Abstract
Objective: To examine the efficacy and safety of infliximab combined with methotrexate compared with methotrexate alone in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) using MRI and DXA to monitor its impact on bone.
Methods: In this single centre study 42 subjects with active AS were treated with methotrexate and were randomly assigned, in a ratio of 2:1, to receive five infusions of either 5 mg/kg infliximab or placebo over 30 weeks. The primary outcome was improvement in disease activity as shown by the BASDAI at week 30. MRI was used to assess the effect of treatments on sacroiliac and spinal enthesitis/osteitis and DXA to monitor bone mineral density.
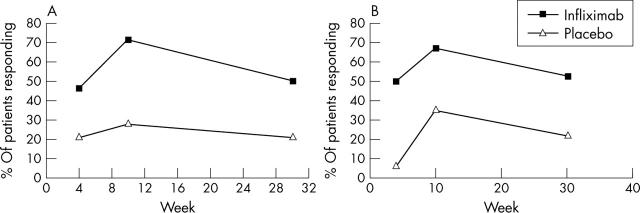
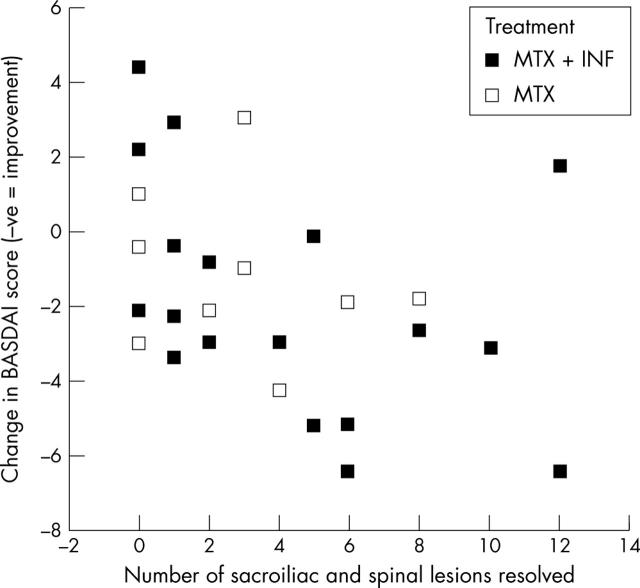
Results: Both therapeutic agents were well tolerated with no dropouts due to adverse events. A significantly greater improvement in mean BASDAI score was seen in the infliximab arm at week 10 (p = 0.017) than in the placebo arm, but this was not maintained by week 30 (p = 0.195), 8 weeks after the last infusion, at which stage disease flares were reported by some subjects. MRI showed that the mean number of lesions resolving for each subject from week 0 to week 30 was significantly greater in the combination group than in the methotrexate monotherapy group (p = 0.016).
Conclusions: Infliximab in combination with methotrexate was a safe and efficacious treatment in AS over 6 months and was associated with significant regression in enthesitis/osteitis as determined by MRI. However, disease flares were reported 8 weeks after the last infusion, indicating that addition of methotrexate failed to extend the infliximab dosing interval.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (166.2 KB).
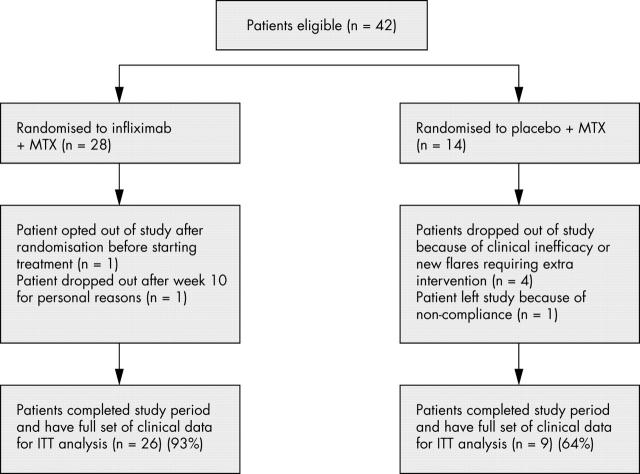
Figure 1.
Randomisation, reasons for treatment discontinuation, and numbers of patients who completed the 30 week study period. ITT, intention to treat.
