey C. J., Hochberg M. C. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 23;343(21):1520-8, 2 p following 1528. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011233432103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burssens A., Thiery J., Kohl P., Molderez A., Haazen L. Prevention of heterotopic ossification with tenoxicam following total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-finding study. Acta Orthop Belg. 1995;61(3):205–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson J. L., Strom B. L., Soper K. A., West S. L., Morse M. L. The association of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Jan;147(1):85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case L. Douglas, Kimmick Gretchen, Paskett Electra D., Lohman Kurt, Tucker Robert. Interpreting measures of treatment effect in cancer clinical trials. Oncologist. 2002;7(3):181–187. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.7-3-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash J. M., Klippel J. H. Second-line drug therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 12;330(19):1368–1375. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405123301908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz G. A., Miller J. N., Mosteller F. How study design affects outcomes in comparisons of therapy. I: Medical. Stat Med. 1989 Apr;8(4):441–454. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780080408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. M., Wallace J. L. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: new insights into an old problem. J Gastroenterol. 1997 Feb;32(1):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01213310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derry S., Loke Y. K. Risk of gastrointestinal haemorrhage with long term use of aspirin: meta-analysis. BMJ. 2000 Nov 11;321(7270):1183–1187. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7270.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickersin K., Scherer R., Lefebvre C. Identifying relevant studies for systematic reviews. BMJ. 1994 Nov 12;309(6964):1286–1291. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6964.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., Gueguen A., Nakache J. P., Velicitat P., Veys E. M., Zeidler H., Calin A. Ankylosing spondylitis: what is the optimum duration of a clinical study? A one year versus a 6 weeks non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug trial. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Mar;38(3):235–244. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.3.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., Nguyen M., Caporal R., Legeais J., Bouxin-Sauzet A., Pellegri-Guegnault B., Gomeni C. Ximoprofen in ankylosing spondylitis. A double blind placebo controlled dose ranging study. Scand J Rheumatol. 1994;23(5):243–248. doi: 10.3109/03009749409103723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle G., Furey S., Berlin R., Cooper S., Jayawardena S., Ashraf E., Baird L. Gastrointestinal safety and tolerance of ibuprofen at maximum over-the-counter dose. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Jul;13(7):897–906. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger M., Davey Smith G., Schneider M., Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997 Sep 13;315(7109):629–634. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Ophir M., Rachmilewitz D. Duodenal mucosal injury with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Aug;9(4):395–399. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198708000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmstedt E., Lindholm T. S., Nilsson O. S., Törnkvist H. Effect of ibuprofen on heterotopic ossification after hip replacement. Acta Orthop Scand. 1985 Feb;56(1):25–27. doi: 10.3109/17453678508992973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: back to the future. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Aug;38(8):693–696. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.8.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Williams C. A., Bloch D. A., Michel B. A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated gastropathy: incidence and risk factor models. Am J Med. 1991 Sep;91(3):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90118-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. E., Jaakkimainen L., Bombardier C. Risk for serious gastrointestinal complications related to use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 15;115(10):787–796. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-10-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García Rodríguez L. A., Cattaruzzi C., Troncon M. G., Agostinis L. Risk of hospitalization for upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding associated with ketorolac, other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, calcium antagonists, and other antihypertensive drugs. Arch Intern Med. 1998 Jan 12;158(1):33–39. doi: 10.1001/archinte.158.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner A. Adaptation in the pharmaceutical industry, with particular reference to gastrointestinal drugs and diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1992;193:83–89. doi: 10.3109/00365529209096011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebuhr P., Sletgård J., Dalsgård J., Soelberg M., Keisu K., Hänninen A., Crawford M. Heterotopic ossification after hip arthroplasty: a randomized double-blind multicenter study tenoxicam in 147 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996 Feb;67(1):29–32. doi: 10.3109/17453679608995604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebuhr P., Soelberg M., Orsnes T., Wilbek H. Naproxen prevention of heterotopic ossification after hip arthroplasty. A prospective control study of 55 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991 Jun;62(3):226–229. doi: 10.3109/17453679108993597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. R., Piper J. M., Daugherty J. R., Snowden M., Ray W. A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and increased risk for peptic ulcer disease in elderly persons. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 15;114(4):257–263. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-4-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guess H. A., West R., Strand L. M., Helston D., Lydick E. G., Bergman U., Wolski K. Fatal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage or perforation among users and nonusers of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Saskatchewan, Canada 1983. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(88)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey Chris J. NSAID toxicity: where are we and how do we go forward? J Rheumatol. 