Abstract
Case report: The first case of lupus erythematosus in a 58 year old white woman after administration of leflunomide for primary Sjögren's syndrome is reported. The relationship between induced lupus and leflunomide was confirmed by the resolution of the skin rash when the drug was stopped and its recurrence when it was reintroduced following a dose-response effect.
Discussion: Peripheral blood cells from this patient, from 15 patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and from healthy controls were used in a bioassay, which suggested that leflunomide affected the Th1/Th2 balance. Such a side effect might be related, in part, to the anti-tumour necrosis factor α activity of leflunomide.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (94.6 KB).
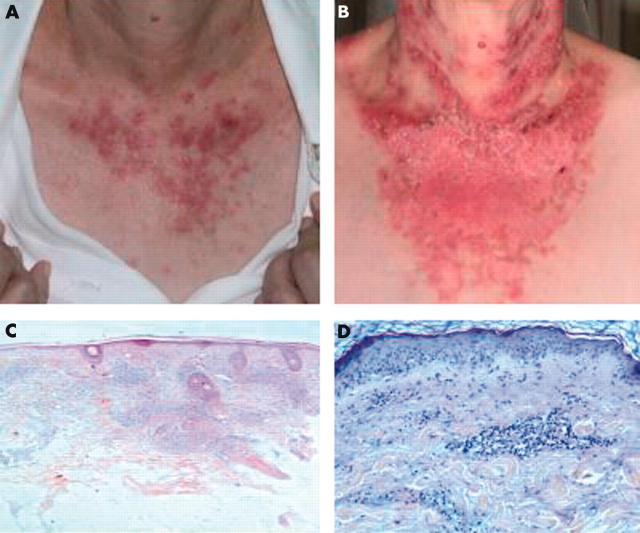
Figure 1.
Skin clinical and pathology changes: a typical lupus skin rash seen in July 2003 (A) and in September 2003 (B). Skin biopsy in November 2000 (face) showing signs of discoid lupus (C) and in July 2003 (arm) showing signs of subacute lupus (D).
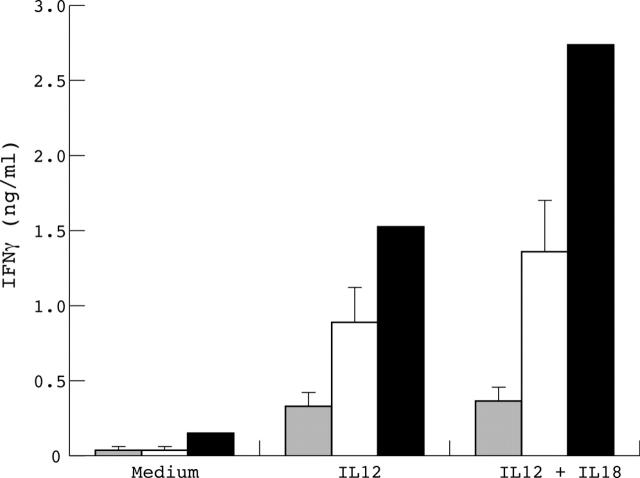
Figure 2.
Th1 immune modulation in patients with RA, healthy controls, and our patient. PBMC from the patient (black bar), control patients with RA (n = 15, grey bar), and healthy controls (n = 14, white bar), were stimulated with or without 1 ng/ml IL12 or a combination of IL12 (1 ng/ml) and IL18 (5 ng/ml). IFNγ concentrations in culture supernatants were measured by ELISA.