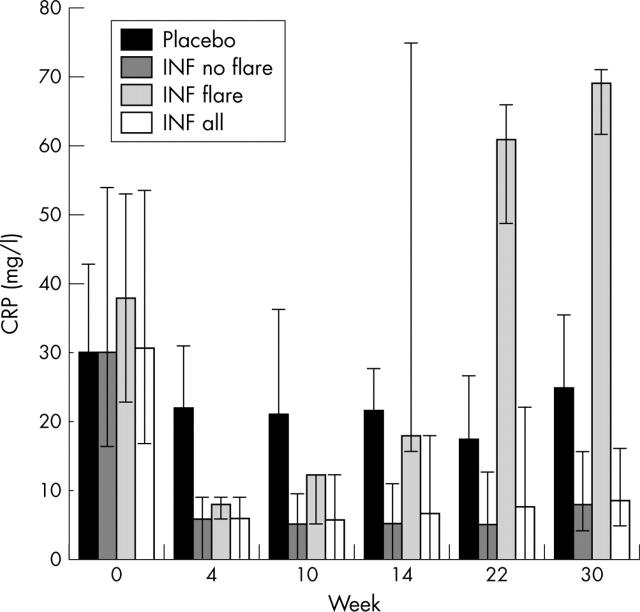
Figure 2.
Analysis of CRP results at all study visits examining the subset of patients in the infliximab treated group who reported a flare of disease in the interim visits.
Figure 3.
(A) ASAS20 and (B) ASASBIO (composite ASAS response criteria for biological agents) responses.
Figure 4.
Association between change in BASDAI score and numbers of lesions resolved.
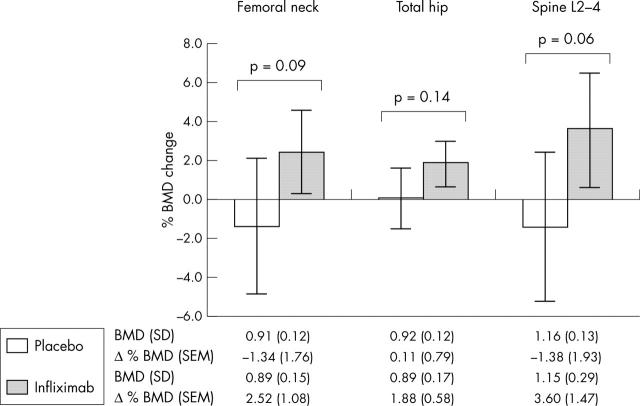
Figure 5.
DXA results.
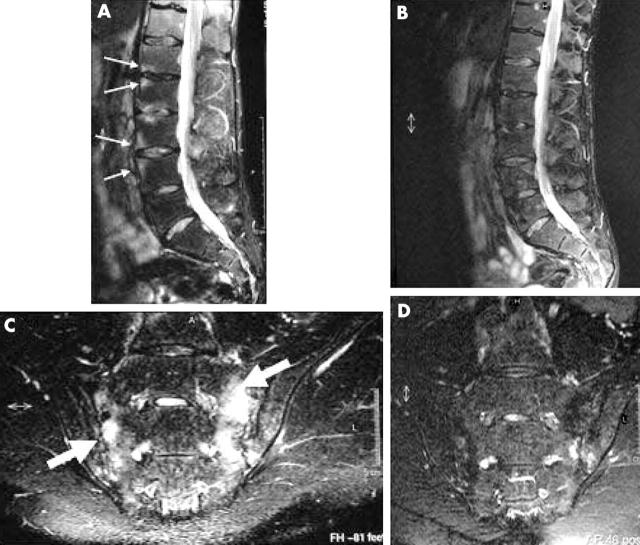
Figure 6.
