Abstract
Objective: To determine the frequency and clinical impact of anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and etanercept.
Methods: 121 patients from the Stockholm tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) follow up registry (STURE) treated with infliximab or etanercept were studied.
Results: At baseline 9/65 (14%) infliximab and 10/56 (18%) etanercept treated patients had positive aCL. After 3 months the frequencies of aCL positivity were 29% (p<0.05 compared with baseline) and 27%, respectively, and after 6 months 28% and 25%. Increases were seen for both IgG and IgM aCL. Increasing age, a higher number of prior DMARDs, and higher DAS28 were predictors for the development of aCL. In the infliximab treated patients, 26/30 (87%) aCL(–) but only 7/14 (50%) aCL(+) patients met the ACR20 criteria (p<0.05), and the frequency of treatment limiting infusion reactions in the aCL(+) patients was higher than expected (17%). aCL positivity in the etanercept treated patients did not show such a clinical correlate. Four patients had thromboembolic events, of whom two were aCL(+) and two aCL(–).
Conclusion: Frequencies of both IgM and IgG aCL positivity increase in patients treated with these TNFα antagonists for 3 months or longer. Increasing age, a greater number of prior DMARDs and a greater disease activity at baseline are predictors for the development of aCL. The development of aCL during treatment with infliximab, but not etanercept, is associated with worse clinical results and more frequent serious infusion reactions. aCL are an important class of autoantibodies associated with TNFα blocking therapy.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (121.5 KB).
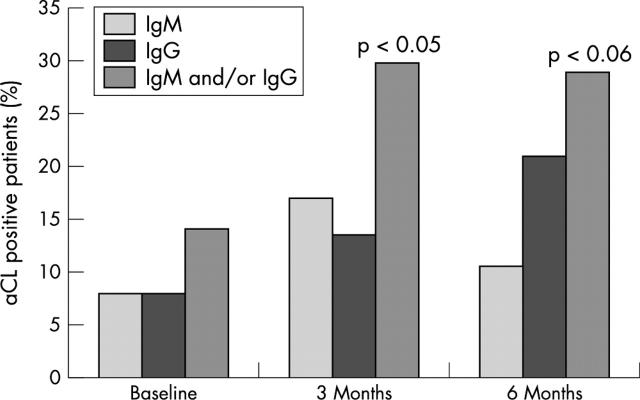
Figure 1.
Percentage of aCL(+)patients at baseline and after 3 and 6 months of treatment with infliximab. Percentage positive for IgG aCL: p<0.05 for linear trend.
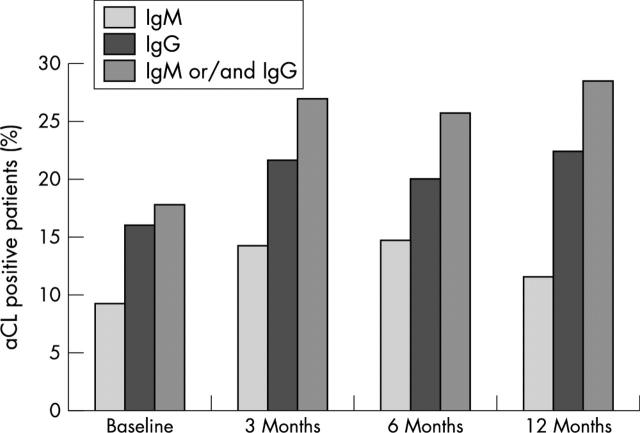
Figure 2.
Percentage of aCL(+)patients at baseline and after 3, 6, and 12 months of treatment with etanercept.
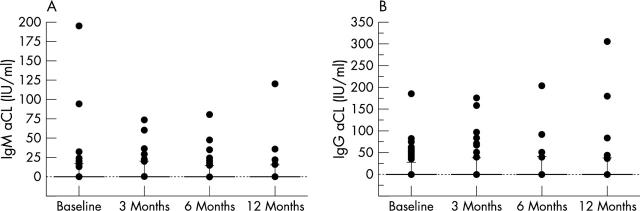
Figure 3.
