Abstract
Objectives: To explore the efficacy of a tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) inhibitor (etanercept, Enbrel) in patients with severe sciatica.
Methods: A pilot study of etanercept was conducted in patients admitted to hospital for acute severe sciatica. Ten consecutive patients received three subcutaneous injections of etanercept (25 mg every 3 days) in addition to standard analgesia. Response was evaluated at day 10 (T1) and week 6 (T2) using a visual analogue scale for leg pain (VASL) and for low back pain (VASB), and two validated functional scores: the Oswestry disability index (ODI) and the Roland Morris disability questionnaire (RMDQ). The control group consisted of 10 patients with severe sciatica, who took part in an observational study on IV methylprednisolone.
Results: In the etanercept group all variables improved: VASB from 36 to 7; VASL from 74 to 12; RMDQ from 17.8 to 5.8, and ODI from 75.4 to 17.3; all p<0.001. Pain (VASL and VASB: p<0.001) and ODI (p<0.05) were significantly better in the etanercept group than in the methylprednisolone group.
Conclusion: In this open, historical group controlled study, patients with severe sciatica had sustained improvement after a short treatment with etanercept that was better than standard care plus a short course of methylprednisolone. These results suggest that inhibition of TNFα is beneficial in the treatment of sciatica and support a pathological role for TNFα in the pathogenesis of sciatica. These results need to be confirmed by a randomised controlled trial.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (70.3 KB).
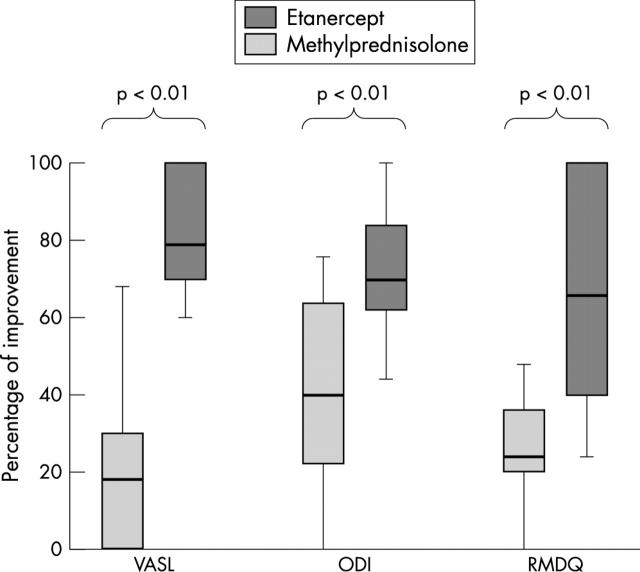
Figure 1.
Percentage of improvement between T0 and T2. The length of the box plots represents the interquartile range; means and extremes are also given. 0% = no improvement, 100% total recovery. VASL, visual analogue scale for leg pain; ODI, Oswestry Disability Index; RMDQ, Roland Morris Disease Questionnaire.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn Sang-Ho, Cho Yoon-Woo, Ahn Myun-Whan, Jang Sung-Ho, Sohn Yoon-Kyung, Kim Hee-Sun. mRNA expression of cytokines and chemokines in herniated lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2002 May 1;27(9):911–917. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200205010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baert Filip, Noman Maja, Vermeire Severine, Van Assche Gert, D' Haens Geert, Carbonez An, Rutgeerts Paul. Influence of immunogenicity on the long-term efficacy of infliximab in Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003 Feb 13;348(7):601–608. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deyo R. A., Tsui-Wu Y. J. Descriptive epidemiology of low-back pain and its related medical care in the United States. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1987 Apr;12(3):264–268. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198704000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbank J. C., Couper J., Davies J. B., O'Brien J. P. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy. 1980 Aug;66(8):271–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardam Michael A., Keystone Edward C., Menzies Richard, Manners Steven, Skamene Emil, Long Richard, Vinh Donald C. Anti-tumour necrosis factor agents and tuberculosis risk: mechanisms of action and clinical management. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003 Mar;3(3):148–155. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(03)00545-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfin S. R., Rydevik B., Lind B., Massie J. Spinal nerve root compression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995 Aug 15;20(16):1810–1820. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199508150-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goupille P., Jayson M. I., Valat J. P., Freemont A. J. The role of inflammation in disk herniation-associated radiculopathy. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Aug;28(1):60–71. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(98)80029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi T., Kikuchi S., Shubayev V., Myers R. R. 2000 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies: Exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus pulposus-induced neuropathology. Molecular, histologic, and behavioral comparisons in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000 Dec 1;25(23):2975–2980. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200012010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J. D., Georgescu H. I., McIntyre-Larkin L., Stefanovic-Racic M., Donaldson W. F., 3rd, Evans C. H. Herniated lumbar intervertebral discs spontaneously produce matrix metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and prostaglandin E2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996 Feb 1;21(3):271–277. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199602010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karppinen Jaro, Korhonen Timo, Malmivaara Antti, Paimela Leena, Kyllönen Eero, Lindgren Karl-August, Rantanen Pekka, Tervonen Osmo, Niinimäki Jaakko, Seitsalo Seppo. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody, infliximab, used to manage severe sciatica. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003 Apr 15;28(8):750–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmarker K., Nordborg C., Larsson K., Rydevik B. Ultrastructural changes in spinal nerve roots induced by autologous nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996 Feb 15;21(4):411–414. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199602150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmarker K., Rydevik B., Nordborg C. Autologous nucleus pulposus induces neurophysiologic and histologic changes in porcine cauda equina nerve roots. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993 Sep 1;18(11):1425–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmarker K., Rydevik B. Selective inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents nucleus pulposus-induced thrombus formation, intraneural edema, and reduction of nerve conduction velocity: possible implications for future pharmacologic treatment strategies of sciatica. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001 Apr 15;26(8):863–869. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200104150-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onda Akira, Yabuki Shoji, Kikuchi Shinichi. Effects of neutralizing antibodies to tumor necrosis factor-alpha on nucleus pulposus-induced abnormal nociresponses in rat dorsal horn neurons. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003 May 15;28(10):967–972. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000061984.08703.0C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland M., Morris R. A study of the natural history of back pain. Part I: development of a reliable and sensitive measure of disability in low-back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1983 Mar;8(2):141–144. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198303000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specchia Nicola, Pagnotta Alessia, Toesca Amelia, Greco Francesco. Cytokines and growth factors in the protruded intervertebral disc of the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2002 Jan 11;11(2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/s00586-001-0361-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell G. Low back pain: a twentieth century health care enigma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1996 Dec 15;21(24):2820–2825. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199612150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Myers R. R. Endoneurial injection of TNF-alpha produces neuropathic pain behaviors. Neuroreport. 1996 Nov 25;7(18):2897–2901. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199611250-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesel S. W., Tsourmas N., Feffer H. L., Citrin C. M., Patronas N. A study of computer-assisted tomography. I. The incidence of positive CAT scans in an asymptomatic group of patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1984 Sep;9(6):549–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]