Abstract
Methods: A retrospective study, in 197 patients with ANCA associated vasculitis, of the history of cigarette smoking at onset of symptoms. Prevalence of smoking in patients with ANCA associated vasculitis was compared with age-specific values for the general population in Germany.
Results: 27 (14%) patients were smokers at the time of first disease manifestation (p<0.001, compared with the entire population); 54 (27%) had smoked previously with 1–110 pack-years (median 18) but had stopped ⩾2 years before onset of vasculitis; 116 (59%) patients were lifelong non-smokers. At onset of symptoms, active smokers were younger (median age 42 years) than patients with vasculitis (median 54 years, p<0.01, Mann-Whitney U test) with a lower percentage of women (15%, p<0.005, Fisher's exact test) than in the entire group (47%). Smokers, non-smokers, or ex-smokers did not differ in organ manifestation, mortality, and development of end stage renal disease and relapse rate.
Conclusions: The proportion of active smokers in the group of patients with ANCA associated vasculitis is significantly lower than in the entire population. Cigarette smoking may be associated with a reduced risk of ANCA associated vasculitis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (53.2 KB).
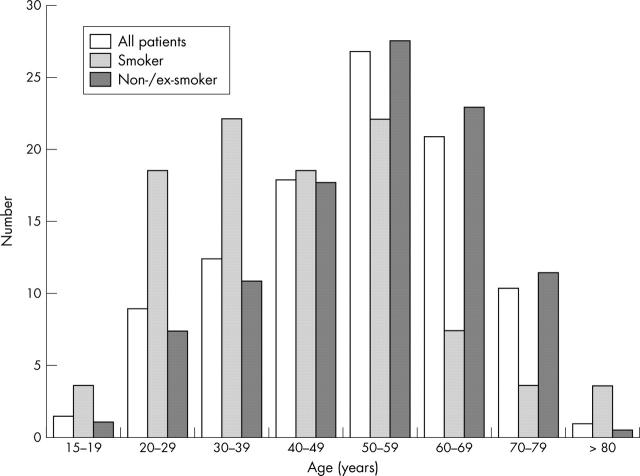
Figure 1.
Age distribution and smoking status.