(A) IgM aCL titres (IU/ml) in all patients at baseline and after 3, 6, and 12 months of treatment. (B) IgG aCL titres (IU/ml) in all patients at baseline and after 3, 6, and 12 months of treatment.
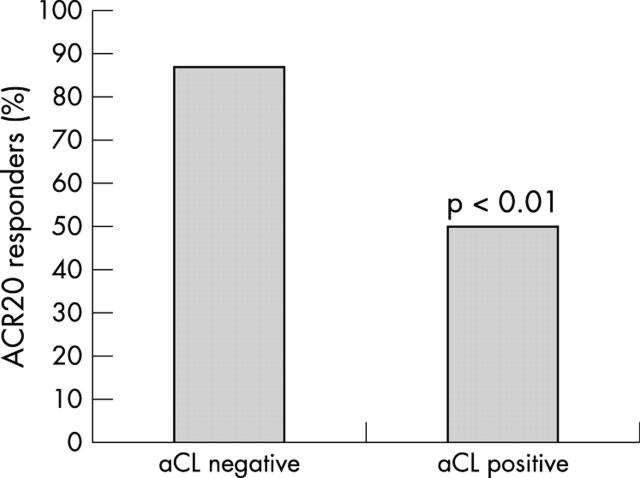
Figure 4.
Percentage of ACR20 responders to treatment with infliximab in aCL(–) and aCL(+) patients. Comparison is by χ2 test.
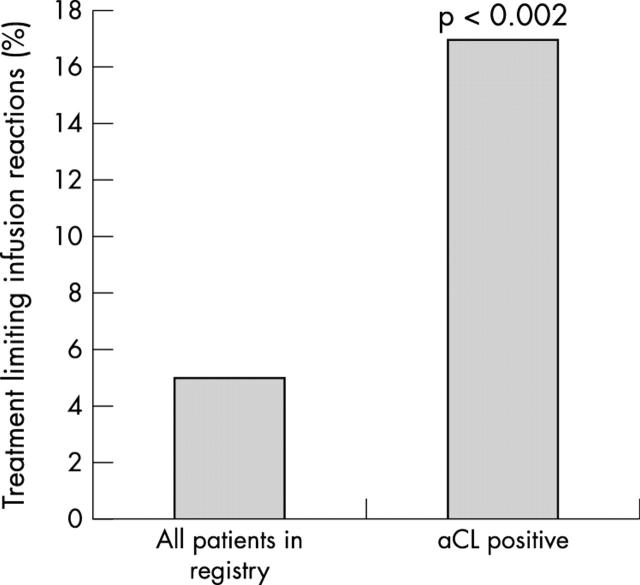
Figure 5.