2002 Apr;29(4):650–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D., Lim L. L., Garcia Rodriguez L. A., Perez Gutthann S., Carson J. L., Griffin M., Savage R., Logan R., Moride Y., Hawkey C. Variability in risk of gastrointestinal complications with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: results of a collaborative meta-analysis. BMJ. 1996 Jun 22;312(7046):1563–1566. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7046.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D., Lim L. L., Garcia Rodriguez L. A., Perez Gutthann S., Carson J. L., Griffin M., Savage R., Logan R., Moride Y., Hawkey C. Variability in risk of gastrointestinal complications with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: results of a collaborative meta-analysis. BMJ. 1996 Jun 22;312(7046):1563–1566. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7046.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D., Lim L. L., Garcia Rodriguez L. A., Perez Gutthann S., Carson J. L., Griffin M., Savage R., Logan R., Moride Y., Hawkey C. Variability in risk of gastrointestinal complications with individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: results of a collaborative meta-analysis. BMJ. 1996 Jun 22;312(7046):1563–1566. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7046.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoikka V., Lindholm T. S., Eskola A. Flurbiprofen inhibits heterotopic bone formation in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;109(4):224–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00453146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Jia Qing, Sridhar Subbaramiah, Hunt Richard H. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in peptic-ulcer disease: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2002 Jan 5;359(9300):14–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jadad A. R., Moore R. A., Carroll D., Jenkinson C., Reynolds D. J., Gavaghan D. J., McQuay H. J. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996 Feb;17(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz Nathaniel. Coxibs: Evolving role in pain management. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Dec;32(3 Suppl 1):15–24. doi: 10.1053/sarh.2002.37218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaersgaard-Andersen P., Nafei A., Teichert G., Kristensen O., Schmidt S. A., Keller J., Lucht U. Indomethacin for prevention of heterotopic ossification. A randomized controlled study in 41 hip arthroplasties. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993 Dec;64(6):639–642. doi: 10.3109/17453679308994587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata J. H., Nogawa A. N. Meta-analysis of risk factors for peptic ulcer. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, Helicobacter pylori, and smoking. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997 Jan;24(1):2–17. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199701000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata J. H., Nogawa A. N., Noritake D. NSAIDs increase risk of gastrointestinal bleeding in primary care patients with dyspepsia. J Fam Pract. 1997 Sep;45(3):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laerum E., Ommundsen O. E., Grønseth J. E., Christiansen A., Fagertun H. E. Oral diclofenac in the prophylactic treatment of recurrent renal colic. A double-blind comparison with placebo. Eur Urol. 1995;28(2):108–111. doi: 10.1159/000475031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine L. Approaches to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in the high-risk patient. Gastroenterology. 2001 Feb;120(3):594–606. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.21907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine L., Sloane R., Ferretti M., Cominelli F. A randomized double-blind comparison of placebo, etodolac, and naproxen on gastrointestinal injury and prostaglandin production. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995 Nov;42(5):428–433. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(95)70045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine Loren. Coxibs were not cost-effective for arthritis pain in patients with average risk for ulcer complications. ACP J Club. 2003 Sep-Oct;139(2):53–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman M. J., Jensen D. M., Watson D. J., Harper S. E., Zhao P. L., Quan H., Bolognese J. A., Simon T. J. Adverse upper gastrointestinal effects of rofecoxib compared with NSAIDs. JAMA. 1999 Nov 24;282(20):1929–1933. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.20.1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanza F. L. A review of gastric ulcer and gastroduodenal injury in normal volunteers receiving aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;163:24–31. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent J., Belghiti D., Bruneau C., Lagrue G. Diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, decreases proteinuria in some glomerular diseases: a controlled study. Am J Nephrol. 1987;7(3):198–202. doi: 10.1159/000167463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmel E. M., Bolten W., Burgos-Vargas R., Platt P., Nissilä M., Sahlberg D., Björneboe O., Baumgartner H., Valat J. P., Franchimont P. Efficacy and safety of meloxicam in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997 Feb;24(2):282–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein D. R., Syngal S., Wolfe M. M. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and the gastrointestinal tract. The double-edged sword. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):5–18. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijmer J. G., Mol B. W., Heisterkamp S., Bonsel G. J., Prins M. H., van der Meulen J. H., Bossuyt P. M. Empirical evidence of design-related bias in studies of diagnostic tests. JAMA. 1999 Sep 15;282(11):1061–1066. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.11.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb G. R., Wallis N., Armstrong G., Rees W. D. Gastrointestinal tolerability of meloxicam and piroxicam: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Aug;46(2):133–137. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B., Distel M., Bluhmki E. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of efficacy and tolerance of meloxicam treatment in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(1):32–37. doi: 10.1080/030097498441146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. M., Morant S. V., Robinson G. C., Shield M. J., McGilchrist M. M., Murray F. E., McDevitt D. G. Association of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with continued exposure: cohort study. BMJ. 1997 Nov 22;315(7119):1333–1337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7119.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamdani Muhammad, Rochon Paula A., Juurlink David N., Kopp Alex, Anderson Geoffrey M., Naglie Gary, Austin Peter C., Laupacis Andreas. Observational study of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage in elderly patients given selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors or conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. BMJ. 2002 Sep 21;325(7365):624–624. doi: 10.1136/bmj.325.7365.