Magnetic resonance images of spine and sacroiliac joints before and after treatment. (A) T2 weighted fat suppressed sagittal sequence of the lumbar spine of a patient showing acute Romanus lesions (thin white arrows) at the anterior inferior aspects of L1 and L3, and anterior superior aspects of L2 and L4 vertebral bodies; (B) complete resolution of the lesions after treatment with infliximab and methotrexate; (C) T2 weighted fat suppressed coronal oblique image of the SIJ of another patient showing active sacroiliitis (thick white arrow) and (D) marked improvement after treatment with infliximab and methotrexate.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biasi D., Carletto A., Caramaschi P., Pacor M. L., Maleknia T., Bambara L. M. Efficacy of methotrexate in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a three-year open study. Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19(2):114–117. doi: 10.1007/s100670050027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Haibel H., Cornely D., Golder W., Gonzalez J., Reddig J., Thriene W., Sieper J., Braun J. Successful treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jun;43(6):1346–1352. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200006)43:6<1346::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Listing J., Bollow M., Sieper J., Van Der Heijde D. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1126–1136. doi: 10.1002/art.10883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Eggens U., König H., Distler A., Sieper J. Use of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with fast imaging in the detection of early and advanced sacroiliitis in spondylarthropathy patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jul;37(7):1039–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Burmester G., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Schneider M. Long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: an open, observational, extension study of a three-month, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2224–2233. doi: 10.1002/art.11104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Pham T., Sieper J., Davis J., van der Linden Sj, Dougados M., van der Heijde D., ASAS Working Group International ASAS consensus statement for the use of anti-tumour necrosis factor agents in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Sep;62(9):817–824. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.9.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Garrett S., Whitelock H., Kennedy L. G., O'Hea J., Mallorie P., Jenkinson T. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2281–2285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carette S., Graham D., Little H., Rubenstein J., Rosen P. The natural disease course of ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Feb;26(2):186–190. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rycke Leen, Kruithof Elli, Van Damme Nancy, Hoffman Ilse E. A., Van den Bossche Nancy, Van den Bosch Filip, Veys Eric M., De Keyser Filip. Antinuclear antibodies following infliximab treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1015–1023. doi: 10.1002/art.10876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doward L. C., Spoorenberg A., Cook S. A., Whalley D., Helliwell P. S., Kay L. J., McKenna S. P., Tennant A., van der Heijde D., Chamberlain M. A. Development of the ASQoL: a quality of life instrument specific to ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Jan;62(1):20–26. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Long-Fox A., Charles P., Katsikis P., Brennan F. M., Walker J., Bijl H., Ghrayeb J. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;36(12):1681–1690. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman Jennifer D., Sack Kenneth E., Davis John C., Jr Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha. N Engl J Med. 2002 May 2;346(18):1349–1356. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratacós J., Collado A., Pons F., Osaba M., Sanmartí R., Roqué M., Larrosa M., Múoz-Gómez J. Significant loss of bone mass in patients with early, active ankylosing spondylitis: a followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Nov;42(11):2319–2324. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199911)42:11<2319::AID-ANR9>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Breedveld F. C., Kalden J. R., Smolen J. S., Davis D., Macfarlane J. D., Antoni C., Leeb B., Elliott M. J., Woody J. N. Therapeutic efficacy of multiple intravenous infusions of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody combined with low-dose weekly methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1552–1563. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199809)41:9<1552::AID-ART5>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzo-Ortega H., McGonagle D., Haugeberg G., Green M. J., Stewart S. P., Emery P. Bone mineral density improvement in spondyloarthropathy after treatment with etanercept. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Oct;62(10):1020–1021. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.10.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzo-Ortega H., McGonagle D., O'Connor P., Emery P. Efficacy of etanercept in the treatment of the entheseal pathology in resistant spondylarthropathy: a clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):2112–2117. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2112::AID-ART363>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland L. W. Initial experience combining methotrexate with biologic agents for treating rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1996 Mar;44:78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio-Barros P. D., Costallat L. T., Bertolo M. B., Neto J. F., Samara A. M. Methotrexate in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000;29(3):160–162. doi: 10.1080/030097400750002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Feltkamp T. E., Smolen J. S., Butcher B., Dawkins R., Fritzler M. J., Gordon T., Hardin J. A., Kalden J. R., Lahita R. G. Range of antinuclear antibodies in "healthy" individuals. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1601–1611. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bosch Filip, Kruithof Elli, Baeten Dominique, Herssens Annemie, de Keyser Filip, Mielants Herman, Veys Eric M. Randomized double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) versus placebo in active spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):755–765. doi: 10.1002/art.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Baeten D., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. M. Health-related quality of life in ankylosing spondylitis: a survey of 175 patients. Arthritis Care Res. 1999 Aug;12(4):247–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden S., Valkenburg H. A., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):361–368. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]