Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of 100 mg daily anakinra (Kineret), a recombinant form of the naturally occurring interleukin 1 receptor antagonist, plus methotrexate (MTX) in reducing the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Patients with active RA (n = 506) despite current treatment with MTX were enrolled in this multicentre, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled study. Patients received subcutaneous injections of anakinra 100 mg/day or placebo. They were assessed monthly for 6 months for improvement in signs and symptoms of RA and for adverse events. The primary efficacy measure was the percentage of patients attaining ACR20 response at week 24.
Results: Significantly greater proportions of patients treated with anakinra compared with placebo achieved ACR20 (38% v 22%; p<0.001), ACR50 (17% v 8%; p<0.01), and ACR70 (6% v 2%; p<0.05) responses. The response to anakinra was rapid; the proportion of patients with an ACR20 response at the first study assessment (4 weeks) was twice as high with anakinra as with placebo (p<0.005). Clinically meaningful and statistically significant responses were also seen in individual components of the ACR response (for example, Health Assessment Questionnaire, pain, C reactive protein levels, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate). Anakinra was well tolerated, with a safety profile, similar to that of placebo with one exception: mild to moderate injection site reactions were more common with anakinra than with placebo (65% v 24%).
Conclusions: This study confirms previous observations from a dose-ranging study showing that anakinra, in combination with MTX, is an effective and safe treatment for patients with RA who have inadequate responses to MTX alone.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (178.1 KB).
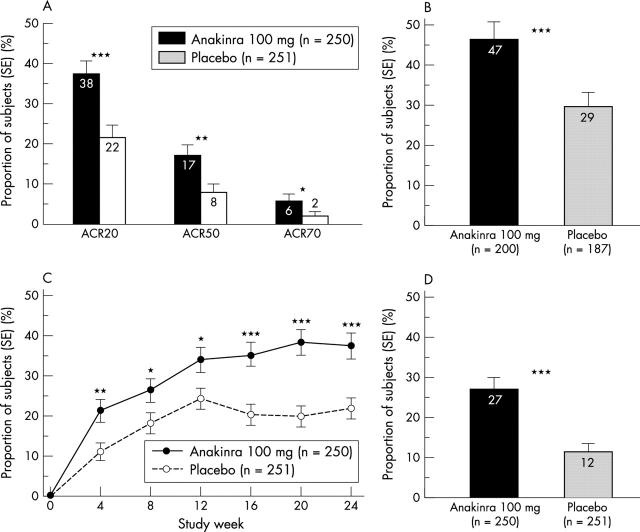
Figure 1.
(A) Proportions of patients in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups with ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses at the end of the 24 week study period. (B) Proportions of patients completing the study in the anakinra (n = 200) and placebo (n = 187) groups with ACR20 responses at the end of the 24 week study period. (C) Proportions of patients in the anakinra and placebo groups with an ACR20 response, by study week. (D) Proportions of patients in the placebo and anakinra groups with a sustained ACR20 response, defined as an ACR20 response in at least four of the six monthly assessments. Comparisons between study drugs shown as *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
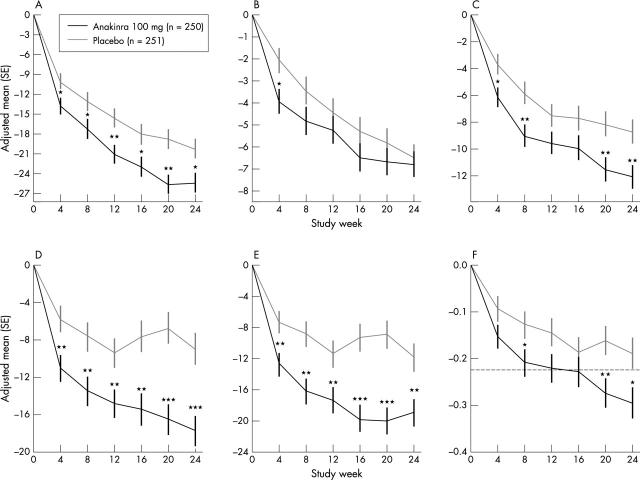
Figure 2.
(A) Changes in physician assessment of patient disease activity in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups, by study week. (B) Changes in swollen joint count in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups. (C) Changes in tender/painful joint count in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups. (D) Changes in patient perceptions of overall disease activity in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups. (E) Changes in patient ratings of pain in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups. (F) Changes in patient assessments of functional disability, as measured by the HAQ, in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups. The dashed line indicates the minimal clinically important difference in score. Comparisons between study drugs is shown as *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001.
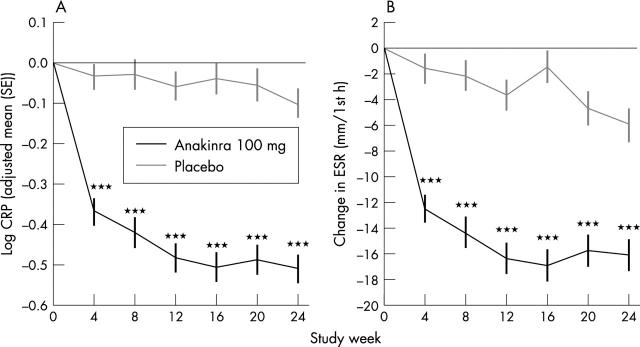
Figure 3.