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. D., Evans J. M., White G., Murray F. E., McGilchrist M. M., McDevitt D. G., MacDonald T. M. A cohort study (with re-sampled comparator groups) to measure the association between new NSAID prescribing and upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage and perforation. J Clin Epidemiol. 1997 Mar;50(3):351–356. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(96)00361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina Santillán R., Reyes García G., Mateos García E. Prevention of gastroduodenal injury induced by NSAIDs with low-dose misoprostol. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1999;42:33–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal B. C., Rodgers A., Clark T., Gray H., Reid I. R., Dunn L., MacMahon S. W. A systematic survey of 13 randomized trials of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of heterotopic bone formation after major hip surgery. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000 Apr;71(2):122–128. doi: 10.1080/000164700317413076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofman Joshua J., MacLean Catherine H., Straus Walter L., Morton Sally C., Berger Marc L., Roth Elizabeth A., Shekelle Paul. A metaanalysis of severe upper gastrointestinal complications of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. J Rheumatol. 2002 Apr;29(4):804–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson P. E., Sodemann B., Nilsson O. S. Preventive effects of ibuprofen on periarticular heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. A randomized double-blind prospective study of treatment time. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998 Apr;69(2):111–115. doi: 10.3109/17453679809117608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prupas H. M., Loose L. D., Spindler J. S., Dietz A. J., Jr, Gum O. B., Weisman M. H., Gordon G., Wolf R. E., Turner R. A., Collins R. L. Tenidap in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A 4-week, placebo-controlled study. Scand J Rheumatol. 1996;25(6):345–351. doi: 10.3109/03009749609065645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahme E., Joseph L., Kong S. X., Watson D. J., Pellissier J. M., LeLorier J. Gastrointestinal-related healthcare resource usage associated with a fixed combination of diclofenac and misoprostol versus other NSAIDs. Pharmacoeconomics. 2001;19(5 Pt 2):577–588. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200119050-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis H. J., Küsswetter W., Schellinger T. The suppression of heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 1992;16(2):140–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00180205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richy Florent, Bousquet Jean, Ehrlich George E., Meunier Pierre J., Israel Elliot, Morii Hirotoshi, Devogelaer Jean-Pierre, Peel Nicola, Haim Muriel, Bruyere Olivier. Inhaled corticosteroids effects on bone in asthmatic and COPD patients: a quantitative systematic review. Osteoporos Int. 2003 Apr 23;14(3):179–190. doi: 10.1007/s00198-003-1398-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff M. H. A comparison of Naprelan and Naprosyn in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 1996 Sep;25(9 Suppl):14–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt S. A., Kjaersgaard-Andersen P., Pedersen N. W., Kristensen S. S., Pedersen P., Nielsen J. B. The use of indomethacin to prevent the formation of heterotopic bone after total hip replacement. A randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988 Jul;70(6):834–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J., Ballard I. M., Constantine G., McDonald P. Double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of the safety and efficacy of orally administered etodolac and nabumetone in patients with active osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Ther. 1995 Jul-Aug;17(4):602–612. doi: 10.1016/0149-2918(95)80037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Berry H., Capell H., Coppock J., Daymond T., Doyle D. V., Fernandes L., Hazleman B., Hunter J., Huskisson E. C. The long-term effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Oct;39(10):1095–1101. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.10.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. S., Weaver A. L., Graham D. Y., Kivitz A. J., Lipsky P. E., Hubbard R. C., Isakson P. C., Verburg K. M., Yu S. S., Zhao W. W. Anti-inflammatory and upper gastrointestinal effects of celecoxib in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1999 Nov 24;282(20):1921–1928. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.20.1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Triadafilopoulos G. Epidemiology of NSAID induced gastrointestinal complications. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1999 Apr;56:18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley W. E., Ray W. A., Daugherty J. R., Griffin M. R. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the incidence of hospitalizations for peptic ulcer disease in elderly persons. Am J Epidemiol. 1995 Mar 15;141(6):539–545. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpalski M., Hayez J. P. Objective functional assessment of the efficacy of tenoxicam in the treatment of acute low back pain. A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Jan;33(1):74–78. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramèr M. R., Moore R. A., Reynolds D. J., McQuay H. J. Quantitative estimation of rare adverse events which follow a biological progression: a new model applied to chronic NSAID use. Pain. 2000 Mar;85(1-2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(99)00267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström O., Risto O., Djerf K., Hammerby S. Heterotopic bone formation prevented by diclofenac. Prospective study of 100 hip arthroplasties. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991 Oct;62(5):419–421. doi: 10.3109/17453679108996636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. C., Brookes S. T., Kirwan J. R., Faulkner A. Non-aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD000142–CD000142. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum D., Fleischmann R., Dalgin P., Caldwell J., Hall D., Roszko P. Safety and efficacy of meloxicam in the treatment of osteoarthritis: a 12-week, double-blind, multiple-dose, placebo-controlled trial. The Meloxicam Osteoarthritis Investigators. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Oct 23;160(19):2947–2954. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.19.2947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]