Abstract
Methods: Anti-CCP1 and anti-CCP2 antibody tests were performed on the same serum samples obtained from 467 patients with early arthritis from the Leiden Arthritis Cohort. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value for discriminating between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and non-RA at 1 year's follow up were calculated for both tests. Results were graphically presented using receiver operating characteristic curves. Progression of radiological joint damage was assessed over 4 years in patients with RA and used to assess the prognostics values of the CCP tests.
Results: At a similar specificity the CCP2 test had a higher sensitivity than the CCP1 test. Both tests identified a subgroup of patients with RA with an increased rate of joint damage progression. The anti-CCP2 test identified more patients with an increased rate of joint damage progression than the anti-CCP1 test, and in multiple regression analysis CCP2 was the better predictor of joint damage.
Conclusions: The CCP2 test had better diagnostic and prognostic ability than the CCP1 test.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (56.5 KB).
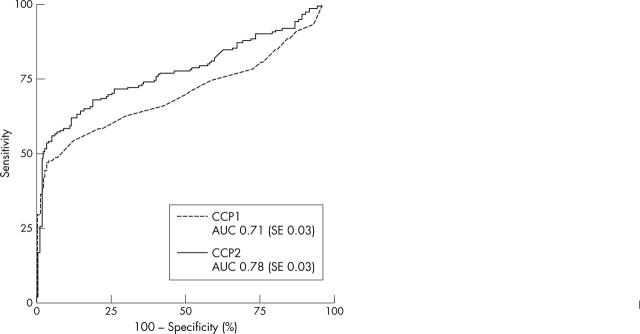
Figure 1.
ROC curves of the first (CCP1) and second (CCP2) generation anti-CCP ELISAs as tested on 467 patients with early arthritis with RA at 1 year as the outcome. The difference between the AUC of the ROC of CCP1 and CCP2 was significant (Z = 2.42). When standard cut off points were used the diagnostic properties were as follows (95% confidence interval (CI)): CCP1: sensitivity 42% (95% CI 35% to 50%), specificity 97% (95% CI 95% to 99%), positive predictive value 89% (95% CI 79% to 94%), and negative predictive value 78% (95% CI 73% to 81%); CCP2: sensitivity 54% (95% CI 46% to 61%), specificity 96% (95% CI 93% to 98%), positive predictive value 86% (95% CI 78% to 92%), and negative predictive value 81% (95% CI 77% to 85%).