Abstract
Objectives: To identify the immunodominant T cell epitopes of the topoisomerase I protein in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and control subjects, using computational analysis software (TEPITOPE) and T cell proliferation assays.
Methods: Six oligopeptides, predicted by TEPITOPE software as potential topoisomerase protein epitopes, were used to perform T cell proliferation assays in 21 patients with SSc and 15 healthy controls.
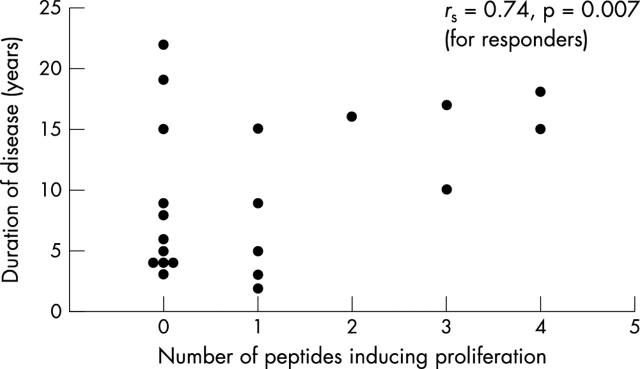
Results: A positive response to at least one of the peptides was seen in 10/21 patients and 7/15 healthy controls. Among responders, the proliferative response was limited to a single peptide in 6/7 healthy controls, whereas 5/10 patients responded to more than one peptide. In responding patients a significant correlation was found between disease duration and number of peptides inducing a response (p = 0.007).
Conclusions: Several T cell epitopes of the topoisomerase I protein have been identified and evidence has been found to suggest epitope spreading in patients with SSc.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (109.4 KB).
Figure 1.
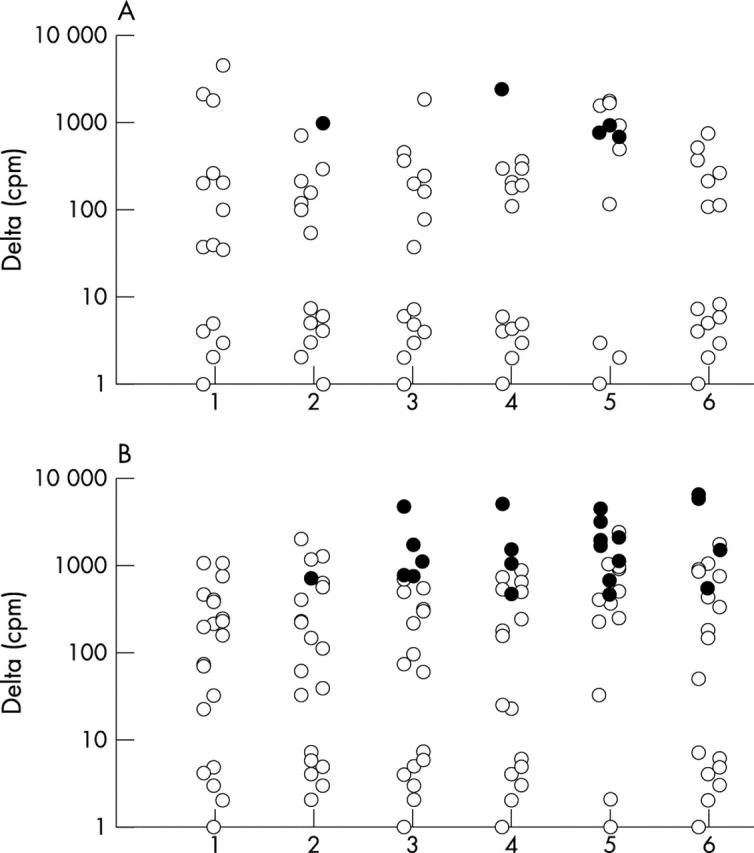
Dot histogram showing the average change in the number of counts per minute (Δcpm) for the proliferation assays to each of the peptides in controls (A) and patients with SSc (B). Filled circles show reactions with an SI >2.