(A) Log transformed changes in CRP levels in the anakinra (n = 250) and placebo (n = 251) groups at each study assessment. (B) Changes in ESR in the anakinra and placebo groups at each study assessment. Comparisons between study drugs shown as ***p<0.001.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Malyak M., Guthridge C. J., Gabay C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: role in biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:27–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.16.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Cobby M., Doherty M., Domljan Z., Emery P., Nuki G., Pavelka K., Rau R., Rozman B. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Dec;41(12):2196–2204. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199812)41:12<2196::AID-ART15>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cnaan A., Laird N. M., Slasor P. Using the general linear mixed model to analyse unbalanced repeated measures and longitudinal data. Stat Med. 1997 Oct 30;16(20):2349–2380. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19971030)16:20<2349::aid-sim667>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen Stanley, Hurd Eric, Cush John, Schiff Michael, Weinblatt Michael E., Moreland Larry W., Kremer Joel, Bear Moraye B., Rich William J., McCabe Dorothy. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, in combination with methotrexate: results of a twenty-four-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):614–624. doi: 10.1002/art.10141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dripps D. J., Brandhuber B. J., Thompson R. C., Eisenberg S. P. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist binds to the 80-kDa IL-1 receptor but does not initiate IL-1 signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10331–10336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Chernoff M., Fried B., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Kieszak S., Lightfoot R. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jun;36(6):729–740. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann Roy M., Schechtman Joy, Bennett Ralph, Handel Malcolm L., Burmester Gerd-Rudiger, Tesser John, Modafferi Dennis, Poulakos Jennifer, Sun Gordon. Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (r-metHuIL-1ra), in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A large, international, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):927–934. doi: 10.1002/art.10870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong K. Y., Boey M. L., Koh W. H., Feng P. H. Cytokine concentrations in the synovial fluid and plasma of rheumatoid arthritis patients: correlation with bony erosions. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Jan-Feb;12(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graudal N. A., Svenson M., Tarp U., Garred P., Jurik A-G, Bendtzen K. Autoantibodies against interleukin 1alpha in rheumatoid arthritis: association with long term radiographic outcome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Jul;61(7):598–602. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.7.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Genant H. K., Watt I., Cobby M., Bresnihan B., Aitchison R., McCabe D. A multicenter, double-blind, dose-ranging, randomized, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: radiologic progression and correlation of Genant and Larsen scores. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 May;43(5):1001–1009. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200005)43:5<1001::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosinski Mark, Kujawski Sara C., Martin Richard, Wanke Lee A., Buatti Mary C., Ware John E., Jr, Perfetto Eleanor M. Health-related quality of life in early rheumatoid arthritis: impact of disease and treatment response. Am J Manag Care. 2002 Mar;8(3):231–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho K., Mäenpä H., Kautiainen H., Kauppi M., Kaarela K., Lehto M., Belt E. Rise in serum C reactive protein after hip and knee arthroplasties in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Mar;60(3):275–277. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maetzel A., Bombardier C., Strand V., Tugwell P., Wells G. How Canadian and US rheumatologists treat moderate or aggressive rheumatoid arthritis: a survey. J Rheumatol. 1998 Dec;25(12):2331–2338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. C., Lynch E. A., Isa S., Logan J. W., Dinarello C. A., Steere A. C. Balance of synovial fluid IL-1 beta and IL-1 receptor antagonist and recovery from Lyme arthritis. Lancet. 1993 Jan 16;341(8838):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W., Cohen S. B., Baumgartner S. W., Tindall E. A., Bulpitt K., Martin R., Weinblatt M., Taborn J., Weaver A., Burge D. J. Long-term safety and efficacy of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001 Jun;28(6):1238–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan S. L., Baggott J. E., Vaughn W. H., Austin J. S., Veitch T. A., Lee J. Y., Koopman W. J., Krumdieck C. L., Alarcón G. S. Supplementation with folic acid during methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Dec 1;121(11):833–841. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-11-199412010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney M., Symons J. A., Duff G. W. Interleukin 1 beta in synovial fluid is related to local disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(5):217–219. doi: 10.1007/BF02274836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Loetscher P., Dewald B., Towbin H., Rordorf C., Gallati H., Baggiolini M., Gerber N. J. Methotrexate action in rheumatoid arthritis: stimulation of cytokine inhibitor and inhibition of chemokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Jul;34(7):602–609. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.7.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Loetscher P., Dewald B., Towbin H., Rordorf C., Gallati H., Gerber N. J. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors, IL-1 beta, and IL-8--markers of remission in rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with methotrexate. J Rheumatol. 1996 Sep;23(9):1512–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand V., Cohen S., Schiff M., Weaver A., Fleischmann R., Cannon G., Fox R., Moreland L., Olsen N., Furst D. Treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with placebo and methotrexate. Leflunomide Rheumatoid Arthritis Investigators Group. Arch Intern Med. 1999 Nov 22;159(21):2542–2550. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.21.2542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömbeck B., Ekdahl C., Manthorpe R., Wikström I., Jacobsson L. Health-related quality of life in primary Sjögren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia compared to normal population data using SF-36. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000;29(1):20–28. doi: 10.1080/030097400750001761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Kaplan H., Germain B. F., Block S., Solomon S. D., Merriman R. C., Wolfe F., Wall B., Anderson L., Gall E. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. A five-year prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Oct;37(10):1492–1498. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells G. A., Tugwell P., Kraag G. R., Baker P. R., Groh J., Redelmeier D. A. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient's perspective. J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20(3):557–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]