Percentage of treatment limiting infusion reactions in aCL(+) patients compared with all patients in the registry (infliximab treatment only). Comparison is by χ2 test.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathon J. M., Martin R. W., Fleischmann R. M., Tesser J. R., Schiff M. H., Keystone E. C., Genovese M. C., Wasko M. C., Moreland L. W., Weaver A. L. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1586–1593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles P. J., Smeenk R. J., De Jong J., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Assessment of antibodies to double-stranded DNA induced in rheumatoid arthritis patients following treatment with infliximab, a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha: findings in open-label and randomized placebo-controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Nov;43(11):2383–2390. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200011)43:11<2383::AID-ANR2>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke Leen, Kruithof Elli, Van Damme Nancy, Hoffman Ilse E. A., Van den Bossche Nancy, Van den Bosch Filip, Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip. Antinuclear antibodies following infliximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1015–1023. doi: 10.1002/art.10876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vita Salvatore, Zaja Francesco, Sacco Stefania, De Candia Alessandro, Fanin Renato, Ferraccioli Gianfranco. Efficacy of selective B cell blockade in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for a pathogenetic role of B cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Aug;46(8):2029–2033. doi: 10.1002/art.10467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Long-Fox A., Charles P., Bijl H., Woody J. N. Repeated therapy with monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1125–1127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Long-Fox A., Charles P., Katsikis P., Brennan F. M., Walker J., Bijl H., Ghrayeb J. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;36(12):1681–1690. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Chernoff M., Fried B., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Kieszak S., Lightfoot R. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jun;36(6):729–740. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraccioli G., Mecchia F., Di Poi E., Fabris M. Anticardiolipin antibodies in rheumatoid patients treated with etanercept or conventional combination therapy: direct and indirect evidence for a possible association with infections. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Apr;61(4):358–361. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.4.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields R. A., Toubbeh H., Searles R. P., Bankhurst A. D. The prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies in a healthy elderly population and its association with antinuclear antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1989 May;16(5):623–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Spitz P. W., Young D. Y. The dimensions of health outcomes: the health assessment questionnaire, disability and pain scales. J Rheumatol. 1982 Sep-Oct;9(5):789–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomäki P., Punnonen J. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Med. 1997 Dec;29(6):499–507. doi: 10.3109/07853899709007474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapiotis S., Speiser W., Pabinger-Fasching I., Kyrle P. A., Lechner K. Anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with venous thrombosis. Haemostasis. 1991;21(1):19–24. doi: 10.1159/000216197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane A., Woods R., Dowding V., Roden D., Barry C. Anticardiolipin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1987 Oct;26(5):346–350. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/26.5.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., van der Heijde D. M., St Clair E. W., Furst D. E., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Weisman M., Emery P., Feldmann M. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1594–1602. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin M. D., Druzin M. L., Qamar T. Prednisone does not prevent recurrent fetal death in women with antiphospholipid antibody. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Feb;160(2):439–443. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(89)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Davis D., Macfarlane J. D., Antoni C., Leeb B., Elliott M. J., Woody J. N. Therapeutic efficacy of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody combined with low-dose weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1552–1563. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1552::AID-ART5>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R., St Clair E. W., Breedveld F., Furst D., Kalden J., Weisman M., Smolen J., Emery P., Harriman G., Feldmann M. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)05246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W., Baumgartner S. W., Schiff M. H., Tindall E. A., Fleischmann R. M., Weaver A. L., Ettlinger R. E., Cohen S., Koopman W. J., Mohler K. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med. 1997 Jul 17;337(3):141–147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199707173370301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W., Schiff M. H., Baumgartner S. W., Tindall E. A., Fleischmann R. M., Bulpitt K. J., Weaver A. L., Keystone E. C., Furst D. E., Mease P. J. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Mar 16;130(6):478–486. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-6-199903160-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Dhavalkumar D. B cell-ablative therapy for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Aug;46(8):1984–1985. doi: 10.1002/art.10476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi W., Krilis S. A., Chong B. H., Gordon S., Chesterman C. N. Prevalence of lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in a healthy population. Aust N Z J Med. 1990 Jun;20(3):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1990.tb01025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair E. William, Wagner Carrie L., Fasanmade Adedigbo A., Wang Benjamin, Schaible Thomas, Kavanaugh Arthur, Keystone Edward C. The relationship of serum infliximab concentrations to clinical improvement in rheumatoid arthritis: results from ATTRACT, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jun;46(6):1451–1459. doi: 10.1002/art.10302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinblatt M. E., Kremer J. M., Bankhurst A. D., Bulpitt K. J., Fleischmann R. M., Fox R. I., Jackson C. G., Lange M., Burge D. J. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999 Jan 28;340(4):253–259. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199901283400401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf P., Gretler J., Aglas F., Auer-Grumbach P., Rainer F. Anticardiolipin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: their relation to rheumatoid nodules and cutaneous vascular manifestations. Br J Dermatol. 1994 Jul;131(1):48–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1994.tb08456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M., van Riel P. L., van de Putte L. B. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20(3):579–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]