Figure 2.
Significant correlation between disease duration and number of peptides inducing proliferation in patients with SSc.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abulafia-Lapid R., Elias D., Raz I., Keren-Zur Y., Atlan H., Cohen I. R. T cell proliferative responses of type 1 diabetes patients and healthy individuals to human hsp60 and its peptides. J Autoimmun. 1999 Mar;12(2):121–129. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1998.0262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. C., Nicholson L. B., Legge K. L., Turchin V., Zaghouani H., Kuchroo V. K. High frequency of autoreactive myelin proteolipid protein-specific T cells in the periphery of naive mice: mechanisms of selection of the self-reactive repertoire. J Exp Med. 2000 Mar 6;191(5):761–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernasconi Nadia L., Traggiai Elisabetta, Lanzavecchia Antonio. Maintenance of serological memory by polyclonal activation of human memory B cells. Science. 2002 Dec 13;298(5601):2199–2202. doi: 10.1126/science.1076071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunce M., Fanning G. C., Welsh K. I. Comprehensive, serologically equivalent DNA typing for HLA-B by PCR using sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP). Tissue Antigens. 1995 Feb;45(2):81–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1995.tb02422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning G. C., Welsh K. I., Bunn C., Du Bois R., Black C. M. HLA associations in three mutually exclusive autoantibody subgroups in UK systemic sclerosis patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Feb;37(2):201–207. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Hasegawa M., Takehara K., Mukaida N., Sato S. Abnormal expression of intracellular cytokines and chemokine receptors in peripheral blood T lymphocytes from patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Dec;130(3):548–556. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.02017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist F. C., Bunn C., Foley P. J., Lympany P. A., Black C. M., Welsh K. I., du Bois R. M. Class II HLA associations with autoantibodies in scleroderma: a highly significant role for HLA-DP. Genes Immun. 2001 Apr;2(2):76–81. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey G. R., Butts S., Rands A. L., Patel Y., McHugh N. J. Clinical and serological associations with anti-RNA polymerase antibodies in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Aug;117(2):395–402. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. A., Atamas S. P., Yurovsky V. V., Luzina I., Wigley F. M., White B. Diversity and plasticity of the anti-DNA topoisomerase I autoantibody response in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Dec;43(12):2733–2742. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200012)43:12<2733::AID-ANR13>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallenberg C. G., Wouda A. A., Hoet M. H., van Venrooij W. J. Development of connective tissue disease in patients presenting with Raynaud's phenomenon: a six year follow up with emphasis on the predictive value of antinuclear antibodies as detected by immunoblotting. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Aug;47(8):634–641. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.8.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karandikar N. J., Eagar T. N., Vanderlugt C. L., Bluestone J. A., Miller S. D. CTLA-4 downregulates epitope spreading and mediates remission in relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2000 Sep 22;109(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karandikar N. J., Vanderlugt C. L., Walunas T. L., Miller S. D., Bluestone J. A. CTLA-4: a negative regulator of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1996 Aug 1;184(2):783–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Feghali C. A., Medsger T. A., Jr, Wright T. M. Autoreactive T cells to topoisomerase I in monozygotic twins discordant for systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Jul;44(7):1654–1659. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200107)44:7<1654::AID-ART288>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Kaburaki J., Mimori T., Kawakami Y., Tojo T. Longitudinal analysis of autoantibody response to topoisomerase I in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 May;43(5):1074–1084. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200005)43:5<1074::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Kaburaki J., Okano Y., Inoko H., Tsuji K. The HLA-DR and DQ genes control the autoimmune response to DNA topoisomerase I in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1296–1301. doi: 10.1172/JCI116703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Kaburaki J., Okano Y., Tojo T., Homma M. Clinical and prognostic associations based on serum antinuclear antibodies in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jan;37(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Medsger T. A., Jr, Wright T. M. Highly restricted TCR-alpha beta usage by autoreactive human T cell clones specific for DNA topoisomerase I: recognition of an immunodominant epitope. J Immunol. 1997 Jan 1;158(1):485–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Medsger T. A., Jr, Wright T. M. T and B cell collaboration is essential for the autoantibody response to DNA topoisomerase I in systemic sclerosis. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 1;155(5):2703–2714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwana M., Medsger T. A., Jr, Wright T. M. T cell proliferative response induced by DNA topoisomerase I in patients with systemic sclerosis and healthy donors. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jul;96(1):586–596. doi: 10.1172/JCI118071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok W. W., Gebe J. A., Liu A., Agar S., Ptacek N., Hammer J., Koelle D. M., Nepom G. T. Rapid epitope identification from complex class-II-restricted T-cell antigens. Trends Immunol. 2001 Nov;22(11):583–588. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(01)02038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavalia C., Scaletti C., Romagnani P., Carossino A. M., Pignone A., Emmi L., Pupilli C., Pizzolo G., Maggi E., Romagnani S. Type 2 helper T-cell predominance and high CD30 expression in systemic sclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1997 Dec;151(6):1751–1758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRae B. L., Vanderlugt C. L., Dal Canto M. C., Miller S. D. Functional evidence for epitope spreading in the relapsing pathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):75–85. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman B. W., Wigley F. M., Stair R. W. Interleukin-1, interleukin-2, interleukin-4, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interferon-gamma levels in sera from patients with scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jan;35(1):67–72. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriss T. B., Hu P. Q., Wright T. M. Distinct autoreactive T cell responses to native and fragmented DNA topoisomerase I: influence of APC type and IL-2. J Immunol. 2001 May 1;166(9):5456–5463. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.9.5456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rands A. L., Whyte J., Cox B., Hall N. D., McHugh N. J. MHC class II associations with autoantibody and T cell immune responses to the scleroderma autoantigen topoisomerase I. J Autoimmun. 2000 Dec;15(4):451–458. doi: 10.1006/jaut.2000.0447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Hamaguchi Y., Hasegawa M., Takehara K. Clinical significance of anti-topoisomerase I antibody levels determined by ELISA in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Oct;40(10):1135–1140. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.10.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturniolo T., Bono E., Ding J., Raddrizzani L., Tuereci O., Sahin U., Braxenthaler M., Gallazzi F., Protti M. P., Sinigaglia F. Generation of tissue-specific and promiscuous HLA ligand databases using DNA microarrays and virtual HLA class II matrices. Nat Biotechnol. 1999 Jun;17(6):555–561. doi: 10.1038/9858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J. L., Pelfrey C. M., Trotter A. L., Selvidge J. A., Gushleff K. C., Mohanakumar T., McFarland H. F. T cell recognition of myelin proteolipid protein and myelin proteolipid protein peptides in the peripheral blood of multiple sclerosis and control subjects. J Neuroimmunol. 1998 Apr 15;84(2):172–178. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(97)00260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentini G., Baroni A., Esposito K., Naclerio C., Buommino E., Farzati A., Cuomo G., Farzati B. Peripheral blood T lymphocytes from systemic sclerosis patients show both Th1 and Th2 activation. J Clin Immunol. 2001 May;21(3):210–217. doi: 10.1023/a:1011024313525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderlugt C. L., Neville K. L., Nikcevich K. M., Eagar T. N., Bluestone J. A., Miller S. D. Pathologic role and temporal appearance of newly emerging autoepitopes in relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2000 Jan 15;164(2):670–678. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderlugt Carol L., Miller Stephen D. Epitope spreading in immune-mediated diseases: implications for immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002 Feb;2(2):85–95. doi: 10.1038/nri724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner E. S., Hildebrandt S., Senécal J. L., Daniels L., Noell S., Joyal F., Roussin A., Earnshaw W., Rothfield N. F. Prognostic significance of anticentromere antibodies and anti-topoisomerase I antibodies in Raynaud's disease. A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jan;34(1):68–77. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]